What Causes Urinary Incontinence?
- Updated on: Jul 9, 2024
- 6 min Read
By
- Published on Oct 3, 2019

People suffering from urinary incontinence experience leakage of urine. The leakage can be occasional (minor leakage) or more frequent (small to moderate amount of urine). Urinary incontinence is a very common problem faced by men and women both. But it is more common in women.
Causes of Urinary Incontinence
We cannot describe urinary incontinence as a disease but, it is a symptom. It is usually caused by everyday habits, underlying medical conditions, or physical problems.
A thorough evaluation of the symptoms by the doctor can help find the real cause of the problem. Like symptoms, the causes of urinary incontinence are different for different types. The main causes of urinary incontinence are described below:
Causes of stress incontinence
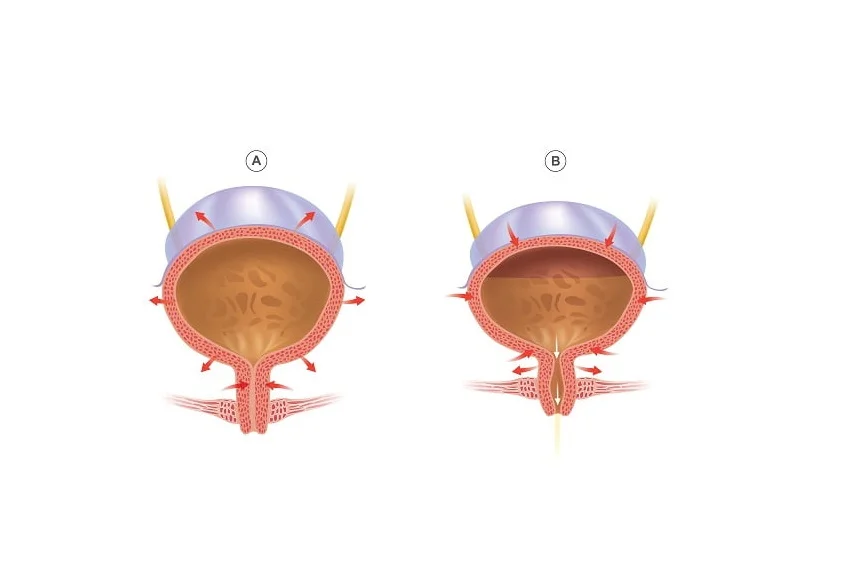
Stress incontinence is caused due to problems with the pelvic floor muscles. The pelvic floor muscles get stretched. These muscles are unable to hold the bladder well and hence, the bladder becomes loose.
The muscles that close the urethra cannot be tightened and the urine may leak whenever the patient sneezes or coughs. The reasons for stretching of pelvic floor muscles may be one of the following:
Pregnancy – Pregnancy is responsible for stretching almost all the muscles of the body.
Childbirth (labor) – Normal delivery makes a lot of changes in a woman’s body. Childbirth causes a lot of damage to the body and internal muscles.
Menopause – In menopause, the estrogen levels in the women body drop, and the muscles may get weaker.
Hysterectomy – In women, surgical removal of the uterus (womb) may weaken the internal muscles.
Prostatectomy – removal of the prostate gland in men, which causes damage to the bladder.
Age – Stress incontinence is very common in old age.
Obesity – It increases pressure on the tummy and thus stretches the internal muscles.
Parkinson’s disease – It is a neurological condition that affects the patient’s brain or spinal cord.
Causes of urge incontinence
Urge incontinence occurs when the muscles of the bladder contract involuntarily (without any stimuli) and push the urine forcefully out of the bladder.
The following causes of urge incontinence have been identified:
Cystitis – It is the inflammation of the inner walls of the bladder.
Parkinson’s disease – It is a neurological condition affecting the brain and spinal cord of the patient. A patient suffering from it has no control over his brain.
Problem with prostate – Problems like enlargement of the prostate may cause the bladder to drop down, which in turn irritates the urethra.
Alcohol or caffeine consumption – The more alcohol is consumed by an individual, the more urine will be produced. It creates a pressure on the bladder.
Less intake of fluid – If a patient consumes fewer fluids, strong and concentrated urine is collected in the bladder and can irritate.
Constipation – Any problem with bowel movement can weaken the pelvic muscles which are responsible for controlling the bladder.
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) – It affects part of the urinary tract. Such infections can irritate the bladder and may cause a strong urge to urinate.
Causes of overflow incontinence
Overflow incontinence happens when there is an obstruction or blockage to the bladder. The bladder becomes full and yet there is no urge to urinate.
The following may cause an obstruction:
Problem with detrusor muscle – Detrusor muscle is found in the walls of the bladder. This muscle remains relaxed to allow the bladder to fill the urine and then contracts to allow the bladder to pass the urine. If the detrusor muscle does not contract fully, the bladder will not empty completely and eventually will stretch. The detrusor muscle may not contract fully due to a few reasons like:
- Nerves are damaged
- The patient is on certain medications that affect the detrusor muscle in a bad way
An enlarged prostate gland – This may cause blockage in the prostate gland. The bladder does not empty.
A tumor in the bladder – Bladder cancer can cause blockage of the urethra.
