Understanding Ovulation: A Comprehensive Guide
- Updated on: Aug 8, 2024
- 12 min Read
- Published on Jun 30, 2023

Ovulation is a natural process that occurs in women of reproductive age. It is the release of a mature egg from one of the ovaries, which travels down the fallopian tube and awaits fertilization by sperm. Ovulation is a crucial part of the menstrual cycle, as it is the time when a woman is most fertile and can conceive a child.
Importance of Understanding Ovulation
For menstruating women who are trying to conceive, understanding ovulation is essential. Knowing when ovulation occurs can help them identify their most fertile days and maximize their chances of getting pregnant. Using a Due Date Calculator can also help in planning and understanding the timeline of pregnancy. According to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), the chance of conceiving during each menstrual cycle is about 20%, but this increases to about 30% if a woman has intercourse during her fertile window.
Understanding ovulation can also help women to identify any potential problems with their reproductive health. For instance, irregular periods or absence of ovulation may be indicative of underlying hormonal imbalances or other health conditions that can affect fertility. In such cases, seeking medical advice early on can help women to receive timely treatment and improve their chances of conceiving.
Research has shown that many women lack knowledge about ovulation and fertility. A study published in the Journal of Women’s Health in 2017 found that only 18% of women could accurately identify the fertile window of their menstrual cycle. Another study published in the journal Fertility and Sterility in 2018 found that many women overestimated their chances of conception and had unrealistic expectations about how long it would take to get pregnant.
Educating women about ovulation and fertility can help them make informed decisions about their reproductive health and improve their chances of achieving a healthy pregnancy. In the following sections, we will delve into the details of the ovarian cycle, factors affecting ovulation, signs and symptoms of ovulation, and treatments for ovulation disorders.
The Ovarian Cycle
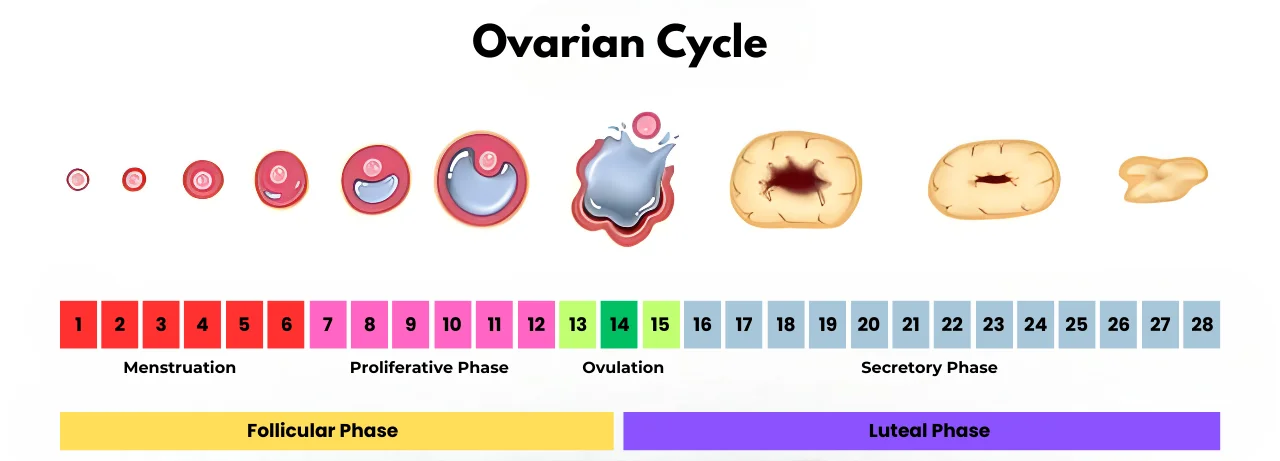
The ovarian cycle is a complex series of events that occur in a woman’s reproductive system each month. Understanding these events is crucial for those who are trying to conceive. The ovarian cycle can be divided into three main phases: the follicular phase, ovulation, and the luteal phase.
Follicular Phase
The follicular phase is the first phase of the ovarian cycle and begins on the first day of menstruation. During this phase, the pituitary gland releases follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which stimulates the growth of follicles in the ovaries. Each follicle contains an immature egg, and as they grow, they produce estrogen, which prepares the uterus for pregnancy.
This phase typically lasts about 14 days but can vary from woman to woman. It ends with the release of the dominant follicle, which contains a mature egg that is ready for fertilization.
Ovulation
Ovulation is the second phase of the ovarian cycle, and it is the most crucial phase for those trying to conceive. Ovulation occurs when the mature follicle ruptures and releases the mature egg into the fallopian tube. This typically occurs around day 14 of the menstrual cycle, but can vary depending on the length of a woman’s cycle.
