Browsing: Colorectal Cancer Graphics
Comprehensive Information, Resources, and Support on Colorectal Cancer
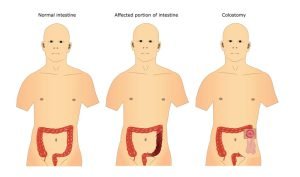
Images of normal intestine, cancer- (or other disease) affected intestine, and intestine after a portion is removed through colostomy.
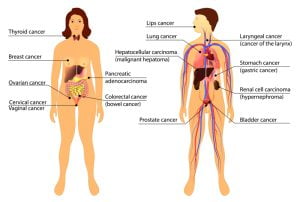
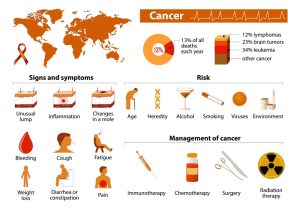
Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells anywhere in a body. These abnormal cells are termed cancer cells, malignant cells, or tumor cells. Cancer is not just one disease but a group of diseases that involve the abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. The image shows cancers of certain body parts. But, practically, any body part has the potential to develop cancer.
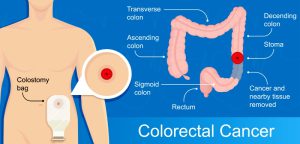
Your surgeon may remove all or a part of the bowel in a colostomy procedure. The surgeon may perform a colostomy if there’s not enough healthy intestine after surgery. In a colostomy, one end of your large intestine is moved to the outside of the abdomen and is attached to a colostomy bag to expel the waste.
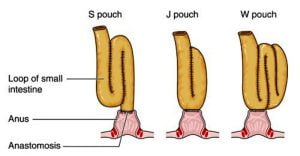
Formation of S J and W pouches after colostomy. Ihe ileal pouch-anal anastomosis (IPAA), also called an ileo-anal pouch, restorative proctocolectomy, ileal-anal pullthrough, or sometimes a j-pouch, s-pouch, w-pouch or an internal pouch (or Kock pouch), is a surgically created internal reservoir to expel the waste from the body after entire or a part of the colon is rmeoved due to problems such as colon cancer, appendicitis, etc.
The infographic shows risk factors that can increase the chances of someone getting colorectal cancer.
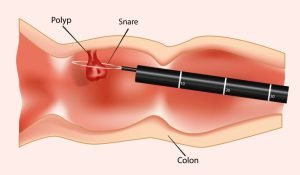
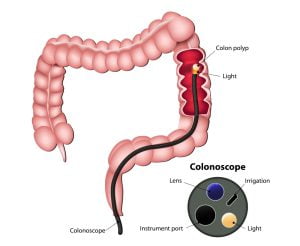
During a colonoscopy, a doctor can find and remove any polyps in the large intestine. The removal of polyps is called polypectomy. It generally causes no pain and keeps cancer colorectal cancer from developing.
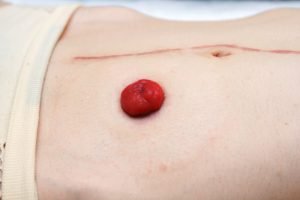
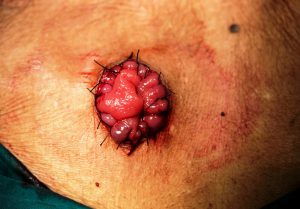
Side view of closeup stoma with long abdominal surgical scar, after colon cancer surgery.
Photograph showing illustration of cancer signs, symptoms and management, malignant tumors.
Colorectal cancer generally begins as a “polyp,” a term used to describe a growth on the inner surface of the colon. Polyps are often non-cancerous masses, but some can develop into cancer too. Malignant polyps are polyps that are identified under microscopic examination to have cancer.
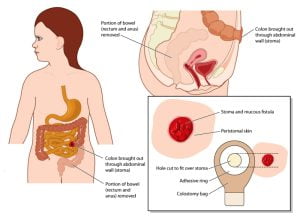
During a colostomy, a surgeon diverts one end of the large intestine into an opening called a stoma on the patient’s abdomen. A small pouch, called colostomy bag, is then placed over the stoma to collect waste products that the patient would otherwise pass through rectum and anus.
The image shows an end sigmoid colostomy procedure in operation of rupture rectal carcinoma. As stoma (opening) is created in the abdomen to expel the wastes.
Colonoscopy is a procedure that allows a doctor (usually a gastroenterologist) to evaluate the inside of the colon (such as large intestine). The colonoscope is a long, flexible tube about the thickness of a finger with a camera and a source of light at its tip that is inserted in the colon for diagnosis of colorectal cancer and other colon diseases.
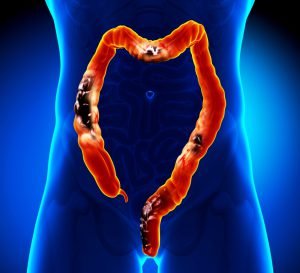
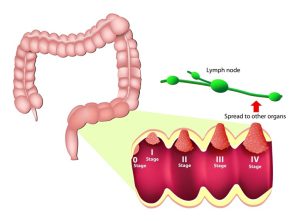
The earliest stage of colorectal cancer is called stage 0 (indicates a very early cancer), and then it ranges from stage I (1) through IV (4). The lower the number, the less the cancer has spread. A higher number, such as stage IV, indicates cancer has spread more. And within a stage, an earlier letter means a lower stage.
ADVERTISEMENT