Diagnosing Hyperthyroidism
Physical examination and medical history check up are the first steps towards the diagnosis of an overactive thyroid. Some common signs that doctors and physicians look for are:
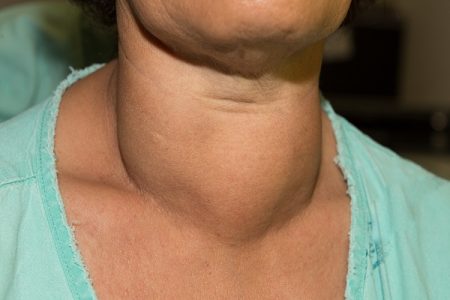
- Enlarged Thyroid gland
- Sudden weight loss
- Rapid pulse rate with high blood pressure
- Bulging out of eye balls
Read about signs and symptoms of overactive thyroid.
Apart from looking for the above-mentioned symptoms, several other tests and scans are performed to confirm the diagnosis. Availability of a wide range of blood tests to confirm and rule out the possibility of hyperthyroidism has made diagnosis more easy and accurate. These diagnostic tests give results in a day or two. The level of the thyroid hormones is measured in blood in some of these tests.
Measuring the level of the hormone that stimulates the thyroid gland to function i.e. thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH), is helpful in diagnosis. This hormone is secreted by the pituitary gland to regulate thyroid gland.
The pituitary gland constantly monitors the level of thyroid hormone. It can sense a slight change in the blood level of thyroid hormone and stops or starts production of TSH accordingly. A low level of TSH suggests that the thyroid gland is overproducing hormone without any stimulation from pituitary gland.
Diagnosis of hyperthyroidism, in usual cases, is associated with the suppressed level of Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) produced by the pituitary. If the TSH levels are not low, then other tests must be carried out. Sometimes, the level of all thyroid hormones is not increased, instead the level of one or two hormones is found to be relatively high. This case is a rare one though.
Another rare event is the failure of the pituitary gland or inhibition of pituitary gland due to euthyroid sick syndrome or any other disease.
Special tests are used to distinguish between the various causes of the condition. Thyroid scans and radioactive tests are used to know what treatment should be given to the patient and particularly whether you have the Graves’s disease. However, before taking any test or scan, a person should talk to a doctor or physician first.
Following are the tests that are commonly used to diagnose hyperthyroidism and its various causes. You can read about causes of hyperthyroidism here.
Tests and Exams for Hyperthyroidism
Measurement of Serum Thyroid (T4 and T3) Hormones
If the patient does not take any type of thyroid medication, this test is usually a good measure of thyroid function. Thyroid hormone tests are blood tests that are used to measure your levels of two types of thyroid hormones – T3 and T4.
T4 hormone (Thyroxine) level testing is done using Radioimmunoassay (RIA) and it is the most commonly used thyroid test.
Some medications such as birth control pills, other hormones, seizure medication, cardiac drugs, or even aspirin may alter the routine T4 test. Thyroxine (T4) contributes to about 80% of the thyroid hormone produced by the Thyroid gland in a normal state. It generally represents the overall function of the gland. The remaining 20% is triiodothyronine or T3. Triiodothyronine or T3 is also measured by RIA method.
Sometimes, the diseased thyroid gland produces a normal level of T4 hormone but a very high level of T3 hormone. Thus, the levels of both hormones should be measured for accurate diagnosis.
Measurement of TSH level
Production of TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone) by the pituitary gland is measured by a method called as Immuno-radiometric assay (IRMA). A lower than normal level of TSH suggests that the thyroid gland is overproducing hormone without any stimulation from pituitary gland.
If you are going through a treatment for hyperthyroidism, your doctor will test your thyroid hormones and TSH frequently to see how well your treatment is working. Read about treatment of hyperthyroidism.
Iodine Uptake Scan
The cells in normal thyroid gland absorb iodine indirectly from the blood stream and produces thyroid hormones. This test is performed by giving a dose of radioactive iodine on an empty stomach. This iodine is either concentrated in the thyroid gland or excreted in the urine.
The amount of iodine that goes into the thyroid gland can be measured by a “Thyroid Uptake” test. Radioactive Iodine is used to hit upon the amount of iodine being used. This is because thyroid gland takes up iodine in order to maintain its hormone level. The radiation dosage of this test is very small, thus ruling out any possibility of side effect.
Iodine thyroid scan will be helpful in detecting whether one nodule or complete thyroid gland is overproducing thyroid hormone. This is also called as the “Thyroid scan”. In this scan, a percentage of absorbed iodine is calculated with the help of a gamma camera and imaging software.
At times the gland will concentrate iodine normally but will be unable to convert the iodine into thyroid hormone. In this case, the interpretation of iodine uptake is usually done in conjunction with blood tests.
Some people are allergic to iodine and are unable to tolerate concentrated doses of iodine. In such cases, patients are given antihistamine treatment before using iodine. Excess of iodine is not absorbed but eliminated out of the body with urine.
More Blood Tests
Your doctor may want to do a blood test to look for anti-thyroid antibodies. Anti-thyroid antibodies are usually found if you have Graves’ disease, which is a common cause of an overactive thyroid.
Sometimes, your doctor may do a blood test called erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) to check inflammation in your body. Inflammation may indicate an increase in thyroid hormones due to a condition called thyroiditis.