It’s important to note that ovulation only occurs once per cycle, and the egg is only viable for 12-24 hours. This means that timing intercourse during the fertile window (the days leading up to and including ovulation) is essential for those trying to conceive.
Luteal Phase
The luteal phase is the final phase of the ovarian cycle and begins after ovulation. The ruptured follicle (now called the corpus luteum) begins to produce progesterone, which prepares the uterus for pregnancy. If the egg is fertilized, it will implant in the uterus and begin to develop. If not, the corpus luteum will degenerate, causing a drop in progesterone levels, and menstruation will occur, signaling the start of a new cycle.
This phase typically lasts around 14 days but can vary from woman to woman.
The ovarian cycle is a complex process that involves the growth and release of an egg each month. Understanding the different phases of the cycle can help those who are trying to conceive to time intercourse appropriately and increase their chances of getting pregnant. It’s important to remember that every woman’s cycle is different, and seeking medical advice is always recommended when trying to conceive.
Factors Affecting Ovulation

Age
As women age, their ovarian reserve, which refers to the number of viable eggs in their ovaries, begins to decline. This results in a decrease in the frequency of ovulation, making it harder to conceive. According to the American Society for Reproductive Medicine, the chance of conceiving in any given menstrual cycle for a woman aged 30 is about 20%, while the chance of conceiving for a woman aged 40 is about 5%.
Evidence suggests that advanced maternal age is associated with an increased risk of chromosomal abnormalities, such as Down syndrome, and other pregnancy complications, including miscarriage and preterm birth.
Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal imbalances can have a significant impact on ovulation. Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and hypothalamic amenorrhea (HA) can disrupt the delicate balance of hormones that regulate the menstrual cycle, leading to irregular or absent ovulation.
PCOS is a common hormonal disorder that affects up to 10% of women of reproductive age. Women with PCOS may have high levels of androgens, insulin resistance, and irregular menstrual cycles. These factors can all contribute to ovulatory dysfunction.
HA, on the other hand, is characterized by low levels of hormones such as estrogen and progesterone. It is often caused by factors such as excessive exercise, stress, or a low body weight.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, and stress can also affect ovulation. Maintaining a healthy body weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise, which can be monitored using a BMI Calculator, can improve fertility and increase the likelihood of ovulation. On the other hand, being underweight or overweight can disrupt the hormonal balance in the body, leading to irregular ovulation.
Chronic stress has also been shown to have a negative impact on fertility. Stress can affect the hypothalamus, which plays a key role in regulating the menstrual cycle, leading to irregular ovulation or even anovulation.
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption have also been shown to have a negative impact on fertility, reducing the chances of conception and increasing the risk of pregnancy complications.
It is important for women who are trying to conceive to pay attention to their lifestyle habits and to seek medical advice if they are experiencing irregular periods or other signs of ovulatory dysfunction. With the right support and care, many women can overcome these obstacles and achieve a healthy pregnancy.
Signs and Symptoms of Ovulation
For menstruating women who are trying to conceive, it is important to be able to recognize the signs and symptoms of ovulation. Knowing when you are ovulating can help you time intercourse to increase your chances of getting pregnant.
Basal Body Temperature
Basal body temperature (BBT) is the temperature of your body at rest. Tracking your BBT can help you determine when you are ovulating. Your BBT rises slightly after ovulation due to an increase in progesterone. By tracking your BBT over the course of your menstrual cycle, you can pinpoint when your BBT rises, indicating that you have ovulated.
To track your BBT, use a basal thermometer, which is more sensitive than a regular thermometer. Take your temperature at the same time every morning before getting out of bed, and record your temperature on a chart. You should see a slight increase in temperature after ovulation, typically by about 0.5-1 degree Fahrenheit.
Cervical Mucus Changes
Cervical mucus changes throughout your menstrual cycle, becoming more fertile and stretchy around the time of ovulation. This is due to an increase in estrogen levels, which helps create an optimal environment for sperm to survive and travel to the egg.
To track your cervical mucus changes, check your discharge daily by wiping with toilet paper or using your fingers. Around ovulation, your discharge will become clearer, thinner, and more stretchy, similar to egg whites.
Ovulation Predictor Kits
Ovulation predictor kits (OPKs) detect a surge in luteinizing hormone (LH) in your urine, which occurs 12-36 hours before ovulation. By using an OPK, you can predict when you are about to ovulate and time intercourse accordingly.
To use an OPK, follow the instructions on the package. Typically, you will need to start testing a few days before you expect to ovulate, and continue testing until you get a positive result. A positive result means that you will ovulate within the next 12-36 hours, so it is important to have intercourse during this time to increase your chances of getting pregnant.
