Conditions that Can Increase Risk of a Stroke
- Updated on: Jul 8, 2024
- 2 min Read
- Published on Apr 19, 2021
When do you get a stroke?
A stroke occurs when the blood supply to a portion of your brain is interrupted or reduced, causing the brain tissue deprived of oxygen and other nutrients. Brain cells begin to die soon.
A stroke is a medical emergency and requires an immediate treatment. Prompt action can minimize brain damage and potential complications and even reduce the risk of death.
The different types of strokes have different causes as discussed herein.
Reasons behind ischemic stroke
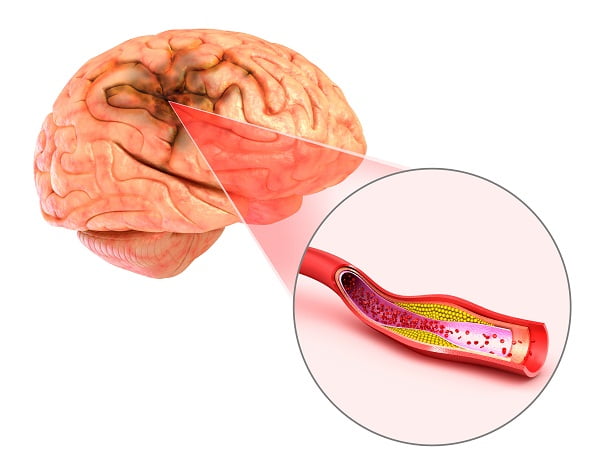
Ischemic stroke is the most common of all stroke forms, accounting for around 80 percent of all stroke cases. This type of stroke is caused by blockages or narrowing of the arteries that supply blood to the brain, thereby resulting in ischemia, which is characterized by severely reduced blood flow causing damage to the brain cells.
These blockages are generally caused by blood clots, which can form either in the arteries within the brain, or in other blood vessels in the body before they are moved into narrower arteries within the brain along with the bloodstream.
Fatty deposits within the arteries (called plaque) can also build clots and result in ischemia.
Reasons behind hemorrhagic stroke
Hemorrhagic strokes are generally caused by arteries in the brain when there is a leakage of blood from them or they burst open. The blood then puts pressure on brain cells and causes damage. It also reduces the blood supply to the brain tissue.
Sometimes, blood vessels in the brain can burst open and spill blood within the brain or near the surface of the brain, leading to the deposit of blood into the space between the brain and the skull.
Causes of transient ischemic attack (TIA)
Transient ischemic attacks are caused when the flow of blood to the brain is interrupted for a short time only. TIAs are similar to ischemic strokes in the way that they are often caused by blood clots.
TIAs should also be regarded as medical emergencies just like the other kinds of stroke, even if the blockage of the artery and symptoms are temporary. TIAs should be treated as warning signs for future strokes and are indicative of a partially blocked artery or clot source in the heart.
Common conditions that make you more likely to have a stroke
You can treat some of these conditions that make you more likely to have a stroke. But not all of them can be changed:
High blood pressure
Hypertension (high blood pressure) is the biggest cause of strokes worldwide. If your blood pressure is generally 140/90 or higher, your doctor will prepare a treatment plan with you to avoid the risk of strokes and other complications.
Use of Tobacco
Smoking or chewing tobacco raises your risks of a stroke. Nicotine causes your blood pressure to go up. Cigarette smoke also causes a plaque buildup in your main neck artery. It thickens your blood and makes it more likely to clot. Even secondhand smoke can harm you.
Heart disease
Heart diseases such as coronary artery disease, defective heart valves, arrhythmia, atrial fibrillation increases the risk of strokes particularly, among the old people. You can also develop clogged arteries from fatty deposits.
Diabetes
Diabetes is generally associated with obesity and high blood pressure. Both of them raise the chance of getting a stroke. Diabetes can damage your blood vessels, which puts you at risk of a stroke. If you have a stroke when your blood sugar levels are high (such as in diabetes), the damages to the brain cells is greater.












