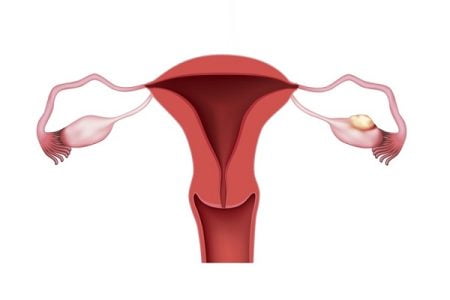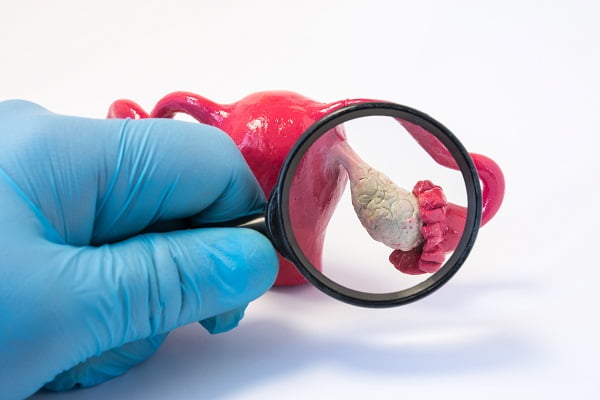
Definition of ovarian cancer: What is an ovarian cancer?
The female reproductive system consists of two ovaries which produce woman’s eggs and many female hormones. Ovarian cancer is a type of cancer in which the any type of cancerous growth is present in the ovaries.
Ovarian cancer is one of the most common types of cancers found in woman. It is considered as the major cause of death in woman.
According to the reports, around 22,000 American women are diagnosed with ovarian cancer every year. Some common warning signs of ovarian cancer involve constant pain in abdomen, nausea, vaginal bleeding, etc. Usually, the ovarian cancer affects the women who are at their stage of menopause but it can also affect young women. Diagnosing this cancer is difficult and therefore doctors perform many tests to get the proper status of the cancer.
What are different types of ovarian cancer?
There are many different types of ovarian cancers that are classified based on their site of origin. The most commonly observed types of ovarian cancers in women are as follows:
Epithelial Tumor Cancer
Epithelial ovarian tumors are the type of tumors which develop from the cells of the outer lining of the ovary. Generally, epithelial ovarian tumors are regarded as noncancerous.
There are various types of benign epithelial tumors, like serous adenomas, Brenner tumors, and mucinous adenomas. Cancerous epithelial tumors are a type of carcinomas which mean that they start in the tissue linings of ovaries.
Germ Cell Tumors
Germ cell tumors are those tumors which develop in the egg producing cells. Most germ cell tumors are non-cancerous in nature, although some tumors are cancerous and are life-threatening.
Primary peritoneal carcinoma
Primary peritoneal carcinoma is the rarest type of ovarian cancer. This type of cancer develops in the cells present in the peritoneum or abdominal lining.
Stromal ovarian cancer
Stromal ovarian cancer is another type of ovarian cancer. It includes Sertoli-Leydig cell tumors and granulose-stromal tumors. This type of ovarian tumor occurs in the supporting tissues present in the ovary.
What are the causes of ovarian cancer? Why do some women get ovarian cancer but others do not?
The exact cause of ovarian cancer is unknown but the researchers think that DNA mutation may be the main cause of ovarian cancer.
There are two types of genetic mutations which can primarily be considered as the main causes of ovarian cancer. Mutations in genes makes one woman more at risk of ovarian cancer compared to others.
Inherited gene mutation
An inherited gene mutation may cause ovarian cancer in women. For example, inherited mutations occur in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, which can increase the risk of ovarian cancer. Such mutations pass on from one generation to another and are considered a leading ovarian cancer cause.
Acquired genetic mutation
In many cases, the mutation are not passed genetically but is passed on from one generation to another but occur due to various environmental conditions during a woman’s lifetime. These environmental conditions can either be cancer-causing chemicals or radiations, etc. These are also considered as potential causes of ovarian cancer.
What are the risk factors for ovarian cancer?
Risk factors for ovarian cancer are referred to as any external triggers which can increase the chances of developing the ovarian cancer. There are various risk factors of ovarian cancer, which can increase the chances of developing the condition. Some of the ovarian cancer risk factors are:
Age
Age is a key risk factor for ovarian cancer. The risk of an ovarian cancer increases with an increase in the age. It is generally rare in women who are younger than 40 years.
Obesity
Obese women are at a higher risk of having an ovarian cancer.
Reproductive history
Reproductive history can be an ovarian cancer risk factor in some women. Women who have been pregnant before the age of 26 years are at a lower risk of having ovarian cancer. Breastfeeding helps in reducing the risk of having ovarian cancer in a woman.
Birth control
Birth control pills are also known as oral contraceptives. Women who use such pills are at a lower risk of having ovarian cancer.
Gynecologic surgery
Tubal ligation, a surgical procedure in which the fallopian tubes are tied, may help in reducing the chances of developing an ovarian cancer. A hysterectomy, a surgical procedure of removing the uterus without removing the ovaries, also reduces the risk of ovarian cancer.
Fertility drugs
A fertility drug, clomiphene citrate, if used for more than a year, can increase the risk of various types of ovarian cancer. Infertile women are at a greater risk of getting ovarian cancer even if they do not use fertility drugs.
What are the signs and symptoms of ovarian cancer?
In the early stages of ovarian cancer, the symptoms may not be easily visible but as the condition advances, the signs and symptoms of ovarian cancer become visible.
