What is spinal osteomyelitis or spinal infection? What are the causes of spinal infection?
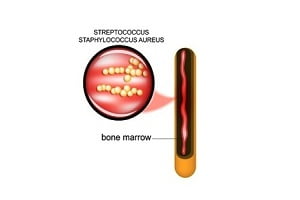
Spinal infection or spinal osteomyelitis refers to an infection of the vertebral body in the spine causing weakness in its structure or pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots. Often referred to as spinal infection or spinal osteomyelitis, it is usually caused by bacteria or fungal organisms, viruses or can occur after a spinal procedure or surgery. Read about osteomyelitis (Bone Infection).
This condition may also occur as result of, urinary or respiratory tract infection, soft tissue infection, or dental infection spreading to the bone. The most common site is lumbar spine followed by thoracic, cervical and sacrum.
Vertebral osteomyelitis can lead to permanent problems with spinal deformities, nerve conduction issues, paralysis and even death. It is rare cause of severe back pain and most common in young children and elderly but can occur at any age.
Acute spinal infection is generally caused by bacteria whereas chronic spinal infection occurs in individuals whose immunity has been already compromised by diseases such as tuberculosis and AIDS etc.
More: How Serious Is Osteomyelitis? Can Osteomyelitis Cause Death?
What are the symptoms of spinal osteomyelitis?
Symptoms of vertebral osteomyelitis may include:
- Chills , fever and shakes
- Severe back pain , gets worse at night
- Weight loss
- Redness, swelling and warmth in the affected area
- Loss of natural spine curve
- Radicular pain
- Sensory loss or numbness
Risk factors for spinal osteomyelitis .
Those individuals having one or more of the following conditions are at greater risk of spinal infection. These include:
- Taking intravenous drug in cervical region
- AIDS
- Insulin dependent diabetes mellitus
- Malnutrition
- Compromised immune system due to cancer or organ transplant
- Long term steroid therapy
Diagnostic approaches for spinal osteomyelitis.
If spinal osteomyelitis is suspected, blood cultures are done to confirm the presence of infecting bacteria. A needle biopsy or open biopsy is performed to obtain the samples.
Combination of X-ray and MRI scans are employed for better visualization and confirmation of the infection. Other diagnostic studies include a myelogram, bone scan or gallium scan.
More: Jawbone Infection (Osteomyelitis In Jawbone): Symptoms, Causes, And Treatment
More: Infection In Hip Bone (Osteomyelitis Of Hip Bone): Causes, Symptoms, Treatment
Treatment options for spinal osteomyelitis.
The treatment plan for spinal osteomyelitis depends on the severity of symptoms and degree of bone damage and usually starts with rest and IV antibiotics, with bracing as needed when there are little or no symptoms.
If diagnostic studies reveal compression on neural structures, surgical removal of compressive infection may be required.
In case of a spinal instability, a spinal fusion procedure may be performed. Fusion is the process in which new bone grows around and into the surgical area healing and joining the spine together eventually.