Anatomy and Function of Human Brain
- Updated on: Jul 24, 2024
- 5 min Read
- Published on Jan 2, 2021
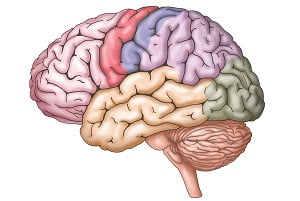
The Human Brain
The brain is a wonderful three-pound organ that controls all the functions of human body and interprets information from the outside world.
Our brain is one of the most complex organs in the body. It is made up of more than 100 billion nerves that communicate in trillions of connections called synapses. Intelligence, creativity, emotion, senses, and memory are a few of the many things that are controlled by the brain.
Brain Anatomy
The brain controls everything about us – how we think, how we feel, and how we act. It gives a meaning to our world and our place in it. The brain is responsible for controlling all major functions in a human body.
The brain is located in the hard skull, which protects it from injury. When a child is born, the size of brain is about a pound. It grows to approximately three pounds by adulthood. The brain, along with the spinal cord is an important component of the central nervous system (CNS).
Brain cells
Two types of cells exist in the brain.
- Neuron cells
- Glial cells
Neurons send and receive signals to and from your brain and the rest of the body. Glial cells, (also called neuroglia or glia) form myelin, which is a fatty and insulating layer around the nerve fibers. The cells maintain stability, and provide nutrition and support to the body.
Each part of our brain performs a specific important function and is linked to other parts of the brain for coordination.
Areas of brains
The brain is made up of several specialized regions that work together. These are listed here:
- Cortex: The cortex is the outermost layer of brain cells. Thinking and voluntary movements happen in the cortex.
- Brain stem: The brain stem is located between the spinal cord and the rest of the brain. It controls basic functions such as breathing and sleep etc.
- Basal ganglia: The basal ganglia are a cluster of structures in the center of the brain. They help coordinate messages between multiple brain areas.
- Cerebellum: The cerebellum is located at the base and the back of the brain. It is responsible for coordination and balance of and within the entire body.
Lobes of the brain
The brain is also divided into lobes. These are:
- Frontal lobes: These are responsible for problem solving, judgment and motor functions.
- Parietal lobes: These lobes manage sensation, handwriting, and body positions.
- Temporal lobes: temporal lobes are responsible with memory and hearing.
- Occipital lobes: They contain the brain’s visual processing system.
The brain is surrounded by a layer of tissue called the meninges. The skull (also called cranium) helps protect the brain from injury.
Meninges
In between your skull and brain, there exist three layers of tissue, called meninges. They protect the brain.
- The strong, outermost layer is called the dura mater.
- The middle layer, called the arachnoid mater, is a thin membrane made of blood vessels and elastic tissue. It covers your entire brain.
- The innermost layer is called pia mater is the innermost layer, and it contains blood vessels that run deep within the brain.
Various parts and functions of the brain
| Brain Region | Location | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Cerebrum | Forebrain, it is the largest part of the brain and is divided into two halves | It controls processes such as vision, hearing, speech, emotion, and movement |
| Left hemisphere | Left side of the cerebrum | It is responsible for language related processes in most right-handed people and about 50 percent of left-handed people; it also controls analytical reasoning and calculations; motor and sensory signals for the right side of the body are processed here |
| Right hemisphere | Right side of the cerebrum | Responsible for visual cues interpretation and spatial processing, such as emotional, artistic, and visual reasoning; responsible for the processing of motor and sensory signals for left side of the body |
| Corpus callosum | Located between the two hemispheres of the brain | It connects the left and right hemispheres |
| Frontal lobe | It is the largest section of brain, located in the front of the head | Responsible for reasoning, emotions, and movement |
| Parietal lobe | Located in the middle part of your brain | It helps in spatial relations to other people and objects; controls touch and pain processing |
| Occipital lobe | Located in the back of the brain | It helps to process visual data |
| Temporal lobes | Located on each side of the brain | Temporal lobes help with memory, language, smell, and facial recognition; also help in interpreting the emotions |
| Cerebellum | Hindbrain | It controls motor movements, balance, and postures |
| Brainstem | Located in front of the cerebellum, and is connected to the spinal cord | It controls elementary bodily functions that are important for survival |
| Midbrain | Located in the top section of the brainstem | It is responsible for the control of eye movements, facial sensation, balance, and hearing |
| Pons | It is in the middle section of the brainstem | Controls sensory analysis, motor skills, sleep, and consciousness etc |
| Medulla oblongata | It is the lowest section of brainstem | Controls respiratory drive, swallowing, coughing, etc; it helps to regulate circulation, blood pressure, and heart rate |
| Limbic system | Above the brainstem | Responsible for emotions processing |
| Thalamus | Located under the cerebrum | It helps in integrating the sensory signals coming from the spinal cord and limbic system |
| Hypothalamus | Located right below the thalamus | Sends messages to pituitary gland and helps to regulate temperature, thirst, water balance, sleep, hormone production, and appetite |
| Amygdala | It is a structure in your limbic system | Helps process aggressive behaviors and fears |
| Hippocampus | It is a structure in the limbic system | Helps us remember new information |
| Pituitary gland | It is located in the base of the brain | Responsible for hormones secretion |
| Basal ganglia | Located deep within the cerebrum | Coordinates movements |
Common diseases of brain
Headache: There are many types of headaches. Some can be serious but most are not.
Stroke (brain infarction): A blood clot or bleeding in the brain is the main cause of most strokes.
Brain aneurysm: An artery in the brain develops a weak area that gets inflamed.
Subdural hematoma: It is characterized with bleeding within or under the dura (lining inside of the skull).
Epidural hematoma: Bleeding between the tough tissue (dura) lining the inside of the skull and the skull itself.
Intracerebral hemorrhage: Any type of bleeding inside the brain.
Concussion: A brain injury that causes a temporary disturbance in brain function.
Cerebral edema: Swelling of the brain tissue in response to injury or electrolyte imbalances.
Brain tumor: Any abnormal tissue growth inside the brain.
Glioblastoma: Aggressive, malignant brain tumor (cancer).
Meningitis: Inflammation of the lining around the brain or spinal cord from infection.
Encephalitis: Inflammation of the brain tissue from infection with a virus.
Brain injury: Permanent brain damage from a traumatic head injury.
Parkinson’s disease: Nerves in a central area of the brain degenerate and cause problems with movement and coordination of the body.
Huntington’s disease: A nerve disorder that affects the brain. Dementia is one of the symptoms.
Epilepsy: Generally characterized with seizures.
Dementia: A decline in cognitive function resulting from death or malfunction of nerve cells in the brain.
Alzheimer’s disease: Nerves in brain areas degenerate, causing dementia among other problems.
Autism: Autism or Autism Spectrum Disorder is a developmental disorder that affects a person’s perspective of observing the environment. Generally occurs in kids and characterized with loss of connect with surroundings.
Schizophrenia: Schizophrenia is a brain disorder that influences how a person thinks, feels, and acts.
Insomnia: Insomnia is a common sleep disorder which is characterized by a difficulty in falling asleep or staying asleep or waking up early and not be able to get back to sleep.












