General Overview of Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
- Updated on: Jun 26, 2024
- 3 min Read
- Published on Feb 21, 2021
What is Urinary Tract Infection?
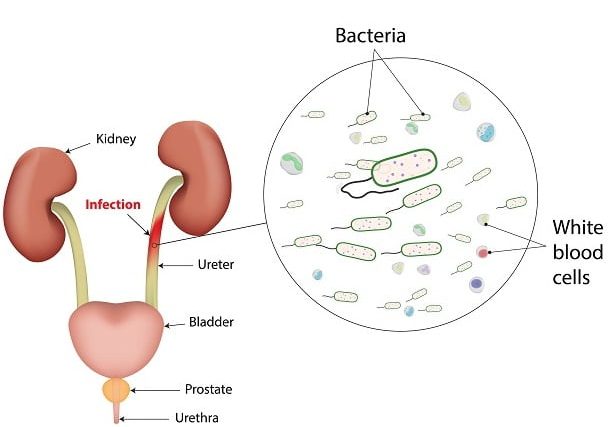
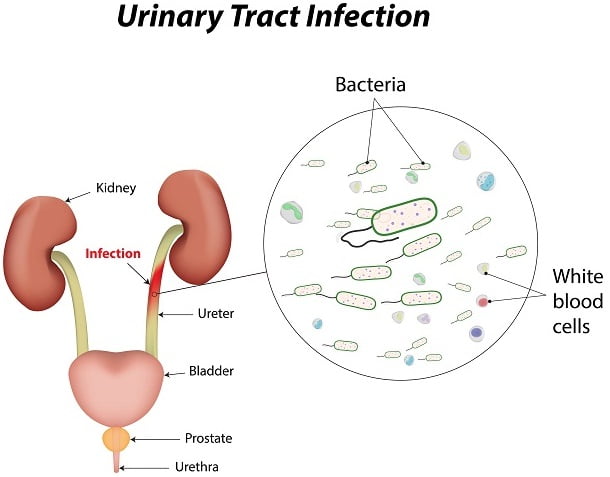
As the name suggests, urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that affects part of the urinary tract. The urinary tract is responsible for removing waste and excess water from our body. It consists of the bladder, the kidneys and the urethra. These are the structures that urine passes through before being eliminated from our body. Urinary tract infections are caused by microbes such as bacteria overcoming the body’s defenses in the urinary tract. Any part of the system can be infected by these microbes. As a general rule, the distant up in the urinary tract the infection is located, the more serious it is.
UTIs are a key reason why we are often told to wipe from front to back after using the bathroom. This is because our urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body, is located close to the anus. Bacteria from the large intestine, such as E. coli, can easily escape the anus and attack the urethra. These bacteria can then easily transfer up to the bladder from there, and if the infection isn’t treated well on time, it can infect the kidneys too. Women may be particularly prone to UTIs because they have smaller urethras. This allows the bacteria an easy and quick access to their bladder. Having sex can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract, too. If you’re a woman, your chance of getting a urinary tract infection, or UTI, is much higher. Some experts rank your lifetime risk of getting one as high as 1 in 2.
Fast Facts on Urinary Tract Infections
Key points about urinary tract infection are list below.
• Women have a lifetime risk of more than 50% of developing a urinary tract infection
• UTIs are generally overlooked or mistaken for other conditions in older adults
• They are one of the most common types of infections in the world accounting to around 8.1 million visits to doctors each year
• Urinary tract infection is diagnosed based on apparent signs symptoms and by testing sample of urine
• Uncomplicated urinary tract infections can be cured early (in about 2-3 days of treatment)
• Many people drink cranberry juice to prevent UTIs. As opposed to the general belief, cranberry extracts do not treat UTIs. They may however help reduce the risk of recurrent UTI
• According to CDC, among the UTIs acquired in the hospital, about 75% are associated with a urinary catheter (catheter-associated UTI). Catheter is a tube which is inserted into the bladder through the urethra to drain urine. Therefore, catheters should be used only for appropriate indications and should be removed as soon as the purpose is over.
• For a severe and complicated UTI, you may need treatment with intravenous antibiotics in a hospital. This might require hospital stay for a few days as well.
• The disease is treatable but can also be prevented to a large extent. There are ways that you can do to prevent the UTIs.
FAQs
What are the common causes of urinary tract infections?
UTIs are often caused by bacteria entering the urinary tract. Factors like sexual activity, dehydration, and weakened immune systems can contribute.
How can UTIs be prevented?
Staying hydrated, practicing good hygiene, and avoiding irritants can help prevent UTIs. Prompt treatment of underlying conditions is also essential.
Are UTIs more common in certain demographics?
Women are more prone to UTIs due to shorter urethras. However, men and individuals of any age can also be affected.
Can UTIs lead to complications?
Untreated UTIs can lead to complications such as kidney infections. Seeking medical attention for persistent symptoms is crucial.
What are the available treatments for UTIs?
Antibiotics are commonly prescribed to treat UTIs. It's important to complete the full course of medication even if symptoms improve.