Appendicitis Tests: How To Know That You Have Appendicitis?
- Updated on: Jul 10, 2024
- 6 min Read
- Published on Oct 3, 2019

Appendicitis
A blockage or obstruction in the appendix leads to a condition known as appendicitis. Appendicitis involves inflammation and infection of the appendix. This blockage occurs due to accumulation of mucus, parasites or fecal matter.
Appendicitis requires immediate treatment as the inflamed appendix can rupture and lead to a serious condition known as peritonitis.
How to test for appendicitis?
Appendicitis testing is a difficult task due to the following reasons:
- Symptoms of appendicitis are quite similar to other medical conditions such as gallbladder problems, bladder or urinary tract infection, crohn’s disease, gastritis, intestinal infection and ovary problems.
- All appendicitis symptoms are not observed in about half of the patients, which further makes it difficult to diagnose.
- In some individuals, the appendix may be located in the pelvis or behind the large intestine or around the small bowel or near the right lower part of liver, rather than being present on the lower right-hand side of the abdomen. This change in location of appendix may cause a difficulty for a doctor to diagnose the root cause of appendix pain.
Generally, these appendix tests are conducted of check for appendicitis:
- Abdominal physical examination
- Urine test
- Rectal examination
- Appendix Blood test
- CT scan and/or ultrasound or MRI
More: Appendicitis In Kids: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
More: What Does Appendix Pain Feel Like?
Diagnostic Test for Appendicitis
The following appendix tests are carried out for its diagnosis:
Medical History Review
A medical practitioner may ask about specific symptoms that you experience and about your family history. This evaluation helps the doctor rule out a possibility of other medical ailments. During a medical history review, the doctor will focus on these factors:
- When did your abdominal pain begin
- The exact location and severity of appendix pain
- When did you observe onset of other symptoms
- If you have experienced any medical issue, previous illness or gone through any surgical procedures
- Are you on any specific medication or consuming alcohol or some type of illegal drug
Physical Examination
When you visit a doctor, he/she will first ask about your symptoms.
A physical examination of the abdomen is an important appendicitis test. It involves applying pressure on the appendix to look for severe pain and inflammation in lower right-hand side of the abdomen. The doctor also looks for tenderness in this region. If perforation occurs in the appendix, your stomach may become hard and swollen.
If you experience any of the following signs when the doctor puts pressure on your abdomen, it may indicate presence of appendicitis. However, in order to confirm that it is not any other disease, the doctor may want to conduct more lab tests as will be discussed later.
Rovsing’s sign
Rovsing’s sign involves severe pain in lower right quadrant due to an increase in palpation in the abdominal region. It is a common clinical test for appendicitis.
Psoas sign
Psoas sign involves an extension of the right hip, which may cause pain in the right iliac fossa. Such a pain will indicate presence of retrocecal (appendix present behind the cecum) or pelvic appendix and lead to retroperitoneal inflammation. It is also referred as llio-psoas sign.
Obturator sign
The obturator sign or cope’s obturator test indicates irritation to the obturator internus muscle. It is performed when the doctor suspects occurrence of acute appendicitis.
Guarding
Abdominal guarding is a process of tensing of abdominal wall muscles to provide protection from inflamed organs which indeed puts pressure on the abdominal wall. Guarding is a significant test for the physical examination of a painful abdomen due to inflammation of the inner abdominal surface during appendicitis.
Appendix rebound test
Appendicitis rebound test is a clinical sign which occurs during a physical examination of your abdomen. It is indicative of peritonitis.
Digital rectal exam
Digital rectal exam is performed by the doctor to look for the occurrence of acute appendicitis.
Pelvic exam
Pelvic examination helps in ruling out the probability of having a reproductive system issue or pelvic infection. It is indicative of the presence of acute appendicitis.
Physical examination of abdomen is mostly sufficient for the diagnosis of appendicitis in the patient. The doctor then recommends an immediate visit to a hospital for further treatment.
If the symptoms are unclear, then the doctor performs other tests to confirm the presence of appendicitis and rule out other possibilities.
Lab Test for Appendicitis Diagnosis
Secondary level examination of appendicitis involves certain lab tests which help in confirming the presence of swollen appendix in a patient.
Blood Test for Appendicitis
The doctor performs a complete blood count (CBC) to identify presence of any bacterial infection in the body. An infection is one of the major causes of appendicitis. A blood test is also indicative of dehydration or fluid and electrolyte imbalance.
