Crohn’s Disease: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, Complications
- Updated on: Jul 10, 2024
- 7 min Read
- Published on Sep 26, 2019
What is crohn’s disease?
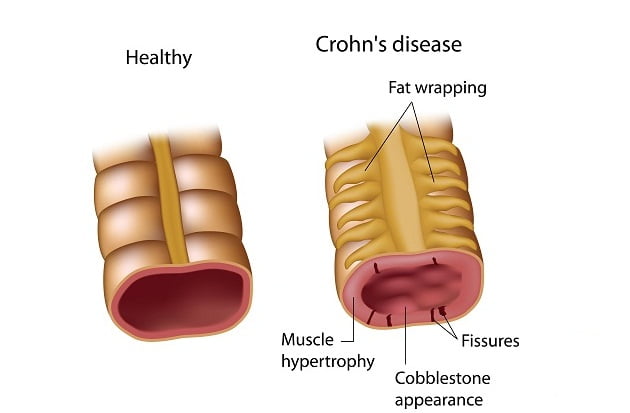
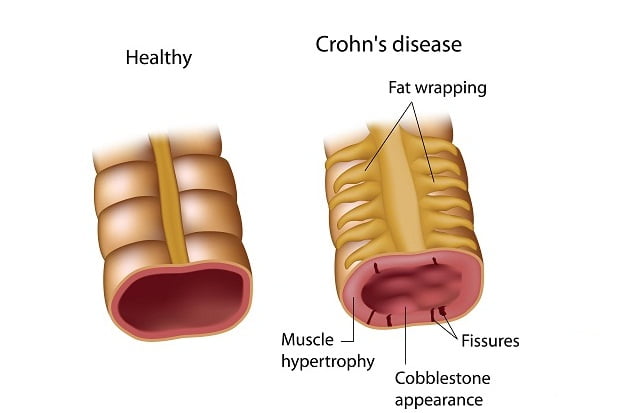
Crohn’s disease is a gastrointestinal complication which involves inflammation of intestine. It is a lifelong disease.
Crohn’s disease results in the formation of breaks or ulcers in the lining of intestine. There are several names given to this disease such as ileitis, granulomatous enteritis or colitis, etc. Crohn’s disease, along with ulcerative colitis, is referred to as inflammatory bowel disease or IBD. The disease does not have any permanent cure.
Crohn’s disease affects both men and women equally. It is more prevalent in Americans, Australians, Europeans, etc. It is unpredictable and its symptoms can relapse with time after the treatment. Patients may also develop certain major life threatening complications due to this disease such as colorectal cancer.
What are the types of crohn’s disease?
The different subtypes of Crohn’s disease and their symptoms are:
Crohn’s colitis
Crohn’s colitis is an intestine inflammation which remains in colon. The common symptoms of crohn’s colitis are abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea.
Crohn’s enteritis
Crohn’s enteritis is an inflammation which is confined to the small intestine. If the disease is only confined in the ileum, it is referred to as Crohn’s ileitis. The common symptoms of crohn’s enteritis are abdomen pain and diarrhea.
Crohn’s terminal ileitis
Crohn’s terminal ileitis is an inflammation that affects only the terminal ileum, the part of the small intestine closest to the colon. Abdominal pain and diarrhea are the common symptoms of crohn’s terminal ileitis.
Crohn’s entero-colitis
Crohn’s entero-colitis is an inflammation which includes both the small intestine and the colon. Its common symptoms are bloody diarrhea and abdominal pain.
What are the causes of crohn’s disease?
Researchers are unable to find the exact cause of crohn’s disease. Some scientists say that an infection by certain bacteria, like mycobacterium, etc might be the reason for its occurrence. Chron’s disease is not contagious.
The disease is believed to be caused due to two basic reasons:
Immune system
According to scientists, immune system activation in the intestine seems to play an important role in IBD. A human immune system is made up of immune cells. Generally, these cells defend the body against harmful agents such as bacteria, viruses, etc.
