What Are the Causes of Celiac Disease?
- Updated on: Jun 12, 2024
- 3 min Read
By
- Published on Oct 2, 2019


What Causes Celiac Disease?
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder that is caused by the reaction of an abnormal immune system to gluten (a protein found in bread, biscuits, pasta and cereals).
In this condition, the immune system mistakes the substance that makes gluten as a threat to the body. Antibodies that are produced attack the inside layer of the intestine and make it swollen and inflamed.
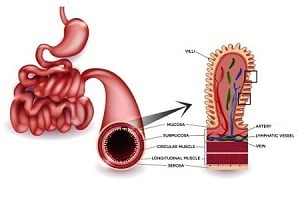
The inside of intestine is covered with millions of tube-like structures called villi. They help in absorption of essential nutrients. In case of celiac disease, the damage to the lining flattens the villi and reduces its capacity. As a result, nutrients are not absorbed and this causes the symptoms of celiac disease.
The reason for some people developing celiac disease is still unknown but there are certain factors as described below that increase the risk of developing the disease:
Family History
Celiac disease is a genetic disorder and runs in families.
- If a person has someone in the family who is having celiac disease, his risk of getting the disease is 10 times higher than the person who has no family history of it.
- If one of the identical twins has celiac disease, there is 75 percent chance that the other twin will also be affected with it.
There is a strong association of celiac disease with the presence of two genes namely HLA DQ2 and HLA DQ8.
Nearly 40 percent people have these genes in their bodies. But all of them do not have celiac disease. This means that presence of HLA DQ2 and HLA DQ8 is necessary but not sufficient for the development of celiac disease. There should be something else that triggers the disorder.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors may play an important role in developing the condition in the following ways:
- Introducing gluten in baby’s diet before they are six months old may increase the chance of the baby developing the disease. Therefore, doctors suggest breastfeeding for the baby for the first six months exclusively.
- After six months, when gluten is introduced in baby’s feed, breastfeeding should be continued. Otherwise, it may pose a risk of developing celiac disease.
- Adults are more likely to develop celiac disease, if in their childhood, they had a digestive system infection like rotavirus infection.
Other Health Problems
There are several health problems, which always give rise to the other. Certain health issues which can cause/trigger celiac disease are listed below.
Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is highly linked to celiac disease. It is estimated that nearly 6 percent of people having diabetes have a high risk of developing celiac disease.
Celiac disease related to diabetes usually shows no symptoms and can only be diagnosed by undergoing screening. Celiac disease is overlooked because diabetes type 2 and celiac disease share same symptoms, which include abdominal pain, bloating, weight loss, and abnormal lever.
Down Syndrome
Down Syndrome is a genetic disorder in which the cells are unusually divided and this develops an extra chromosome in an individual.
A person having an extra chromosome has more genetic material than a normal one. Such an individual may suffer from different intellectual and developmental delays.
Symptoms of Down syndrome may include:
- Flat face, small ears and mouth
- Short neck, arm and legs
- Loose joints
- Low muscle tone
- Below average intelligence
It is believed that approximately 16 percent of people with Down syndrome also develop celiac disease. Because of an increased risk, frequent celiac disease screening and diagnosis is recommended for people with Down syndrome.
Turner Syndrome
Turner syndrome is found in females and it affects the development in them. It is a condition in which the secondary sex chromosome (the X chromosome) goes missing or partially missing. It may cause infertility in women.
Symptoms of Turner syndrome may include:
- Short Stature
- Infertility because of non-functioning ovaries
- Heart problems
- Kidney problems
- High blood pressure
- Swelling
Nearly 5 percent of females with Turner syndrome are at high risk of developing celiac disease. They should get themselves checked regularly for celiac disease.
Neurological Disorders like epilepsy
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder in which the activity of nerve cell in the brain gets disrupted causing unusual seizures. Seizures can affect any process that is coordinated by the brain.
Below are listed common symptoms of epilepsy:
- Loss of consciousness
- Uncontrolled jerky movements of arms and legs
- Temporary confusion
- Psychic behavior
It is estimated that nearly 6 percent of people with epilepsy eventually develop celiac disease.
Ulcerative Colitis
It is a chronic bowel disease that causes inflammation in the digestive tract. People with ulcerative colitis are more likely to develop celiac disease.
Thyroid
Thyroid refers to a condition in which thyroid gland does not function properly. The thyroid gland either does not produce enough hormones or it produces an excessive amount of hormones (increases metabolism of the body).
Most people with thyroid tend to develop celiac disease. It is even likely that thyroid and celiac disease may occur simultaneously because they both are common autoimmune disorders.