Periodontal disease, more commonly known as “gum disease” is an inflammatory disorder that affects teeth and surrounding tissues. Gum disease is a pathological condition caused by a microorganism (periodontal bacteria) that adheres and grows on the surface of teeth. Gums, roots, periodontal ligament and alveolar bone along with teeth are the areas affected by this disease.
Poor dental health has an overall negative effect on the body. Sometimes, increased risk of heart diseases and diabetes are associated with poor oral hygiene. If the person suspects gum disease, he/she should take immediate consultation from the dentist.
Warning signs and symptoms like bleeding gums, bad breath and swollen gums should not be ignored as it would progress and accelerate the disease. Read about the symptoms of gum disease here.
Regular dental check-ups are important to diagnose gum disease. The sooner a person seeks treatment, the better are the chances of saving the teeth. If left untreated, gum infection can cause serious problems and loss of teeth.
Treatment of gum disease
Doctors recommend treatment on the basis of severity and stage of gum disease.
Following are the treatments most commonly advised by dentists.
- Deep cleaning of teeth
- Surgical treatments
- Medicines
The details of the above-mentioned treatments are given below.
Deep cleaning of teeth
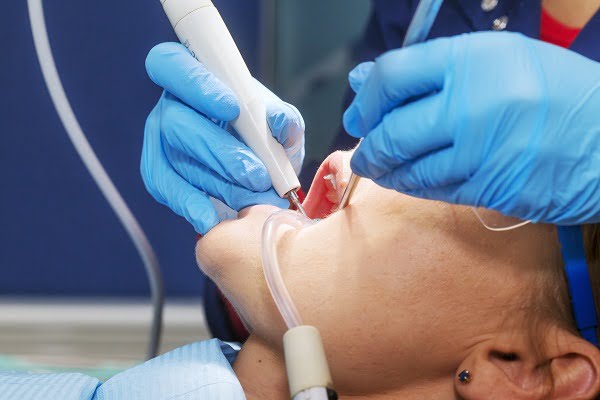
This treatment is generally done by an expert dentist or dental hygienist. At least two dental checkups in a year are recommended by doctors. During a typical checkup, dentists remove the plaque and tartar from the surface and gum line of the teeth. Deep cleaning method involves scaling and root planing.
Scaling and root planing is a non-surgical method done under local anesthesia. In scaling, tartar and plaque are removed from the gum line. Root planning means to get rid of rough spots present on the root of teeth and making its surface plan. These rough spots are the growing grounds of bacteria which contribute to the infection.
Smoothing the rough spots removes the bacteria present there and provides a clean surface for the gum to attach to the teeth.
Earlier, this technique was done manually using a scrapper. However, nowadays laser is used to remove plaque and tartar. Laser technique to remove tartar and plaque may sometimes result in bleeding, swelling and discomfort.
Dental cleaning cannot be used as an effective treatment against active gum disease. They are just a preventive method to avoid gum disease.
Surgical treatment
Surgery sometimes might be necessary for the treatment of periodontal disease especially in the cases where inflammation and deep pockets are present even after deep cleaning.
Following are the main two main types of surgical options used to treat gum disease:
- Pocket reduction surgery
- Bone-tissue grafting
Pocket reduction surgery
Pocket reduction surgery is commonly known as “Flap surgery”. A dentist can perform flap surgery to remove tartar (mineralized plaque) deposits present in deep pockets. The flap surgery involves lifting back the gums and removing tartar from inside. The gums are sutured back in their place so that tissue fits closely around the teeth again.
In some cases, damaged bones are smoothed to limit the growth of disease-causing bacteria. It is also done to reduce the depth of periodontal pocket and to make cleaning these areas easier. This sometimes results in longer-appearing teeth.
Bone-tissue Grafting
Along with flap surgery, doctors may suggest procedures to regenerate any bone or gum tissue lost due to gum disease. It is done by following methods:
- bone grafting
- tissue engineering
- guided tissue regeneration
- soft graft
- bone surgery
The procedures of these treatment methods are given as follows:
Bone grafting
Bone grafting is a technique that can promote bone growth. This is done by placing a bone fragment in the area of loss. The bone fragment can be of the patient or synthetically made. The graft provides a platform for the regrowth of bone and restores the stability of teeth.
Tissue engineering
A new technology is also being used called as tissue engineering which encourages the body to regenerate bone and tissue at an accelerated rate. However, the technique is quite expensive and not so commonly recommended by doctors.
Guided tissue regeneration
Apart from bone grafting, another technique is also used which is called as guided tissue regeneration. This procedure is done when the teeth are already destroyed by the bacterial infection. It stimulates bone and tissue regeneration. This procedure involves insertion of a mesh-like material between bone and gum tissue which keeps the gum from growing into the bone area. Ultimately, the connective tissue between bone and gum tissue regrows. It is often done along with flap surgery.
Soft Graft
In severe cases where gum tissue is completely lost, a soft tissue graft (synthetic or natural) is used to cover exposed roots. This procedure reinforces thin gums and fills the places from where gums have receded. The tissue for grafting is taken from the roof of the mouth and stitched in the affected area.
Bone surgery
Bone surgery is used to smooth shallow and rough depressions in the bone caused due to moderate (or advanced) bone loss. After flap surgery, the bone around the tooth is reshaped to decrease the cavities and depressions. This makes it hard for bacteria to regrow on the smooth surface.
Medicines for gum disease
Doctors sometimes prescribe medicines along with scaling and root planing. Surgery is not an option for every case and for every patient suffering from gum disease. However, research is still going on whether medicines work effectively for a longer period or not.
Antibiotic treatment can be used either in combination with surgery or in other therapies. Sometimes just antibiotics are able to reduce and eliminate the bacteria associated with gum diseases.
Following are the most frequently prescribed medicines:
- chlorhexidine (an antimicrobial drug used to control plaque and gingivitis)
- doxycycline, tetracycline and minocycline (over-the-counter drugs)
- triclosan
Apart from above-mentioned medications, certain other treatments are recommended by doctors like:
- fluoride containing toothpaste
- mouth wash and rinse (liquid form)
- gelatin-cup filled chip (placed in mouth after deep cleaning and releases medicines)
The only way to cure gum disease is by seeking professional help. Treatment results depend on many other things like the stage of disease, amount of receding gum line, smoking etc. Each case differs in its severity and thus it is not possible to predict which method will work in a better way.
However, the person can take few steps to lessen the symptoms and reduce further advancement of infection.
Following are the things that should be taken care of to avoid any oral problem:
- brush your teeth twice a day
- floss at least two times in a day
- clean your tongue regularly
- rinse your mouth with antibacterial mouth wash
- consult a dentist for regular check-ups