Thyroid Pain: What Does Thyroid Pain Feel Like?
- Updated on: Jun 10, 2024
- 4 min Read
- Published on Apr 22, 2021
What is thyroid pain?
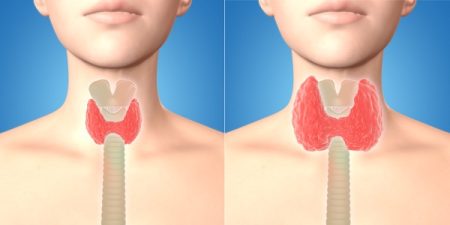
Thyroid pain is any discomfort or pain that originates from your thyroid gland due to problems and diseases within the thyroid gland. Sometimes, the pain may be caused by surrounding structures and not the thyroid gland. But this is not very common. Mostly, the pain occurs due to a problem within your thyroid gland. The pain affects the neck, throat, and upper thorax.
Thyroid Pain Location
The thyroid gland is located between the C5 and T1 vertebrae. Since the position of thyroid gland can change slightly among people, and the position may also change slightly during swallowing and due to enlarged therefore, location of pain is not the only way to recognize and define the pain and its cause.
Thyroid pain can cause discomfort, tenderness or pain in the neck, throat, below the thyroid cartilage (called Adam’s apple) or around the level of the cricoid cartilage. This pain can extend to the superior mediastinum. The pain is often not localized and can radiate to sternocleidomastoid muscles, mouth, chin, jaw, beyond the superior mediastinum to the chest.
See also: Thyroid Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, Risks, Stages, Prevention, Survival
See also: Causes of an Overactive Thyroid (Hyperthyroidism)
What does thyroid pain feel like?
The pain is generally not localized and can radiate to mouth, jaw, chin, beyond the superior mediastinum to the chest. Sometimes, the pain can spread (radiate) to the jaw or ears.
The pain often gets worsened on swallowing and can be associated with tenderness on palpating the thyroid gland.
Characteristics of thyroid pain are:
- It may look like an ache with tenderness to touch and swelling of the thyroid gland
- Thyroid pain can cause swelling
- It is associated with hoarseness of the throat or sore throat
- The pain worsens on touching or swallowing
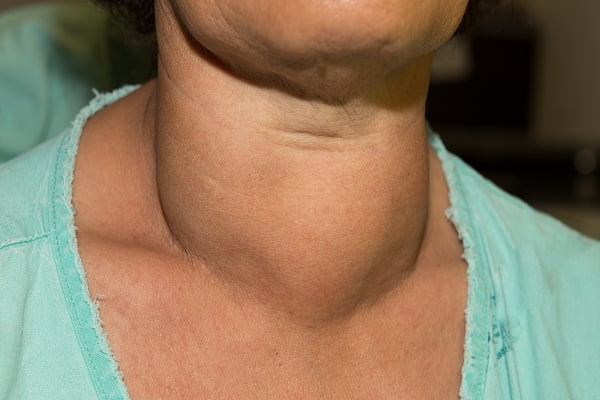
- Thyroid pain in neck or throat along with swelling around the thyroid gland
- The thyroid gland may remain painful and swollen for weeks and in some cases for months. It all depends on the underlying cause of the pain.
Causes of your thyroid pain
While thyroid pain can be caused by many possible reasons; the disorders that are commonly responsible for thyroid pain are as follows:
- Thyroid cyst causes pain in the thyroid gland
- Viral thyroiditis: a viral infection caused by mumps virus, coxsackie virus, adenovirus etc
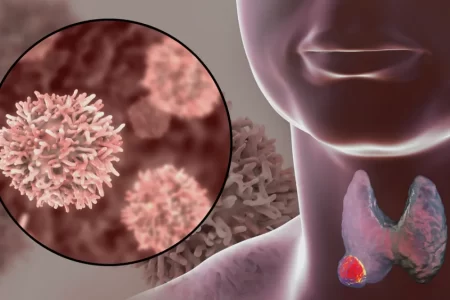
- Thyroid tumor (thyroid cancer) can cause severe thyroid pain
- Subacute granulomatous thyroiditis (SAT), also referred to as painful sub-acute thyroiditisorde Quervain’s thyroiditis is a common thyroid disorder that can cause pain and tenderness in front of the neck or throat.
- Hashimoto’s disease
- Advanced carcinoma of the thyroid gland that spreads to distant body sites causes unbearable thyroid pain along with other complications
- A goiter is benign enlargement of the thyroid gland that can cause pain in the thyroid gland
- Trauma or injury to the neck or throat can also result in severe thyroid pain in neck
- Inflammation of the thyroglossal fistula orthyroglossal cyst is associated with thyroid pain
- Hyperthyroidism can cause thyroid pain
- Hypothyroidism
- Thyroid nodules causes pain and swelling of the thyroid gland
Does having diabetes increase my risk of thyroid disease?
Yes, individuals with diabetes are at a heightened risk for thyroid diseases compared to those without the condition. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition. Having one autoimmune disease makes you more susceptible to contracting another.
While the risk is slightly reduced for those with Type 2 diabetes, there’s still a possibility. If you have Type 2 diabetes, the likelihood of developing thyroid disease increases as you age.
It’s advised to undergo routine screenings for thyroid complications. People with Type 1 diabetes typically receive more frequent checks — soon after diagnosis followed by annual tests. For those with Type 2 diabetes, there isn’t a fixed screening schedule, but your doctor might recommend periodic testing.
If you have diabetes and test positive for a thyroid condition, consider the following recommendations to maintain optimal health:
-
- Ensure adequate sleep.
- Stay active and exercise regularly.
- Monitor and maintain a balanced diet.
- Adhere to medication regimens.
- Undergo consistent testing as advised by your medical professional
See also: Treatment of Over-Active Thyroid (Hyperthyroidism)
See also: Coping with Thyroid Cancer Treatment
Signs and symptoms of thyroid pain
Thyroid pain may vary in intensity. Some people experience a mild discomfort around the thyroid gland, others describe it as tightness particularly when swallowing or a dull ache throughout the thyroid gland.
Common symptoms of the thyroid pain are:
- the pain usually exacerbates when palpated
- in case of an acute thyroid pain, persistent pain can be an indicator of major thyroid problem requiring medical or surgical intervention
- a neck lump or mass may appear in the neck if the pain is due to goiter and cause severe thyroid pain in neck
- discomfort or pain when swallowing
- hoarse voice
- signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism
- signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism
- most of thyroid nodules causing severe pain tend to be malignant. Therefore, it is important to be careful when there is swelling or pain of the thyroid gland.
Treating thyroid pain
The treatment of your thyroid pain will depend on the cause of the pain. Your doctor will perform physical examination and order tests for diagnosing the condition. After the diagnosis is done, the objective will be to treat the underlying cause of the problem that is causing the pain, swelling, and other symptoms.
- a short term treatment for intolerable pain is the use of over-the-counter or prescription painkillers
- thyroiditis is a disease of thyroid gland associated with both pain and inflammation. It can be relieved with pain relieving drugs and anti-inflammatory medicines such as ibuprofen.
- steroids and thyroid hormone replacement drugs to minimize the inflammation and stabilize hormone production
- pain associated with thyroid cancer or tumor is relieved with proper treatment of the cancer
- anti-analgesic medications
- if the pain is due to hyperthyroidism, treatments for hyperthyroidism may include antithyroid medications, radioactive ablation, and surgery