Browsing: Salivary Gland Cancer Graphics
Comprehensive Information, Resources, and Support on Salivary Gland Cancer
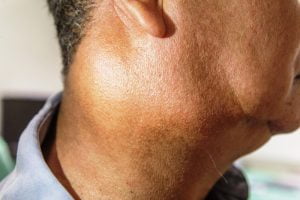
An image showing closeup lateral view of enlarged lymph nodes and submandibular gland on right side of neck in a middle aged Asian male. The patient has a history of chronic slow progressive neck lump and pain. This may be a sign of salivary gland cancer. Other signs associated with salivary gland cancer are numbness in part of the face, muscle weakness on one side of the face, difficulty while swallowing, discomfort while opening the mouth widely, etc.
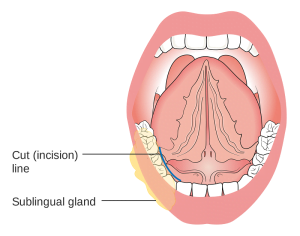
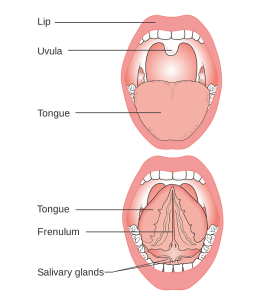
The sublingual glands are almond shaped, smallest of the three major pairs of salivary glands. They lie on the floor of the oral cavity (under the tongue). It is rare for a malignant tumor to start at sublingual salivary gland. The symptoms of salivary gland cancer can be lumps in the mouth or side of the face, difficulty swallowing or opening mouth widely, etc. Accurate diagnosis can be done with the help of biopsy. Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, etc are treatment options for salivary gland cancer.
The salivary glands are present in the head and neck and produce saliva (which is a combination of water, electrolytes, mucus and enzymes). Major salivary glands are parotid, sublingual and submandibular. It is observed that salivary gland tumors most commonly occur in the parotid gland. The most common salivary gland tumor (benign) is a pleomorphic adenoma which grows slowly and occurs most often in the parotid gland. Signs of tumor formation in a salivary gland are lumps in neck or mouth, persistent pain in salivary gland, numbness on face, etc.
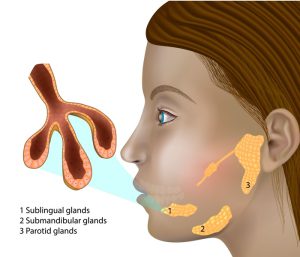
The image shows representative adult female salivary gland location. The largest of the three glands are the parotid glands, which are located in front and just beneath the ears. The second glands are the sublingual glands which are located under the tongue in the floor of the mouth. The third set of salivary glands are called submandibular glands which are located just beneath the lower jaw.
Salivary gland cancer can start in one of the salivary glands found inside and near your mouth. Tumors form cancer and affect different parts of the mouth such as jaw, tongue, sinuses, inside the cheek, nose, larynx, near the ear, etc. Development of salivary gland cancer in mouth leads to swelling, numbness in face, constant pain, etc. Treatment of salivary gland cancer depends on size of tumor, stage of cancer, grade, type, and especially the location of the cancer in the mouth.
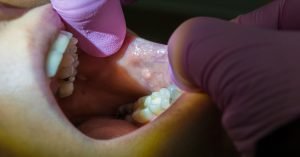
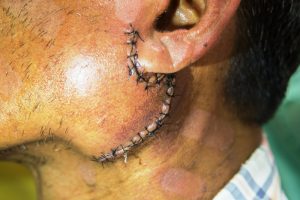
A zoomed close-up view of a sutured wound after cancer surgery of salivary gland on left cheek just below auricle in a patient. Surgery is considered as the main treatment for salivary gland cancers. The type of surgery depends on the salivary gland which is affected such as parotid gland surgery (for facial nerves), submandibular or sublingual gland surgery (for nerves that control movement of tongue, feelings of sensation and taste and the lower half of the face) and minor salivary gland surgery (lips, mouth, throat, voice box (larynx), nose, and sinuses.
ADVERTISEMENT