Being able to recognize the signs and symptoms of ovulation is important for menstruating women who are trying to conceive. By tracking your BBT, monitoring your cervical mucus changes, and using ovulation predictor kits or an Ovulation Calculator, you can pinpoint when you are ovulating and time intercourse accordingly. Remember to speak with your healthcare provider if you have concerns about your fertility or are having difficulty getting pregnant.
Understanding Fertility
The Fertile Window
The fertile window is the period during a woman’s menstrual cycle when she is most likely to conceive. This window includes the days leading up to and including ovulation. The fertile window typically lasts about six days, with the most fertile day being the day of ovulation itself.
Ovulation is the process by which a mature egg is released from the ovary and travels down the fallopian tube, where it may be fertilized by sperm. Because sperm can survive in the female reproductive tract for several days, having intercourse in the days leading up to ovulation can also result in pregnancy.
It is important to note that the timing of the fertile window can vary from woman to woman and even from cycle to cycle. Factors such as age, hormonal imbalances, and stress can all affect the timing of ovulation and the length of the fertile window.
Factors Affecting Fertility
There are a number of factors that can affect a woman’s fertility, including:
- Age: As a woman ages, her fertility naturally declines. This is due to a decrease in the number and quality of eggs in the ovaries.
- Hormonal imbalances: Hormonal imbalances can affect ovulation and the menstrual cycle, making it more difficult to conceive.
- Weight: Both underweight and overweight women may have difficulty conceiving. Excess body fat can cause hormonal imbalances while being underweight can disrupt ovulation.
- Smoking: Smoking has been shown to decrease fertility in women. It can also increase the risk of miscarriage and ectopic pregnancy.
- Alcohol and drug use: Excessive alcohol and drug use can also decrease fertility in women.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and endometriosis, can affect fertility.
Conception
Conception occurs when a sperm fertilizes an egg. Once fertilized, the egg begins to divide and form a blastocyst, which will eventually implant in the lining of the uterus and develop into a fetus.
It is important for women who are trying to conceive to understand their menstrual cycle and the timing of ovulation. By tracking ovulation and having intercourse during the fertile window, women can increase their chances of conception.
There are also a number of lifestyle changes women can make to increase their fertility, such as maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and reducing alcohol and drug use. In some cases, medical treatments may be necessary to address fertility issues.
Overall, understanding fertility is an important part of the journey to parenthood. By learning about the factors that can affect fertility and taking steps to promote reproductive health, women can increase their chances of conceiving and having a healthy pregnancy.
Ovulation Disorders
Ovulation disorders are a common cause of infertility in women. There are several different types of ovulation disorders, each with its own unique set of causes and symptoms. It is important to understand the different types of ovulation disorders, as they can significantly impact a woman’s ability to conceive.
Anovulation
Anovulation is a condition where a woman does not ovulate, or release an egg, during her menstrual cycle. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including hormonal imbalances, stress, excessive exercise, and certain medical conditions.
Anovulation is a common cause of infertility in women, as without ovulation, fertilization cannot occur. Women who experience anovulation may have irregular menstrual cycles or no menstrual cycle at all. They may also experience symptoms such as weight gain, acne, and excessive hair growth.
There are several treatment options available for women with anovulation, including medication to stimulate ovulation, lifestyle changes, and fertility treatments such as in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder that affects up to 10% of women of childbearing age. Women with PCOS have enlarged ovaries that contain multiple small cysts. PCOS can cause a range of symptoms, including irregular menstrual cycles, weight gain, acne, and excessive hair growth.
PCOS is also a common cause of infertility in women, as it can disrupt the ovulation process. Women with PCOS may not ovulate regularly, or they may not ovulate at all.
There are several treatment options available for women with PCOS, including medication to regulate ovulation, lifestyle changes, and fertility treatments such as IVF. Weight loss can also be an effective treatment for PCOS, as it can help to regulate hormonal imbalances and improve ovulation.
Premature Ovarian Failure
Premature ovarian failure (POF), also known as premature menopause, occurs when a woman’s ovaries stop functioning before the age of 40. POF can be caused by a variety of factors, including autoimmune disorders, genetic conditions, and certain medical treatments such as chemotherapy.
Women with POF may experience symptoms such as irregular menstrual cycles, hot flashes, and vaginal dryness. POF can also cause infertility, as it can prevent ovulation from occurring.
There is no cure for POF, but there are treatment options available to manage the symptoms. Hormone replacement therapy can be used to regulate hormonal imbalances and reduce symptoms such as hot flashes and vaginal dryness. Fertility treatments such as IVF may also be an option for women with POF who wish to conceive.