Ovarian cancer can result in a variety of symptoms. Some of the symptoms of ovarian cancer are:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding or vaginal discharge
- Severe pain in abdomen or pelvic area
- Constant back pain
- Bloating
- Having a difficulty in eating
- Increased frequency or urgency to urinate
- Painful sexual intercourse
- Weight loss
- Breathlessness
- Appetite loss
If an individual experiences any of the above listed ovarian cancer symptoms, she must consult a doctor and opt for a proper treatment after detailed diagnosis.
Generally, early signs of ovarian cancer may not be visible and the disease is identified at a stage when the symptoms of ovarian cancer have already affected nearby locations. It is therefore important to be careful of the early stage signs.
How is ovarian cancer diagnosed?
During the early stages of an ovarian cancer, the symptoms are not clearly noticed. But as soon as the symptoms are visible, it is advisable for the woman to consult a doctor. The doctor will ask the woman to undergo some tests which can help in accurately diagnosing the disease.
Some common diagnostic techniques for diagnosing ovarian cancer are as follows:
Blood test or CA 125 Test
CA125 is a protein which is produced by certain kind of ovarian cancer cells. This protein acts as a marker for diagnosing ovarian cancer. If the level of CA125 in the blood increases, it can be a sign of ovarian cancer. But the increased level of CA125 protein does not mean that the woman surely have cancer.
Imaging tests
Certain imaging techniques such as computed tomography or CT scans, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging or MRI studies can confirm the presence of pelvic mass. However, these studies do not confirm that the mass present is a cancer, but they might be useful to observe the spreading of an ovarian cancer and the diagnosis of ovarian cancer.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is also known as ultrasonography. In this technique, sound waves are used to create an image on a screen. These waves are then released from a small probe which is placed in the female’s vagina or on her abdomen surface which creates echo as soon as they strike ovaries and other female reproductive part. The image of the phenomenon is captured on the display screen. The method can be used for ovarian cancer diagnosis.
Computed tomography (CT) scans
The CT scan is the short form of computed tomography scan. It is an x-ray test which produces a cross-sectional image of the body. This test does not show small ovarian tumors properly, but can be used to see larger tumors and its structure.
Barium enema X-ray
Barium enema x-ray is a test to check whether the cancer has invaded the colon or rectum. Barium sulfate is a chalky substance which is put into the colon and rectum and the x-ray is taken. Because x-rays do not go through barium, the colon and rectum are clearly visible in the reports. The test can be used for the diagnosis of ovarian cancer by radiologists and doctors.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans
MRI scans is an imaging test which uses strong magnets and radio waves instead of x-rays. It can be used for evaluation and diagnosis, but is generally not used for ovarian cancer diagnosis.
Tissue biopsy
The only way of determining the presence and diagnosis of cancer is to take a small sample of the abnormal growth from the targeted area and examine it under a microscope. This procedure is known as tissue biopsy.
What are the different stages of ovarian cancer?
When an ovarian cancer is diagnosed, its stage is also identified by the doctor. By identifying the stage of the cancer, the doctor can decide the best possible treatment option for the woman according to its stage.
The stage of an ovarian cancer refers to the cancer’s spread. There are many different ways of staging the ovarian cancer.
- Stage 1 ovarian cancer: In this stage, the cancer does not spread in another area and affects only the ovaries.
- Stage 2 ovarian cancer: In this stage, the cancer has affected either one or both ovaries along with other organs such as the uterus, bladder, fallopian tubes, or rectum.
- Stage 3 ovarian cancer: In this stage, the cancer affects both the ovaries and spreads in the lining of the abdomen.
- Stage 4 ovarian cancer: In this stage, the cancer has metastasized outside the peritoneal cavity. This cavity includes the abdomen, liver, spleen, etc.
Ovarian cancer treatment: How is ovarian cancer treated?
Treatment for ovarian cancer includes surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, targeted therapy, etc. Generally for the treatment of ovarian cancer, more than one treatment option is used.
The kind of treatment option for ovarian cancer greatly depends on various factors, such as the type of ovarian cancer, its stage, patient’s health condition, etc.
The various types of ovarian cancer treatment options usually considered by healthcare professionals are as follows:
Surgery for ovarian cancer
In severe cases, surgery is performed in order to remove the ovarian cancer. The extent of the surgery depends on the stage of the cancer.
- Salpingo-oophorectomy: This surgery is usually performed to remove the ovaries and fallopian tubes so that the cancer is not spread in other organs.
- Hysterectomy: The surgeon removes the whole uterus along with the surrounding tissue which is affected. In case only uterus is removed, this is known as partial hysterectomy.
- Lymph node dissection: In this technique, the surgeon removes the lymph nodes in the pelvis region and near the aorta.
- Cytoreductive or debulking surgery: In case of cancer spreading beyond the pelvic area, the surgeon reduces cancerous tissue as much as possible. The organs include tissue from the gallbladder, etc. This procedure greatly helps in reliving symptoms and making chemotherapy much more effective.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a surgical technique in which certain medications are used to destroy cancer cells for the treatment of ovarian cancer. Cytotoxic medication drugs prevent the cancer cells from dividing and growing. Chemotherapy is used to treat those cancer cells which cannot be removed by surgery.
Chemotherapy treatment generally involves 3 to 6 treatment sessions.
Targeted chemotherapy
There are certain new medications which can be directly targeted on the specific pathways in cancer cells for the treatment of ovarian cancer. Few examples of such medications are bevacizumab (Avastin), olaparib (Lynparza), etc.
Hormone Therapy
Hormone therapy (HT) can also be done to prevent the estrogen from reaching cancer cells. By cutting off the estrogen supply, the growth of the cancer cells can be slowed down. Hormone therapy generally includes goserelin (Zolodex), Tamoxifen, leuprolide (Lupron), etc.
Radiation therapy
Radiation is rarely used in treating ovarian cancer. It may be used in case of small traces of cancer observed in the reproductive system.