Bladder stones – Bladder stones block the urethra and do not allow the bladder to empty.
Constipation – A full bowel can press against the bladder thus, blocking the flow of the urine and making it difficult for the bladder to void completely.
Damage to nerves – When the nerves are damaged, the person may or may not sense that the bladder is full.
Causes of total incontinence
Total incontinence occurs when a person has no control over the urinary process. A continuous loss of urine is experienced. The following can cause total incontinence:
Bladder problem from birth – An anatomical defect the person has had from birth that does not allow the bladder to void completely
Spinal cord injury – If the nerves are damaged, the nerve signals between the brain and the bladder will be disrupted.
A fistula – In women, a channel or a hole is developed between the bladder and a nearby organ like a vagina. It allows urine to pass where it should not. Sometimes urine may come from the vagina due to this abnormal connection.
Medications that may cause incontinence
Some medicines can disturb the normal process of storing and passing urine. Such medications can even increase the amount of urine you produce. These include:
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors – These medications affect lower urinary tract functions and may cause incontinence.
Diuretics – This medicine increases the production of urine from the kidney, thus increasing the urine frequency and urge to urinate.
Antidepressants – Such medicines are given to reduce depression. These medicines can impair the contracting ability of the bladder and the bladder may not function properly.
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) – It uses women’s hormones to treat menopause. Such medicines can worsen the incontinence in women.
Sedatives – These medicines are given to reduce tension and induce peaceful sleep. Such medicines cause grogginess (not recognizing to use the bathroom until it is too late).
Risk factors for Urinary Incontinence
Anyone at any age can develop any type of incontinence. However, certain health conditions can put you at a greater risk of developing urinary incontinence. Such risk factors for urinary incontinence are given below:
Age
Urinary incontinence is very common in old age. More precisely, the chances of urinary incontinence increase after the age of 40. As the age increases the likelihood of urinary incontinence also increases.
Gender
Urinary incontinence is more common in women as compared to men. This is because a woman’s body undergoes a lot of changes in her lifetime. These changes may give rise to incontinence.
Pregnancy
During pregnancy, women undergo a lot of changes. Increased stomach size puts pressure on the internal muscles. It may pose a high risk of developing urinary incontinence.
Multiple childbirths
During the delivery of a child, the internal muscles of a woman’s body undergo relaxation and contraction. It weakens those muscles. In multiple deliveries, the condition is even worse. Weak muscles may no longer support the bladder firmly and may result in incontinence.
Pelvic surgery
Any kind of pelvic surgery may weaken the pelvic area muscles. They may no longer act strongly and may increase the risk of developing any kind of incontinence.
Menopause
During menopause, a lot of hormonal changes take place in a woman’s body. The lack of estrogen (female hormone) can weaken the pelvic muscles. The muscles can no longer hold the bladder. As the level of hormone drops, the risk of incontinence increases.
Urinary tract infections (UTIs)
Urinary tract infection may result in an irritated and inflamed bladder. As a result, the muscles of the bladder may tense up and may cause an urge to urinate frequently.
Neurological conditions
Neurological conditions affect the nervous system of the individual, thus affecting the brain, spinal cord, and other nerves. The damaged brain can no longer coordinate and control the proper functioning of the bladder.
Obesity
The extra weight of the obese person may put continuous pressure on the abdomen and lower abdomen. The bladder also experiences the same pressure. This continuous pressure can give rise to incontinence.
Alcohol consumption
If a person consumes a lot of alcohol, the production of urine will also increase. This will eventually increase the pressure on the kidney, bladder, and urethra. Their functioning will be disturbed which may cause incontinence.
Family history
If a person in a family is suffering from urge incontinence, the risk of developing incontinence in other persons in the family is very high.
Stroke
After a stroke the muscles that control the urination process weaken, thus making it more likely for the person to develop incontinence.
Prostate trouble
Any problem with the prostate gland may block the urethra and may cause urine to leak. The risk of developing incontinence is very high in such situations.
Chronic bladder infections
Some bladder infections can result in irritation of the walls of the bladder or inflammation of the bladder. The functioning of the bladder is disturbed in such cases and the chances of developing urinary incontinence become high.
FAQs
Is pregnancy a common cause of urinary incontinence in women?
Yes, pregnancy and childbirth can weaken pelvic floor muscles, leading to urinary incontinence. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can also contribute to bladder control issues.
Can obesity contribute to urinary incontinence?
Yes, excess weight puts pressure on the bladder and surrounding muscles, increasing the risk of urinary incontinence. Losing weight through lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms.
Are neurological disorders always responsible for urinary incontinence?
While neurological issues can cause urinary incontinence, it can also result from factors like aging, hormonal changes, and urinary tract infections. A comprehensive assessment is necessary for accurate diagnosis.
Can urinary tract infections (UTIs) cause temporary urinary incontinence?
Yes, UTIs can irritate the bladder and lead to temporary urinary incontinence. Treating the infection usually resolves the associated symptoms.
Is smoking linked to urinary incontinence?
Yes, smoking can contribute to urinary incontinence by causing chronic coughing, which strains pelvic floor muscles. Quitting smoking can have positive effects on bladder health.