Browsing: Osteoporosis Graphics
Comprehensive Information, Resources, and Support on Osteoporosis
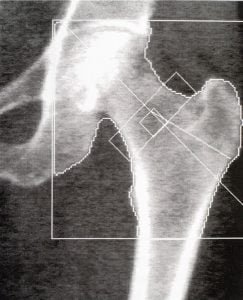
Bone density scanning, also called dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) or bone densitometry, is an enhanced form of x-ray technology that is used to measure bone loss. The image shows a DEXA hip scan in which osteopenia is noted. Osteopenia refers to bone density that is lower than normal density but not low enough to be classified as osteoporosis.
Osteoporosis can cause bones, including hib bone, to become brittle. Elderly people with osteoporosis can decrease their risk for hip fracture by maintaining muscle strength and balance with exercise programs.
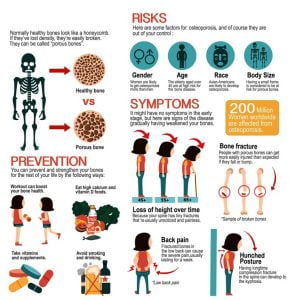
Risks, signs, symptoms, prevention, and treatment of osteoporosis.
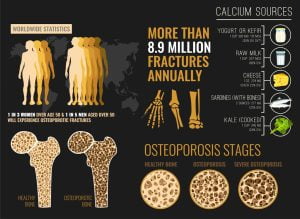
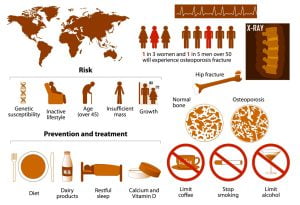
The infographic shows an overview of osteoporosis including risk factors, signs and symptoms, complications, and prevention. When the bone density reduces, it leads to osteoporosis. The bones become weaker and prone to fractures. Increase in age, body weight, gender, low estrogen levels, low calcium, Vitamin D levels, etc increase the risk. There are no specific symptoms but back pain, minor fractures, etc can be signs of osteoporosis. X-ray scan can be used as a diagnostic method. Exercise, healthy diet, and medicines and therapies such as biphosphates, estrogen agonists, hormone therapy, etc are best recommended.
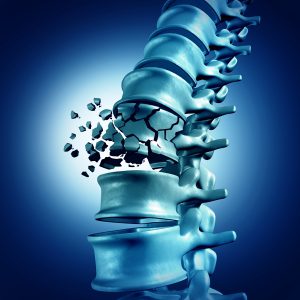
Fractures caused by osteoporosis generally occur in the spine. These spinal fractures (vertebral compression fractures) affect about 700,000 patients each year. They are about twice as common as other fractures due to osteoporosis, such as broken hips and hand joints.
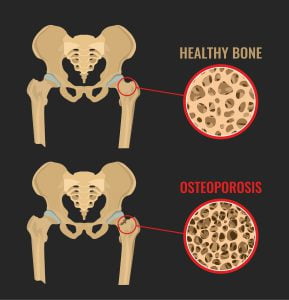
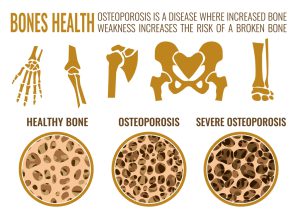
The image shows osteoporosis bone and healthy bone in comparison. Osteoporosis means “porous bone”. In a healthy bone, the bone density is normal while in case of osteoporosis, the bone density is very low. In a healthy bone, the tissues inside appear as a network of mineralized partitions or walls with open spaces in between. In initial stages of osteoporosis, those open spaces enlarge and the bone density reduces. This is known as osteopenia. In later stage of osteoporosis, the spaces become very large which make the bones weak and result in fractures.
Not getting enough calcium in your diet can lead to fragile, brittle bones that are more prone to fractures and diseases such as osteoporosis. Calcium keeps bone and teeth healthy. If intake of calcium is low, it leads to low bone mass, rapid bone loss, and high fracture rates. Osteoporosis has no cure but its severity can only be delayed by ensuring an adequate intake of calcium. Diet enriched with calcium is important to prevent osteoporosis. Low-fat dairy products, leafy green vegetables, certain fish, oatmeal and other grains, tofu, sea vegetables, cereals, orange juice, etc are best calcium sources to consume during osteoporosis.
ADVERTISEMENT