What Are the Complications of Tuberculosis (TB)?
- Updated on: Aug 3, 2024
- 3 min Read
- Published on Sep 27, 2019

Tuberculosis Complications
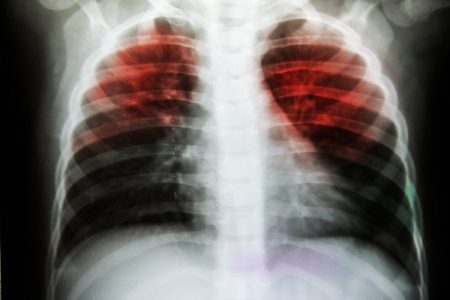
Diagnosis and treatment of tuberculosis is a challenging task because of heterogeneous sites of infection. Even with proper treatment, tuberculosis lead to significant short- and long-term health complications.
Lungs are the major site of infection by M.tuberculosis. The disease can cause various fatal complications if proper treatment is not provided.
Following are the major complications that are associated with tuberculosis:
- Hemoptysis
- Pneumothorax
- Bronchiectasis
- Broncholithiasis
- Septic shock
- Malignancy (Cancer)
- Other complications
Hemoptysis
Hemoptysis is the very first symptom as well as complication of tuberculosis. It can be described as coughing up of blood in mucus from bronchi, trachea and lungs. It is considered severe at 300 milliliters (mL). The primary danger arises from choking rather than blood loss.
The complication may be because of lung cancer too. The risk increases if the person smokes or works in silica dust industry.
Pneumothorax
Pneumothorax is another complication of tuberculosis. It is an abnormal collection of air in the pleural cavity.
Pneumothorax is characterized by sudden onset of sharp pain in one side of chest with shortness of breath. This generally happens because of formation of the one-way valve due to damaged tissue. The condition also causes steady oxygen shortage and low blood pressure.
Sometimes, both the lungs get affected by this complication. Unless reversed, the condition can also cause the death of the patient.
Bronchiectasis
Bronchiectasis is a disease that permanent enlarges the airways of lungs. This is caused by a chronic cough and mucus production in the airways. Shortness of breath, blood in a cough and chest pain is common in this condition. Excessive mucus is an immune response towards the presence of bacteria in the airways. The secretions, however, increase the bacterial multiplication ultimately causing blockage of airways.
Broncholithiasis
Broncholithiasis is deposition of calcified material within bronchi and its branches. The condition is caused due to secretion of calcified substances from lymph nodes. It ultimately results in erosion of bronchus wall. The complication may remain latent and not show any symptom. Recurrent chest infections and tuberculosis are said to cause it.
Septic shock
Septic shock is a serious medical condition when an organ is damaged. In case of tuberculosis, it occurs as a response to lung damage and leads to very low blood pressure and other abnormalities. Due to low blood pressure, tissue perfusion pressure is also reduced. This leads to tissue hypoxia.
A large amount of cytokines is released, that result in massive immune response, causing:
- Increased capability permeability
- Increased vasodilation
- Decreased systemic vascular resistance
- Low blood pressure
- Ventricular dilation
The condition may also result in myocardial dysfunction and death. The mortality rate from septic shock is about 25-50%.
Malignancy (Cancer)
Tuberculosis if left untreated can also lead to lung cancer. It causes malignant tumor characterized by uncontrolled growth of tissue cells in lungs. The growth may also spread in parts other than lungs by the process of metastasis.
Most of the cases of lung cancer caused by tuberculosis are because of a chronic condition. The diagnosis is generally confirmed by biopsy and CT-scan.
Other complications
Tuberculosis if left untreated can be fatal. The untreated disease affects lungs as well as other parts of the body. In addition to above-mentioned major complications, following are other severe conditions caused by tuberculosis:
- Back pain and stiffness
- Joint damage (majorly hip and knee joints)
- Arthritis
- Swelling in meningitis
- Liver and kidney dysfunction
- Cardiac tamponade