In ideal cases, the immune system gets activated when the body is exposed to any foreign agent. In people with IBD, the immune system becomes activated abnormally without the presence of any invader. This constant abnormal immune system activation results in the occurrence of severe inflammation and ulceration.
Heredity
Crohn’s disease is generally an inherited condition and is passed from one generation to another. However, people whose close blood related siblings also have the disease are at a greater risk of getting the disease.
Recently, in a study, a gene known as NOD2 has been being associated with crohn’s disease. The gene plays a major role in determining how the body responds to any foreign invader. A person who carries the mutated gene is at an increased risk of developing the crohn’s disease.
What are the risk factors for crohn’s disease?
There are various risk factors that may increase the chances of getting crohn’s disease in a person. Some of them are as follows:
Age
People of any age can develop crohn’s disease but young people are more prone to this condition. Normally, people who are around 30 years old or less are frequently diagnosed with crohn’s disease.
Ethnicity
Crohn’s disease can affect any ethnic group but people of Eastern European Jewish descent are at a higher risk. Recently, reports suggest that black people of North America and the UK are also suffering from this disease.
Family history
People with a long family history of crohn’s disease are at a greater risk of the disease.
Cigarette smoke
Cigarette smoking is the most common risk factor for developing Crohn’s disease.
What are the symptoms of crohn’s disease?
Crohn’s disease affects only a small area of small intestine and the colon. Symptoms of Crohn’s disease can vary from mild to severe. Some of the common symptoms of crohn’s disease are as follows:
- Stomach pain
- Diarrhea
- Weight loss
- Bleeding from rectum
- Constipation
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Nausea
- Mouth sores
- Reduced appetite and weight loss
Apart from the above symptoms, there are some rare symptoms associated with crohn’s disease. The symptoms are as follows:
- Inflammation of eyes, joints and skin
- Inflammation of the bile ducts and liver
- Delay in growth and sexual development, especially in children.
What are the complications of crohn’s disease?
Crohn’s disease, apart from intestine inflammation, can lead to many complications. Some of these complications are as follows:
Bowel obstruction
Crohn’s disease severely affects the thickness of the intestinal wall. As the time progresses with the disease, some parts of the bowel can scar and become narrow, thus blocking the flow of digestive contents.
A surgery may be required to remove and treat the diseased portion of the bowel.
Ulcers
Chronic inflammation can lead to the occurrence of open sores or ulcers in any part of the digestive tract like mouth and anus, and the genital area (perineum).
Fistulas
Fistulas are an abnormal connection between two different organs. Sometimes, ulcers extend through the intestinal wall, thereby creating a fistula. This fistula can connect intestine and skin, etc. Due to the formation of fistulas, food may bypass the intestinal areas of the bowel which is necessary for absorption.
Anal fissure
Anal fissure is a small tear in the tissue that surrounds the anus or in the skin near the anus. An infection can occur in such places. This condition results in severe pain and irritating bowel movement.
Anal fissures and lumps cam though form due to other reasons also. Read about lump near anus.
Malnutrition
Abdominal pain, diarrhea and cramping make it very difficult for the intestine to absorb enough nutrients to maintain required nutrient levels in the body.
Colon cancer
Crohn’s disease increases the risk of colon cancer.
How is crohn’s disease diagnosed?
The diagnosis of Crohn’s disease is performed in patients who show symptoms such as abdominal pain and tenderness, fever, diarrhea with or without bleeding, etc.
Laboratory blood tests may show increased number of white blood cells which tell about the inflammation in the intestine.
Some common tests for diagnosing crohn’s disease are:
Physical Examination
The doctor first does a physical examination of a person and then opts for an accurate diagnostic test to confirm the crohn’s disease. The doctor may ask few questions related to:
- Diet
- Travel records
- Fever and measure the temperature
- Pain and tenderness in abdomen
- Check pulse rate
- Check blood pressure
Blood tests
Doctors may advice the patient to undergo some more blood tests which will tell a lot about the patient’s health such as:
- Inflammation levels in the body
- Presence of any infection
- Is the patient anemic or not?
