Important Things You Should Know About a Brain Stroke
- Updated on: Jul 8, 2024
- 3 min Read
- Published on Apr 19, 2021

Learning about stroke
A stroke occurs when the blood supply to part of your brain is interrupted or reduced, causing it deprived of oxygen and nutrients. The brain cells begin to die within a few minutes of the stroke.
Stroke is a disease that affects the arteries connecting to and within the brain.
A stroke is a serious, life-threatening, medical emergency. Immediate treatment is needed. If an action is taken immediately, one can minimize the damage of brain tissues and associated complications. The sooner a person receives treatment for a stroke, the less damage is likely to happen.
The good news is that strokes can be treated and prevented. Compared to two decades ago, very few people die of stroke nowadays because of advancement diagnosis and treatment options and a general awareness about brain health among people. But still, it is the No. 5 cause of death and a leading cause of disability in the United States and the rest of the world.
If you suspect that you or someone else is having a stroke, call the emergency immediately and ask for an ambulance.
Unlike in the past, a stroke is now a very much treatable condition and requires an urgent and special attention of a multi-discplinary team particularly involving a neuorlogist. Medical treatment and specialist recovery care are both important for a stroke survivor. While a heart attack can kill a person immediately, a stroke on the contrary does not immediately take the like of a perso, instead the body becomes paralysed from one side.
What are the most common types of strokes?
There are three main types of stroke primarily:
- transient ischemic attack (mini stroke)
- ischemic (blood clots)
- hemorrhagic (vessel ruptures)
It’s considered that 87 percent of strokes are ischemic.
Transient ischemic attack (Mini stroke)
It is also called a warning or a mini stroke. A clot that temporarily blocks blood flow to your brain causes a transient ischemic attack (TIA). The blood clot and TIA symptoms last for a brief period of time.
It should be known that a transient ischemic attack is a warning sign of a future major stroke. Keep in mind that:
- a TIA is a medical emergency
- strokes and TIAs require emergency care and attention. Call emergency immediately if you notice any signs of a stroke or see symptoms in someone around you.
- you cannot know in the beginning whether the symptoms are from a TIA or from a major stroke
- blood clots often occur in TIAs also
- more than a third of people who have a TIA and don’t receive appropriate treatment have a major stroke within 1 year. About 10% to 15% of people will have a major stroke within 3 months of a TIA.
- if a TIA is treated well, you can lower the risk of a major stroke. Your doctor can identify the right cause of the stroke and plan the treatment accordingly.
Ischemic stroke (blot clots)
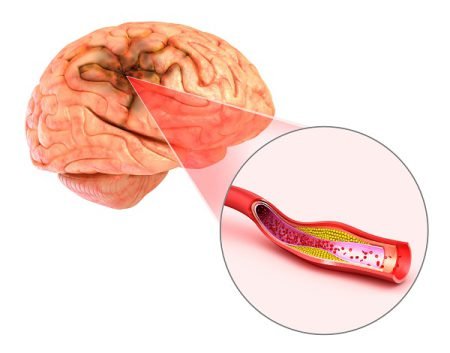
An ischemic stroke occurs when a blood clot keeps blood from flowing to your brain. The blood clot is often due to atherosclerosis, which is caused due to the buildup of fatty deposits on the inner lining of a blood vessel. A portion of these fatty deposits can break off and block the flow of blood in your brain.
It is similar to that of a heart attack, except that in a heart attack, a blood clot blocks blood flow to a portion of your heart and not brain.
An ischemic stroke can be embolic, which means that the blood clot moves from another part of your body to the brain. About 15 percent of embolic strokes occur due to a heart condition called atrial fibrillation (which is characterized by irregular heartbeats).
Another type of ischemic stroke is a thrombotic stroke, which is caused by a clot forming in a blood vessel in your brain.
Unlike a TIA, the blood clot that causes an ischemic stroke cannot go away without proper treatment.
Read about causes of different types of stroke.
Read about treatment of different types of stroke.
Hemorrhagic stroke (blood vessel rupture)
A hemorrhagic stroke results when a blood vessel in your brain ruptures or breaks, causing the blood to spill into the surrounding tissues.
There are two types of hemorrhagic strokes:
- aneurysm: it causes a portion of the blood vessel to inflate outward and sometimes rupture
- arteriovenous malformation: it results in abnormally formed blood vessels. If such types of blood vessels rupture, one can get a hemorrhagic stroke.
Strokes are indicators of nurological deficits and causes death of about one in every three patients at 6 months time duration. Effective management depends on prompt action taken for the correction.