Various options are available for the treatment of vitiligo. The main purpose of treatment is to restore the lost skin colour. The treatment suitable for a particular individual will depend on the person’s overall health, age, and location of the patches (symptoms) on the body.
Few people prefer to avoid any treatment. Patients with a lighter skin may not require any therapy in general. Proper protection from the sun may be sufficient for them in order to avoid the normal skin from becoming more tan and causing the lesions to become more apparent.
Treatments choices for vitiligo
Vitiligo is painless unlike psoriasis. However, the social and psychological impact from vitiligo on a patient is huge. The stress from the disfigurement due to vitiligo among patients with darker complexion can be devastating.
There are a number of therapies that can help reduce the appearance of vitiligo on the affected areas of the skin. These treatments may assist in making the skin look more even. The choice of therapy may depend on a number of factors such as number of patches and widespread they are and also mainly on which treatment the person prefers.
Cosmetics
Cosmetic options mainly comprise makeup, self-tanners, and skin dyes. The main purpose of using them is to hide the white patches and thereby making vitiligo less noticeable.
Self-tanning lotions and skin camouflage are quite useful. Most of the topical applications are waterproof and can last on the body for longer durations. Considering the possible side effects from medicine these are preferred for children.
The only disadvantage is that it is a time consuming process to get the natural look and also needs to be repeatedly applied.
Sunscreens
The aim of sunscreen therapy is the protection of the unpigmented skin from sunburn reaction and to limit the tanning of normal pigmented skin. The sun protection factor of these sunscreens should not be less than 30.
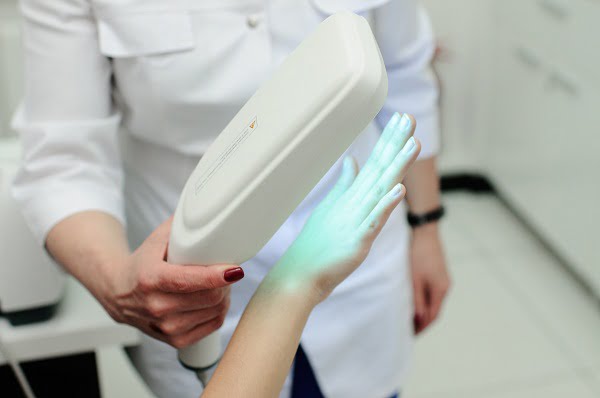
Phototherapy
Exposure to light box or excimer laser treatments are common therapies followed to restore the lost skin colour. Light boxes are used to treat extensive vitiligo whereas lasers are used to treat a small area of it.
UVA light along with a medicine psoralen (may be taken as a pill or applied to the skin directly) therapy can be used in order to restore skin colour in widespread vitiligo.
Depigmentation
Depigmentation removes the balance pigment from the skin. This can be achieved by the use of strong topical lotions or ointments, such as monobenzone, mequinol or hydroquinone.
It is a permanent therapy and very few patients opt for this method. Long exposure to the sun must be avoided after this therapy. Depigmentation can take a few months to years depending on few factors such as the intensity of the original skin tone.
Surgery
Surgery can be an alternative treatment when light therapy and medicines applied to the skin fail. This is not suitable for children. Various surgical procedures are available.
Skin graft
This procedure involves watchful removal of healthy patches of pigmented skin and using them to cover affected areas. Major risk seen in this procedure is scarring and that it is time consuming.
Blister graft
In this method, blisters are made on the pigmented skin with suction. Later, the doctor removes the tops of the blisters and transplants them into an area of discoloured skin. The suction may trigger another patch of vitiligo due the skin damage caused.
Tattooing (micropigmentation)
In this method, the doctor uses a special surgical instrument to implant pigment into the skin. It’s most effective around the lips in people with darker complexions. Tattoos fade way eventually but do not tan. The skin damage caused by tattooing may trigger the onset of another patch of vitiligo.
Topical corticosteroids
Corticosteroid ointments are creams containing steroids which are applied topically to the white patches and can stop the spread of the disease. These should never be used on the face.
Calcipotriene (Dovonex)
Vitamin D is essential for keeping bones and teeth healthy. The main source of vitamin D is sunlight. Calcipotriene is a form of vitamin D and is used as a topical ointment. It may be used along with other corticosteroids or light treatment.
Side effects can include rashes, dry skin and itching. These may be used in combination with other topical steroids. Studies have suggested that topical calcineurin inhibitors with laser therapy or phototherapy may show better treatment results.
Topical calcineurin inhibitors
Pimecrolimus and tacrolimus are calcineurin inhibitors affect the immune system and are used in the treatment of eczema. These are not recommended for vitiligo but are used to help restore skin pigment in these patients too.
Alternative medicine
- Certain vitamins, minerals, amino acids, and enzymes have been shown to return skin colour in people with it.
- The herb Ginkgo biloba, is under clinical trial and may restore skin colour and stop vitiligo from worsening.
- Few other studies show that alpha-lipoic acid, folic acid, vitamin C and vitamin B-12 plus phototherapy may restore skin colour for certain individuals.
Afamelanotide
Studies reveal that the lower levels of melanin in certain people with vitiligo might be due to lower levels of α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (alpha-MSH). Afamelanotide is a synthetic compound that is the analogue of alpha-MSH.
Pseudocatalase
This is a new compound which can provide a cure for the loss of skin colour associated with vitiligo. Individuals treated with a modified pseudocatalase (PC-KUS) showed recovery in the pigmentation of skins and eyelashes. The compound also appeared to restore original hair colour among people with gray hair.