What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Enlarged Prostate (Benign Prostate Enlargement or Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia)?
- Updated on: Jun 11, 2024
- 2 min Read
- Published on Apr 19, 2021
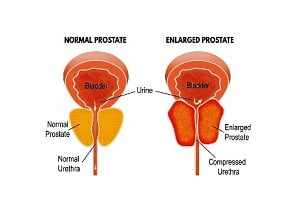
Enlarged prostate symptoms
The symptoms of Benign Prostate Enlargement (BPE) are often very mild in the beginning, but they become more serious if they aren’t treated on time.
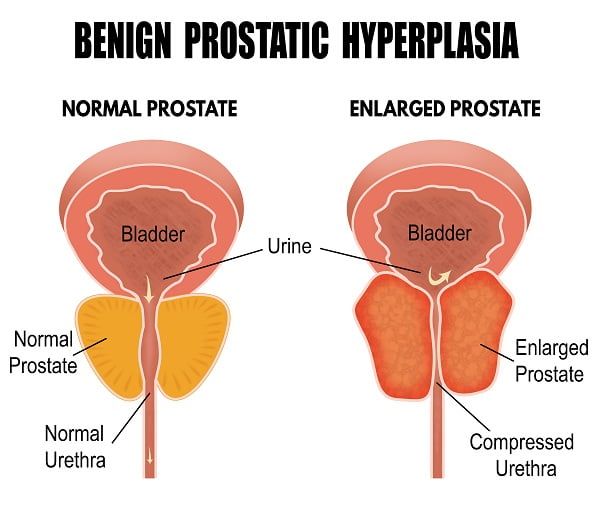
The prostate is a small gland, located in the pelvis region, between the penis and bladder. If the prostate becomes enlarged, it can exert pressure on your bladder and urethra. Urethra is the tube through which urine passes.
Prostate enlargement can affect your urination in several ways.
Symptoms of enlarged prostate can include:
- Difficulty in starting urination
- Painful urination
- A weak urinary stream
- A feeling of incomplete bladder emptying
- Sudden urge to urinate
- A need to strain when urinating
- Waking up frequently at night to pass urine (nocturia)
- Urinating again in minutes after doing once
- Frequent urination
- Urinary stream that stops and starts
- Incontinence or continued leakage of urine
- Blood in urine
See your doctor if you have any of these symptoms. They are treatable, and treatment generally helps prevent serious complications.
When to call a doctor?
In most men, prostate enlargement occurs for weeks, months and years before they notice their symptoms and see a doctor. The urinary problems related to enlarged prostate affect quality of life, initially causing a man to get up at night several times to urinate and also trouble falling asleep again.
It is not necessary that the signs of BPH are always obvious. Sometimes, seemingly minor urinary problems may indicate a serious problem like prostate enlargement.
In order to find out the cause of the problem, it is important for you to see a doctor when you see any changes in your urine pattern or face any urinary problems. It may be a bladder cancer, a prostate cancer, kidney stones or any other problem.
If symptoms such as bladder pain, burning with urination, blood in urine are experienced, you should rush to the doctor immediately or seek evaluation at emergency department of hospital.
For acute or chronic urinary retention, you should rush to the nearest hospital for bladder drainage which is usually done with the help of catheter (a tube inserted into bladder).
Men of age 50 and above should undergo their prostate examination annually by a physician even if the symptoms are not there.