Urinalysis for Appendicitis
A urinalysis is performed to check the presence of kidney stone or urinary tract infection. It involves collection of urine in a small container, which is then tested in a doctor’s clinic or sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Pregnancy Test
A blood or urine sample is collected to carry out a pregnancy test. An ectopic pregnancy causes pain in the lower right side of the abdominal region, due to which there is a need to perform a pregnancy test for women patients.
Imaging Test for Appendicitis
Imaging tests are carried out to confirm the diagnosis of appendicitis or understand the exact cause of severe pain in the abdominal region. These are some imaging tests that are commonly recommended for diagnosing appendicitis.
An Ultrasound
An abdominal ultrasound involves application of a device called transducer. A transducer produces sound waves which help in creating an image of the target organ. A gel is applied on your abdominal region before passing a transducer to the abdomen. This test is carried out in a hospital or outpatient center. Anesthesia is not required for this test.
A radiologist looks for the following sign, which indicates presence of a swollen appendix:
- A blockage in your appendiceal lumen
- A burst appendix
- Inflammation of appendix
Doctor performs this appendicitis test in infants, children, young adults and pregnant women.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
MRI is carried out using specialized machines to produce images of internal body organs and soft tissues with the help of radio waves and magnets. It is performed in an outpatient center or hospital. Most people do not require an anesthesia for the test, but those who have a fear of closed space may be injected with a dye called contrast medium.
A patient is made to lie down on a table which slides into a tunnel-shaped device. The device may be open ended or closed at one end.
The MRI test helps representing the following signs:
- A blockage in your appendiceal lumen
- A burst appendix
- Inflammation
It is a safe and reliable technique for diagnosing appendicitis as compared to a CT scan.
Computerized tomography scan
A CT scan involves using X-rays and computer technology to create organ images. You will be asked to lie down on a table which slides through a tunnel-shape device. Contrast medium dye will be given to patients who fear of closed spaces. This will make the patient unconscious for a short duration of time.
Anesthesia is not given to patients before the test, but a sedative will be provided to children before the scan is carried out.
A CT scan shows the following signs of inflammation if you have appendicitis, such as:
- An enlarged or burst appendix
- An appendiceal abscess
- A blockage in the appendiceal lumen
CT scan is not carried for pregnant women as it can be harmful for the growing fetus.
Chest X-ray
Chest X-ray helps us rule out occurrence of right lower lobe pneumonia as it can also show similar symptoms as that of appendicitis.
What steps will be taken after performing appendicitis tests?
If appendicitis tests indicate presence of swollen appendix, your doctor may recommend immediate removal of the appendix before it gets burst. The appendix is removed through surgery.
In some cases, the doctor will recommend consumption of antibiotics, which will help reduce the infection. After a few days of the antibiotic therapy, he/she may carry out a surgery to remove the infected appendix. Antibiotics also help in preventing onset of the infection after the appendix surgery. This method is known as appendectomy.
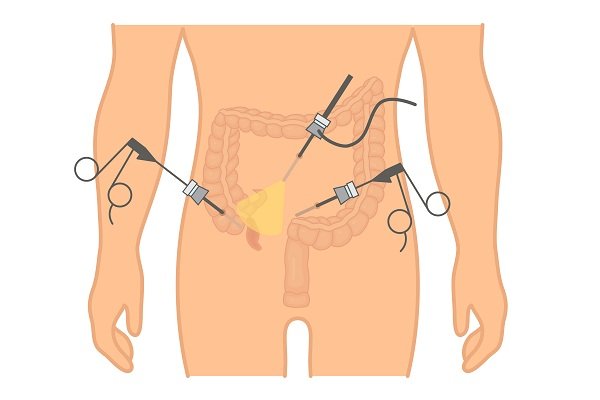
The appendix is removed by either an open appendectomy procedure or laparoscopic appendectomy, depending upon the severity of your conditions.
If the doctor diagnoses the presence of a ruptured appendix, he/she will immediately send the patient to a hospital for its treatment.
If the doctor is uncertain regarding its diagnosis, he/she may wait for 24 hours to observe if the symptoms may improve, stay the same or get worse.
More: How Long Does It Take To Recover From Appendix Surgery?
How can you test appendicitis at home?
Appendicitis self test involves identification of specific symptoms of appendicitis, such as pain in lower right hand side, nausea, vomiting, fever, and loss of appetite.
You can also perform a physical examination of your abdomen yourself to look for signs of Rovsing, Psoas, Obturator, Guarding, and appendix rebound tenderness.
If you are still unclear about the symptoms or clinical signs of appendicitis, you should urgently visit a doctor or rush to a hospital.