Browsing: Spinal Stenosis Graphics
Comprehensive Information, Resources, and Support on Spinal Stenosis
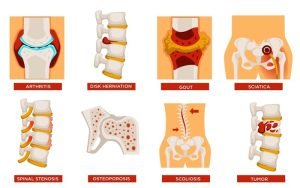
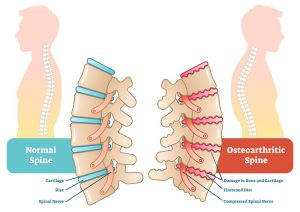
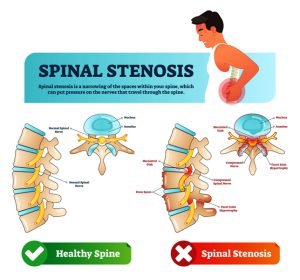
There are various spinal problems such as spinal muscular atrophy, ankylosing spondylitis, lumbar spinal stenosis, spina bifida, spinal tumors, scoliosis, etc as shown in the image above. Spinal stenosis is a very common spine-related problem. It is narrowing of the spine causing a pressure on nerves and spinal cord resulting in pain. Spinal stenosis occurs due to wear-and-tear changes in the spine (due to osteoarthritis). Spinal stenosis in many cases is a result of some other bone or spine problem. For example, the leading reason for spinal stenosis is arthritis, a condition caused by the breakdown of cartilage which serves as the cushiony material between your bones
Osteoporosis is a major medical problem and its prevalence is increasing as the aged population of the world rapidly grows. The disease predisposes patients to fracture, progressive spinal deformities, and stenosis, and is a subject of a major concern before performing spine surgery. Sometimes, treatment of stenosis becomes challenging in patients with osteoporosis. For example, spinal flexion exercises are contraindicated in persons with known Osteoporosis.
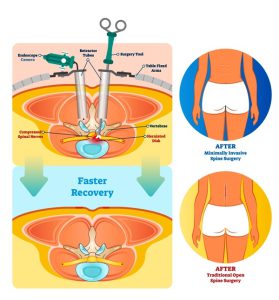
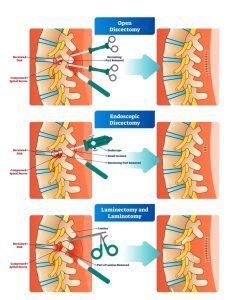
Minimally invasive spine surgery is a safer and effective alternative for spinal stenosis traditional surgery. Minimal invasive surgery can remove the decompression and also stabilize the spine. Less severe cases of spinal stenosis are generally treated with a minimally invasive decompression surgery. Two common minimally invasive decompression surgeries for spinal stenosis are foraminotomy and laminotomy. During a minimally invasive decompression surgery, a small incision in the neck, side, or back (depending on the location of the spinal stenosis) is made to remove the infected area and the nerve is decompressed. During stabilization surgery, the infected area is removed and an implant is inserted into the empty space to balance and stabilize the spine.
Spinal stenosis is the narrowing of your spinal column due to conditions such as arthritis that leads to a bony overgrowth of vertebrae and a thickening of ligaments. If the overgrowth is significant, the narrowing of the spinal column can press on the nerves in the spine. This can cause neural compression. If left untreated, it an cause cauda equina syndrome which can have lasting effects, including a loss of sensation and paralysis.
The spine is divided into segments which form three natural curves. The upper “c-shaped” curve of the neck is the cervical spine and the lower back is the lumbar spine, called lordosis. The central “reverse c-shaped” curve of the chest is the thoracic spine, known as kyphosis. Sometimes, the narrowing of the spine puts a pressure on the nerves and spinal cord which leads to spinal stenosis. Degenerative bone spurs in the spine due to osteoarthritis, formation of tumors in the spinal cord, etc cause stenosis. Changes in a healthy spine occur due to increasing age, trauma or injury, lifestyle, etc.
Diskectomy is a common surgery for herniated disk in the lumbar region. This is a surgical procedure that requires removing all or part of the damaged intervertebral disc. Spinal stenosis due to herniated disk can also be treated through diskectomy. Disk surgery can be open or endoscopic. In some cases, the surgeon may create more space for the disc and nerve by removing a portion (vertebral arch or lamina) of the bone covering the nerve. This is called a laminectomy.
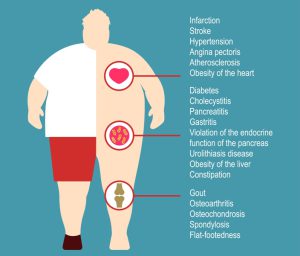
Being overweight or obese is associated with back pain, including spinal stenosis pain. Too much of body weight puts stress on your spine, which can cause spinal disorders that ultimately lead to spinal stenosis and other back problems such as sciatica, osteoporosis, osteoarthritis and low back pain from a herniated disc. Obesity is medically defined as an excess of adipose tissue which can be reduced with the help of physical exercises and intake of proper and healthy diet.
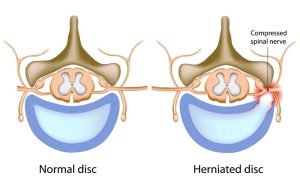
A bulging disc or portions from a herniated disc can protrude into the spinal canal or pinch on the nerve extending through the foramen to cause spinal stenosis. Strong, pliable cushions that rest between the vertebrae of the spine are known as discs. These discs act as shock absorbers and facilitate spinal movement. A herniated disc is when the outer wall of the disc ruptures and the gel-like substance from inside the disc leaks out and compresses the spinal cord or nerve roots. This compression or narrowing of spine leads to spinal stenosis.
Symptomatic spinal stenosis is associated with ankylosing spondylitis. Patients with ankylosing spondylitis usually feel back pain and have a well-known propensity for spinal fractures. But they rarely manifest motor and sensory nerve root impairment.
ADVERTISEMENT