Browsing: Neuroblastoma Graphics
Comprehensive Information, Resources, and Support on Neuroblastoma
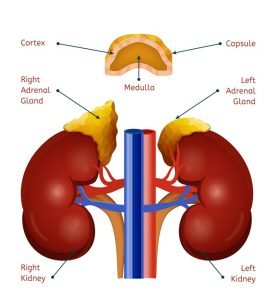
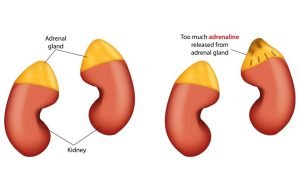
Adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce hormones including adrenaline and steroids aldosterone and cortisol. Adrenal glands are located above the kidneys. The hormones released by them help the body control blood sugar, burn protein and fat, and regulate blood pressure, respond to stressors such as an illness or injury.
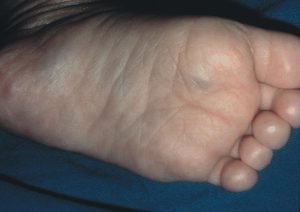
Signs and symptoms of neuroblastoma may include fatigue, loss of appetite, and fever. There may be a lump or compression of tissues in the area affected by the cancer. Since early signs of neuroblastoma can develop slowly and be similar to symptoms of other common childhood illnesses, neuroblastoma can be difficult to diagnose. The image shows stage IV-S neuroblastoma with multiple cutaneous metastases presenting as mobile blue-gray nodules. (Image source: The Armed Forces Institute of Pathology)
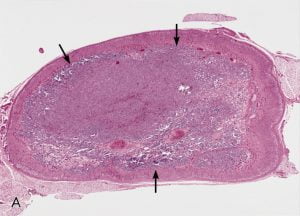
The image shows incidental in situ neuroblastoma in a 26-day-old girl who died of congenital heart disease. The tumor measured 6 mm in diameter. The junction with residual adult or definitive cortex is indicated by arrows. [Image used under Creative Commons License from Wikimedia]
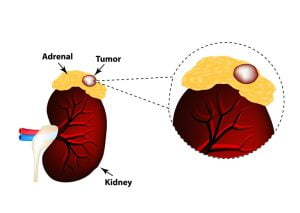
Neuroblastoma is a rare type of cancer that mostly affects babies and young children. It develops from nerve cells (called neuroblasts) that are left behind from a baby’s development in the womb. It mainly affects adrenal glands that are located on top of the kidneys. Neuroblastoma treatment is done through surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, radioactive iodine, and high-dose chemotherapy.
Neuroblastoma is a type of cancer that occurs in the immature nerve cells of several areas of the body. Neuroblastoma most commonly develops in and around the adrenal glands, which have similar origins to nerve cells and are located on top of the kidneys. But it can also develop in other regions such as neck, chest, abdomen, and spine. It’s a deadly cancer.
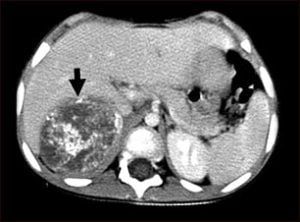
This CT scan of the upper abdomen shows a large neuroblastoma tumor on a person’s right side (lower left side of picture). The tumor is behind the liver and is pushing the liver forward and may have possibly spread into the liver tissue. [Image used under Creative Commons License from Wikimedia]
ADVERTISEMENT