Dental caries is a scientific term used for tooth decay and cavities. It can be defined as the breakdown of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria.
Around the world, about 2.3 billion people have dental caries in their permanent teeth. That is roughly 32% of total world’s population. The cavities may range from yellow to black in color.
This oral pathological condition can occur throughout the life and can cause temporary as well permanent damage to teeth. Read about dental caries causes.
Dental Caries or Tooth Decay Symptoms
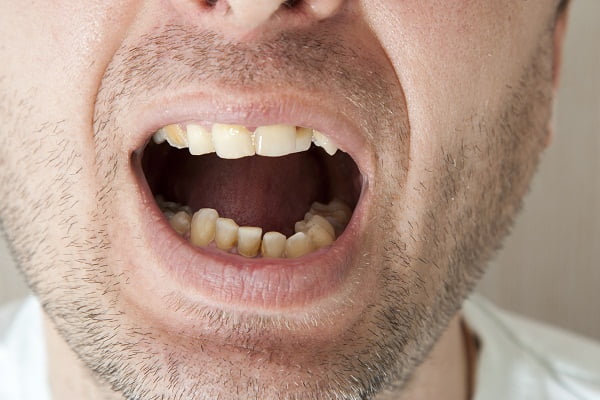
Most of the people suffering from dental caries may not know about it. The early signs of dental caries include a whitish spot on the surface of the tooth. This is a sign of enamel demineralization. This white spot turns into a brownish and shiny lesion later.
A light brown and dull color suggests active decay. When the decay has eaten through enamel, the teeth may show sensitivity to sweet, hot or cold food (or drinks).
The signs of cavities vary and depend on the extent and location of the infection. In the beginning, signs may not be clear but as the infection advances, signs may become obvious. The signs of tooth decay range from mild spot on the tooth to severe pain.
Following are the most common signs of teeth sensitivity:
- Tooth pain when you bite food
- Tooth sensitivity
- Visible holes or pit in your teeth
- Bad breath (Halitosis)
Dental caries is one of the most common and persistent diseases these days. Read – What you can do to prevent cavities from forming.
The lifestyle of a person along with many other factors is responsible for it’s so widespread. If the person notices any of the above-mentioned symptoms, he/she should consult a doctor.
Spots on teeth
When a person is suffering from dental caries, white and chalky spots appear on the surface of teeth. They often appear near the gum line. These spots may turn brown or black as the infection advances. These opaque spots are the earliest signs of dental caries and appear due to demineralization of the upper hard layer of teeth.
Sensitivity
Another sign of dental caries is sensitive teeth or a frequent toothache. Teeth sensitivity towards cold is somewhat normal. However, sensitivity towards hot and sweet food should be taken as a warning sign. It could be a sign of tooth decaying or dying tooth.
Holes in teeth
As the tooth decay advances and acid erodes enamel, a small pit is formed on the surface of the tooth. These pits further degrade to form holes in teeth. In addition, caries can cause teeth to shift from their positions.
Bleeding gums
Bleeding gums should not be ignored. The gaps and cavities formed due to tooth decay may grow in the gum area. The gaps formed in the teeth need to be filled and new gum tissue begins to grow in this area. As the person brushes his/her teeth, this new tissue gets damaged and bleeds. Bleeding gums can lead to serious problems with your gum and teeth which in extreme cases may call for an extraction. Your dentist may suggest that you get a dental implant. If this is the case make sure that you familiarize yourself with dental implant terminology, so you can understand the ins and outs of the procedure a lot better.
Bad breath
Constant deposition of plaque in teeth and oral region serve as a home for many bacteria. These bacteria grow and thrive on the food we eat and release substances that give out foul odor from mouth. This is another indicator for dental caries. Apart from having persistent bad breath (Halitosis), the person might also have an unpleasant taste in the mouth.
Chipped teeth
Dental caries sometimes even results in chipping and fracturing of teeth. As the enamel degrades and wears out, the chances of chipping teeth get higher. Weakened tooth may get fractured quite easily.
Pain in chewing food
The person having dental caries feels mild to severe pain while chewing food from the particular tooth. When the decay reaches innermost part of the tooth known as pulp, the person begins to feel pain while chewing food.
Spots on teeth
Development of spots on teeth and darkening of teeth is another indicator of dental caries. The spots are somewhat chalky in appearance. The color of these opaque spots ranges from white to black. The spots may be present on the surface of teeth or in the grooves of back teeth.
Swelling in gum
Swelling and inflammation in gum is an indicator of infection. Once the decay reaches tooth pulp, it moves into tissues and bones surrounding teeth. This begins to generate pus and leads to swelling in your gums.