Hair Loss in Children: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
- Updated on: Nov 25, 2024
- 4 min Read
- Published on May 26, 2023

The phenomenon of hair loss in children, defined as the partial or complete loss of hair from any part of the body, can be a concerning issue for both the affected child and their caregivers. While it is relatively uncommon in young children, it can cause significant distress when it does occur. The importance of discussing this topic is paramount due to the psychological and social implications that hair loss can have on a child’s life. The effects of hair loss can lead to feelings of anxiety, low self-esteem, and social isolation, which may significantly impact a child’s mental well-being. Therefore, it is essential to increase awareness and educate parents and caregivers about the potential causes, symptoms, and treatment options of hair loss in children. With greater understanding, children and their families can better manage the condition, both physically and emotionally.
Causes of Hair Loss in Children
Hair loss in children can be caused by a multitude of factors, including genetic predisposition, underlying medical conditions, and environmental factors. Understanding these causes is crucial in determining the most effective treatment approach.
Genetic Factors:
Hair loss in children may be due to genetic factors, such as androgenetic alopecia. This condition can be inherited from either parent and affects both males and females. It is caused by a sensitivity to androgen hormones, which results in the gradual miniaturization of hair follicles leading to hair loss.
Medical Conditions:
Medical conditions such as alopecia areata, a type of autoimmune disorder, can cause hair loss in children. This condition is characterized by bald patches on the scalp or other parts of the body, and it occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles. Other medical conditions that can lead to hair loss in children include thyroid disorders, lupus, and tinea capitis.
Environmental Factors:
Environmental factors such as physical trauma, stress, and exposure to harmful chemicals or toxins can also cause hair loss in children. Harsh hair treatments such as bleaching, coloring, and using hot styling tools can also damage hair follicles, leading to hair loss.
Symptoms of Hair Loss in Children:
The symptoms of hair loss in children can vary depending on the underlying cause.
However, some common symptoms include:
- Thinning Hair: Thinning hair is a common symptom of hair loss in children. This can be observed as a decrease in hair volume, leading to a sparser appearance.
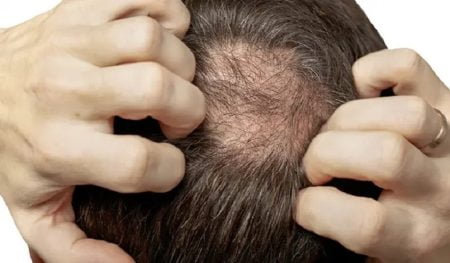
- Bald Patches: Bald patches, also known as alopecia, are a hallmark symptom of hair loss in children. These patches can appear anywhere on the scalp and may be small or large.
- Excessive Shedding: Excessive shedding of hair is another common symptom of hair loss in children. This may be observed as an increase in hair fall during brushing, combing, or washing.
- Scalp Irritation: In some cases, hair loss in children may be accompanied by scalp irritation, which can cause redness, itching, and inflammation. This may be due to an underlying skin condition, such as eczema or psoriasis.
Diagnosis of Hair Loss in Children
When diagnosing hair loss in children, several methods are used to determine the cause of the condition.
The following are some of the most commonly used diagnostic methods:
- Physical Examination: A physical examination of the affected area is usually the first step in diagnosing hair loss in children. This helps the doctor to identify any physical symptoms, such as redness or scarring, which may help to determine the cause of the hair loss.
- Medical History: Obtaining a detailed medical history is also an essential component of the diagnosis. The doctor may ask questions about the child’s hair care routine, family history of hair loss, and any underlying medical conditions that could be contributing factors.
- Laboratory Tests: Laboratory tests, such as blood tests or scalp biopsies, may also be performed to help diagnose hair loss in children. These tests can help to identify any underlying medical conditions that may be causing the hair loss.
- Biopsy: A scalp biopsy involves taking a small sample of skin from the affected area and examining it under a microscope. This can help to determine the cause of the hair loss, such as a fungal infection or an autoimmune disorder.
Treatment Options for Hair Loss in Children
The treatment options for hair loss in children will depend on the underlying cause of the condition. The following are some of the most commonly used treatment options:
- Medications: Medications, such as topical or oral corticosteroids, can be used to treat hair loss caused by autoimmune disorders or inflammation.
- Topical Treatments: Topical treatments, such as minoxidil, can be used to promote hair growth and prevent further hair loss in children.
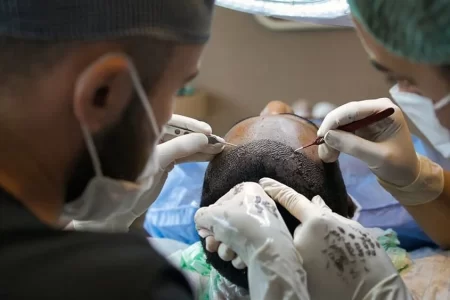
- Surgical Procedures: In some cases, surgical procedures may be necessary to treat hair loss in children. This may include hair transplant surgery or scalp reduction surgery.
- Lifestyle Changes: Making lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet, managing stress, and avoiding harsh hair treatments, can also help to prevent and manage hair loss in children.
Prevention of Hair Loss in Children
Hair loss in children can be prevented or minimized by taking appropriate measures to promote overall health and well-being.
The following are some prevention strategies that can help prevent hair loss in children:
- Proper Hair Care: Hair hygiene is vital to prevent hair loss in children. Regular washing and brushing of the hair, and avoiding the use of harsh chemicals and tight hairstyles can help maintain healthy hair.
- Healthy Diet: A nutritious diet rich in essential vitamins and minerals is essential for hair growth and maintenance. Foods such as fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can provide the necessary nutrients for healthy hair.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity helps improve blood flow to the scalp, which can promote healthy hair growth. Regular exercise can also help reduce stress, which is a known factor in hair loss.
- Stress Management: Stress can have a significant impact on hair loss in children. Learning and practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing and meditation, can help manage stress levels and reduce the risk of hair loss.
Emotional Impact of Hair Loss in Children
Hair loss in children can have a profound emotional impact that may affect their mental health and social well-being. Understanding the psychological effects, social consequences, and coping strategies for children with hair loss can help parents and caregivers support them through this challenging experience.
Here are some points to be considered:
- Psychological Effects: Hair loss can lead to feelings of low self-esteem, anxiety, and depression in children. It is essential to recognize and address these psychological effects to help the child maintain a positive self-image and mental well-being.
- Social Consequences: Children with hair loss may experience social consequences such as teasing, bullying, or social exclusion. Educating peers and creating a supportive environment can help reduce these social consequences.
- Coping Strategies: Various coping strategies can help children manage the emotional and physical challenges of hair loss. These strategies include talking with a trusted adult, participating in support groups, and engaging in activities that promote self-esteem and self-care.