Appendicitis in Kids: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
- Updated on: Jun 28, 2024
- 4 min Read
- Published on Apr 19, 2021


What is Appendicitis and what happens when it is not immediately treated?
Appendicitis refers to inflammation or an infection in the appendix, a small, tube-like organ connected to the large intestine, located on the lower right side of the belly. If your child shows signs of an inflamed appendix, immediate medical attention is crucial.
Untreated appendicitis poses significant risks. The appendix can rupture if not addressed, releasing bacteria into the abdominal cavity. This can lead to peritonitis, a severe infection of the abdominal lining. Additionally, these bacteria could enter the bloodstream, resulting in sepsis, a potentially fatal condition.
Appendicitis in children: How common is appendicitis in kids?
Appendicitis in kids is a very rare condition to occur specially in infants. If it occurs, it is mostly in the age group of 2-12 years. Most of the times, it occurs in teens and adults in their twenties.
Appendicitis affects about 80,000 children every year in the United States. Genetics is a major factor in its prevalence. Fifty percent of children will have a family history of appendicitis.
Ruptured (perforated) appendicitis occurs in 30 percent of patients with appendicitis and is more common in children under five years of age.
The children under 5 years of age may suffer from acute appendicitis. In such cases, a surgical emergency is required.
Causes of Appendicitis in kids
The reason behind the occurrence of abdominal pain in your kid persisting over a period of time may be due to appendicitis caused due to infection in the body. The main reason of appendicitis is the infection that might have spread to the appendix or some blockage or obstruction causing the appendix to swell leaving it blocked further, with no supply of blood. The loss of blood supply makes the condition worsened further leaving it to be ruptured in chronic cases. For a body part to remain healthy, adequate blood flow to the organ is required.
Read about basics of appendicitis in adults.
Symptoms of appendicitis in kids
These are the common appendicitis symptoms in children:
- Appendix pain in children: The pain in the belly button and right side of the abdomen is a common sign of appendicitis in children. The pain can worsen continuously with time on movement, deep breaths, coughing or sneezing. The pain should be closely looked upon as it might indicate a possibility of appendicitis.
- Mild fever along with the pain in the abdomen
- Children may also have a high white blood cell count which is due to the infection. The doctor can also easily make out through an investigation which can give a clear indication of appendicitis.
- Other than the pain with movement, there is one more prominent symptom of appendicitis in children known as rebound tenderness. It is a sharp pain that develops after pressure is exerted on the lower right abdominal area and quickly released.
- Symptoms may vary to an extent according to the age group but are not easily diagnosed with the condition. As for the age-group of 2-5 years, the symptoms are that of common illness causing pain in stomach with vomiting, loss of appetite, nausea, along with fever.
- For the age group of below 2 years, the symptoms are same as above but diarrhoea is also common in this age group.
Diagnosis of appendicitis in children
Appendicitis is diagnosed by reviewing medical history, looking through the symptoms such as pain in the right lower portion of the abdomen followed by vomiting and low-grade fever, and tenderness and rigidity in the same location, and a physical examination performed by the doctor.
Sometimes, the doctor will require imaging of the abdomen with ultrasound and/or a computed tomography (CT) scan or any other technique.
Blood and urine tests may also be performed.
No one test can find the disease 100 percent accurately. The doctor uses the available evidences together to diagnose appendicitis.
Misdiagnosis of the appendicitis
The ratio of children being affected by this condition and diagnosed compared to that of the children being affected with it but being misunderstood many a times with a minor stomach ache and remaining undiagnosed is pretty high.
Instead of immense advancement in technology, the diagnosis of acute appendicitis continues to be a challenge among kids. Mostly, in the case of chronic appendicitis where the appendix is highly inflamed and swollen, the complications can lead to rupturing of the appendix due to misdiagnosis.
Misdiagnosis of appendicitis in children occurs due to various reasons. One of the reasons is the inability of the child to express the pain and explain the condition precisely due to small age. The overlapping of symptoms of the appendicitis in kids with that of normal growing illness of children such as fever, stomach ache, vomiting, and nausea can also cause misdiagnosis.
Misdiagnosis rate in appendicitis ranges from 28 – 57% in the age-group 2 to 12 year old children and approaches to near about 100% in the children younger than 2 years [i.e. – 6-8 months].
Diagnosing the condition early is important
The condition should be noted and treated in its early stages to prevent a kid from deathly complications such as rupturing (perforating) of the appendix. The rupture may involve the infection to be likely spread to the surrounding body organs, in particular, around the abdomen and the membrane around the abdominal cavity.
The infection can spread very quickly and can even cause death of the child.
Treatment of Appendicitis in Children
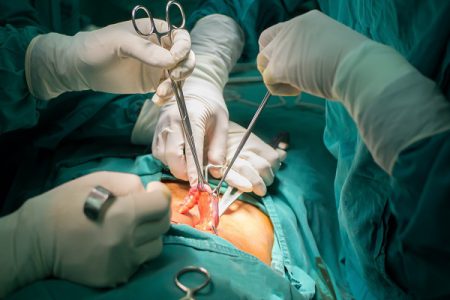
There are various methods to treat appendicitis in children but the prime treatment method is appendectomy (surgical removal of the appendix) which is most common as well as reliable in adults as well. It is even considered as the standard way of treatment of appendicitis in children and adults.
What happens during the surgery?
An anesthesiologist gives your child anaesthesia, which brings him or her on sleep. If the procedure is done through a laparoscopic and minimally invasive technique, the surgeon will enter the abdomen using small tools and trocars along with a camera. These are inserted through several tiny incisions made in the skin and tissue underneath.
Sometimes, a slightly larger incision is made to pull out the appendix. The appendix is removed and the infected is washed out of the abdominal cavity. Sometimes, drains are placed to remove the infected fluid.
The surgery usually requires less than an hour to complete.