Stool test
The doctor may also ask the patient to provide a stool sample, which can be further checked for the presence of blood and mucus. This test is also used to know whether an infection is the main cause of crohn’s disease.
Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is a diagnostic test which allows the doctor to examine the patient’s entire colon and ileum with the help of a flexible, thin, lighted tube with a camera attached to it. During the test, the doctor may also perform tissue biopsy in which a small piece of tissue is collected from the body and sent for laboratory analysis.
Computerized tomography (CT)
CT scan is a widely used test which uses an x-ray technique to clearly view status of the disease. With the help of this test, the doctor can examine the entire small intestine along with the nearby tissues. A CT scan provides better image of the organs.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
In an MRI scan, the combination of magnetic field and the radio waves are used to capture the detailed images of the organs and tissues. This test is generally used to examine the position and status of fistula near the anal area or small intestine.
Capsule endoscopy
In a capsule endoscopy, the patient swallows a capsule which has a camera in it. The camera then takes pictures of the small intestine, which are transmitted to a recorder present on the patient’s belt. The images are then displayed on a monitor and analyzed for signs of Crohn’s disease. The camera exits body through the stool.
What are the treatment options for crohn’s disease?
Currently, there is no possible cure for crohn’s disease. The treatment options which are practiced by the doctors are not applicable for all the patients. Therefore, the best possible treatment method is the use of medicines to control the level of inflammation.
Medication
There are various categories of medicines which are used to control the symptoms of crohn’s disease. Some of the medications are as follows:
Anti-inflammatory drugs
These types of drugs are the first step in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. They include:
- Corticosteroids: Drugs such as prednisone, budesonide, etc helps in reducing the inflammation in the body. However, these drugs do not work for all patients with Crohn’s disease. Doctors generally recommend these drugs only if the patient doesn’t respond to other treatments.
- Oral 5-aminosalicylates: Oral 5-aminosalicylates drugs include sulfasalazine, which has sulfa, and mesalamine in it. This drug was extensively used in the past but now is considered of limited benefit only.
Immune system suppressors
Immune system suppressors are the drugs which are used to reduce inflammation. The body in response to such medicines secretes certain chemicals which can result in the inflammation of organs. These drugs are usually used in combination with some other drugs.
- Azathioprine and mercaptopurine– These are used as immunosuppressant drugs for the treatment of IBD.
- Infliximab, adalimumab and certolizumab pegol– These drugs are known as TNF inhibitors which neutralize a protein in the body known as tumor necrosis factor.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics help in reducing drainage amount and heal fistulas in people with Crohn’s disease. According to some scientists, these antibiotics help in reducing harmful bacteria present in the intestine that plays a major role in the activation of intestinal immune system, causing chronic inflammation.
Commonly prescribed antibiotics are ciprofloxacin (Cipro), metronidazole (Flagyl), etc.
Nutrition therapy
The doctor usually recommends a special diet which is given by a feeding tube or the nutrients are directly injected into a vein to treat Crohn’s disease. This can help improve the overall nutrition and allow the bowel to have some rest.
Bowel rest can help in reducing the inflammation in a short period of time.
Your healthcare provider may use nutrition therapy in combination with medications, such as immune system suppressors. He or she may also recommend a low-fiber diet to reduce the risk of any blockage in the intestine.
Surgery
If any of the above therapy doesn’t work for a patient and his or her condition becomes worse, then the doctor may recommend a surgery.
Almost all patients in crohn’s disease undergo a surgery once in their lifetime. During a surgery, the surgeon removes the damaged portion of the intestine and then reconnects healthy sections together. Surgery may also be used to treat fistulas and drain abscesses.