Understanding the different types of ovulation disorders is essential for women who are trying to conceive. Anovulation, PCOS, and POF can all impact a woman’s ability to ovulate and conceive. It is important for women to seek medical advice if they are experiencing irregular menstrual cycles or other symptoms of ovulation disorders. With proper diagnosis and treatment, many women with ovulation disorders are able to successfully conceive and start a family.
Treatments for Ovulation Disorders
If you are trying to conceive, it is essential to have a healthy ovulation cycle. However, some women may experience ovulation disorders that can hinder their chances of conceiving. Fortunately, there are several treatments available to help women with ovulation disorders. In this section, we will discuss the three most common treatments for ovulation disorders: medications, surgery, and assisted reproductive technologies.
Medications
One of the most common treatments for ovulation disorders is medication. Medications can help regulate hormones and stimulate ovulation. The most commonly used medication for ovulation induction is clomiphene citrate. Clomiphene citrate is a selective estrogen receptor modulator that stimulates the release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) from the pituitary gland. FSH and LH are essential hormones for ovulation, and clomiphene citrate helps increase their levels in the body. Studies have shown that clomiphene citrate is successful in inducing ovulation in up to 80% of women with ovulation disorders.
Another medication used to induce ovulation is human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). HCG is a hormone that triggers ovulation in women. HCG is usually used in combination with clomiphene citrate to increase the chances of ovulation. A study conducted on 154 infertile women with ovulation disorders showed that the combination of clomiphene citrate and hCG resulted in a 70% pregnancy rate.
Surgery
Surgery may be necessary for women with ovulation disorders caused by structural problems such as ovarian cysts or uterine fibroids. Surgical procedures such as laparoscopy or hysteroscopy can help remove these structural problems and improve ovulation. A study conducted on 70 women with ovulation disorders found that laparoscopic ovarian drilling (LOD) improved ovulation in 80% of women and resulted in a pregnancy rate of 70%.
Assisted Reproductive Technologies
Assisted reproductive technologies (ART) are used for women who are unable to conceive naturally. ART involves the use of medical procedures to fertilize eggs and implant them in the uterus. The most common forms of ART are in vitro fertilization (IVF) and intrauterine insemination (IUI).
IVF involves the fertilization of eggs and sperm in a laboratory. The resulting embryos are then transferred into the uterus. IVF has a success rate of 30% to 40% per cycle for women under the age of 35.
IUI involves the insertion of sperm directly into the uterus. IUI is often used for women with mild ovulation disorders or for couples with male factor infertility. A study conducted on 1,348 women found that IUI resulted in a pregnancy rate of 18.7% per cycle.
If you are trying to conceive and have an ovulation disorder, there are several treatment options available. Medications such as clomiphene citrate and hCG can help induce ovulation, while surgery can correct structural problems that may be hindering ovulation. ART, such as IVF and IUI, can also be used for women who are unable to conceive naturally. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best treatment option for your individual needs.
Importance of Seeking Medical Advice
If you are a menstruating woman who is trying to conceive, understanding ovulation is crucial. Knowing when you are most fertile can increase your chances of conception and help you plan accordingly. However, it is important to seek medical advice if you have any concerns about your ovulation or fertility.
Visiting a healthcare provider can help you identify any underlying issues that may be affecting your ovulation, such as hormonal imbalances or ovulation disorders. They can also provide guidance on lifestyle changes that may improve your chances of conceiving, such as maintaining a healthy weight and managing stress levels.
In addition, seeking medical advice early on can help you avoid unnecessary delays in achieving pregnancy. Studies have shown that early diagnosis and treatment of ovulation disorders can significantly improve a woman’s chances of conceiving.
Future Directions in Ovulation Research
Research in the field of ovulation is constantly evolving, with new discoveries being made each year. In the future, advancements in technology and medical research may offer new options for women who are trying to conceive.
For example, researchers are currently exploring the use of artificial intelligence (AI) to predict ovulation with greater accuracy. By analyzing data from a variety of sources, including basal body temperature, cervical mucus, and hormone levels, AI algorithms may be able to identify patterns that can help women predict their ovulation more accurately.
In addition, researchers are investigating the use of new fertility treatments, such as in vitro maturation (IVM), which involves maturing eggs outside of the body and then fertilizing them with sperm. This technique may offer a less invasive alternative to traditional in vitro fertilization (IVF), which involves retrieving eggs directly from the ovaries.
Overall, by staying informed about the latest research and seeking medical advice when necessary, women who are trying to conceive can increase their chances of achieving a successful pregnancy.









