Tests and Diagnosis of Colorectal Cancer
- Updated on: Aug 8, 2024
- 3 min Read
- Published on Feb 21, 2021

When you first meet your doctor, he or she will ask about your symptoms and whether you have a family history of any cancer, in particular, colorectal cancer or if you are a high risk.
Early diagnosis can however help detecting the cancer before it spreads and also possibly get a cure for it. This is why it is important to get screened for colorectal cancer. American Cancer Society recommends screening for colorectal cancer as part of early detection before any symptoms appear.
Your doctor can find if there is something suspicious during a screening exam, or if your body shows possible symptoms of colorectal cancer.
He or she will recommend suitable examinations and tests to find the cause of the problem. The tests that your doctor may do are outlined below.
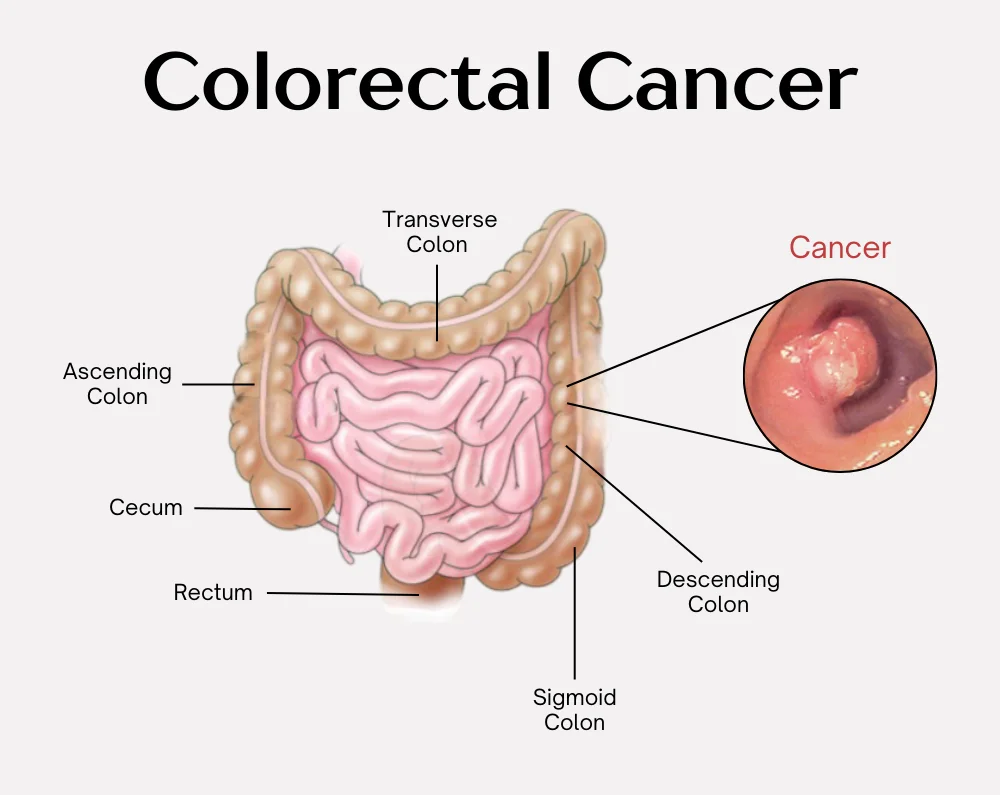
Tests for Colorectal Cancer
Physical Exams
When you meet your doctor, he may first carry out a simple examination of your abdomen and bottom. This is called digital rectal examination (DRE) and its aim is to examine your abdomen.
This helps in checking whether there are any extra growths or lumps in your abdomen. Sometimes, these tests can be uncomfortable. Most people find them embarrassing because they involve reaching out the abdomen through the back passage, but they take only a little time – a few minutes only.
Blood Test
Your doctor may ask you to get some blood tests to understand the underlying cause of the symptoms. No blood test can confirm colorectal cancer. These tests are done only to rule out other diseases. Blood tests may involve such as liver function, complete blood count tests etc.
Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy involves the use of a long thin tube that is inserted inside your colon to examine the inner colon walls. The tube is fitted with a camera for visualization purposes.The procedure enables your doctor to view inside your colon and rectum and identify anything unusual there. Your doctor can also extract tissues from the colon walls through colonoscopy so they can be sent to a laboratory for detailed analysis.
Your bowel has to be empty when a colonoscopy is performed.
You’ll be given a sedative so that you feel relaxed during the procedure. He will then insert a colonoscope into your rectum and move it along the length of your large bowel for visualization of different areas inside the colon. This isn’t generally painful, but it can make you feel a bit uncomfortable.
Flexible sigmoidoscopy
A flexible sigmoidoscopy is an examination of your rectum and a portion of your large bowel using a device called a sigmoidoscope. A sigmoidoscope is a thin, long, and flexible tube that is connected to a camera a light source.
The camera transmits images to an external display for visualization.
A sigmoidoscopy can be slightly uncomfortable, but it only takes a few minutes. You can go home after the examination is complete. There is no need of hospital stay. Sigmoidoscopy is similar to a colonoscopy except that a sigmoidoscope does not go as deep as a colonoscope goes. A colonoscope is longer than the sigmoidoscope.
CT Scan
CT scans provide a detailed image of your colon. For the purpose of colorectal cancer diagnosis, it is also called virtual colonoscopy or CT colonography.
A CT colonography is a less invasive test than a normal. However, your doctor may still need to have colonoscopy or flexible sigmoidoscopy at a later stage if any abnormalities are detected in the CT scan or if a biopsy is required.











