Browsing: Leukemia (Blood Cells Cancer) Graphics
Comprehensive Information, Resources, and Support on Leukemia (blood cells cancer)
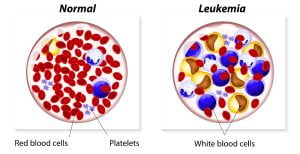
Leukemia is a type of cancer of the blood forming tissues of the body. Excessive amount of white blood cells are produced which which makes a body unable to work properly and weakens your immune system.
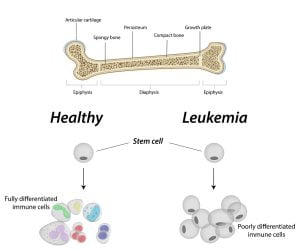
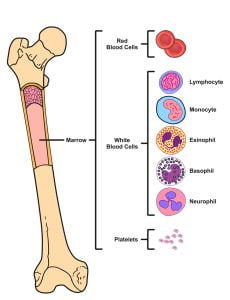
Leukemia begins in the immature or developing cells of the bone marrow, which is a soft, spongy tissue found in the central cavities of your bones. The bone marrow produces different types of blood cells. Bone marrow is mainly in our pelvis and backbone (spine). Bone marrow makes blood stem cells. These stem cells produce lymphocytes, red blood cells, platelets and other white blood cells. In case of leukemia, white blood cells divide and grow in an uncontrolled manner and numerous immature blood cells are produced. These immature cells fill the bone marrow and leave no space for healthy cells.
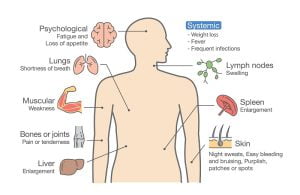
The most common signs and symptoms experienced by a leukemia patient can be understood through this infographic. Leukemia is a cancer of the blood cells (leucocytes) and can be fatal in several cases. It can be acute or chronic. Some common symptoms of leukemia are anemia, fatigue, weakness or tiredness, shortness of breath, severe infections, swollen lymph nodes, enlarged liver or spleen, bruises or red spots in skin (petechiae), bone pain or tenderness, thrombocytopenia, etc.
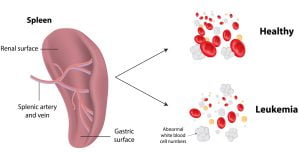
Leukemia is assoicated with white blood cells. It leads to an increase in the white blood cell count mainly consisting of immature and unhealthy white blood cells. Normal bone marrow cells are displaced by malignant cells, which results in the lack of blood platelets and regular white blood cells needed for immune activity.
The bone marrow diagram represents femur reproduction of red blood cells, white blood cells (lymphocyte, monocyte, neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils) and platelets.
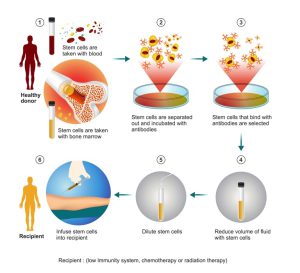
The allogeneic bone marrow transplant process involves donation of stem cells from the blood of a healthy person to a recipient. Genetic matching is carried out between the recipient and donor stem cells.
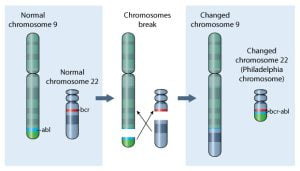
Genetic abnormality of chromosome 22 acts as a major factor in chronic myeloid leukemia. Some researchers suggest that certain changes in DNA leads to the formation of leukemia cells from normal bone marrow cells. As shown in the image, during cell division, the DNA is “swapped” between chromosomes 9 and 22. Part of chromosome 9 goes to 22 and part of 22 goes to 9. The interchange of part of DNA is known as a translocation. This reduces the length of chromosome 22 than normal and initiates chronic myeloid leukemia. This new abnormal chromosome is called the Philadelphia chromosome.
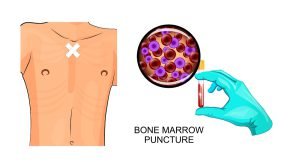
Bone marrow examination involves pathologic analysis of bone marrow samples obtained through bone marrow biopsy and bone marrow aspiration. It is used to diagnose a number of conditions, such as leukemia, multiple myeloma, lymphoma, anemia, and pancytopenia. Depending on the symptoms, the doctors perform blood tests, bone marrow aspiration and biopsy, or lymph node biopsy. In some cases, lumbar puncture is also performed to check for leukemic cells in the fluid around the brain and spinal cord. Depending upon the diagnosis, the type of leukemia and any chromosomal abnormality in leukemia cells and bone marrow are found according to which the treatment is provided.
ADVERTISEMENT