Browsing: Digestive Health

The page provides quick access to a list of common gastro-intestinal tract diseases, syndromes, health conditions, and other topics of health importance. The list is organized alphabetically. Links are provided to respective diseases sections that serve as a comprehensive and ultimate guide about the disease or health condition.
Some people experience certain gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms on a regular basis, such as heartburn, indigestion/dyspepsia, bloating and constipation. These symptoms may occur due to various digestive problems. Depending upon the condition, the gastrointestinal disease (GI disease) may be acute or chronic. The best way to prevent occurrence of any such disease is exercising on a regular basis and have a healthy diet.
Healthcare professionals indicate such prevalent occurrence of gastric diseases throughout the world, across all age groups. This is due to improper diet, obesity, gastroenteritis, inflammatory bowel disease, various gastric cancers and ulcers. Some doctors believe that digestive disorders occur due to malabsorption disorders and lack of gastric microbiome in an individual.
Gastrointestinal disorders include conditions such as constipation, irritable bowel syndrome, diverticular diseases, colitis, piles, gall stones and colon cancer, which are extremely common. These lead to inefficient digestion and absorption of nutrients in the body, causing severe effects in growth and development of an individual. Constipation and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) are two most widespread gastric diseases.
Appendicitis in Kids: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Appendicitis in kids is a rare condition especially in infants. If it occurs, it usually affects kids in the age group of 2-12 years. Mostly, it occurs in teens and adults in their twenties. Appendicitis affects about 80,000 children every year in the United States. The children below 5 may suffer from acute appendicitis.
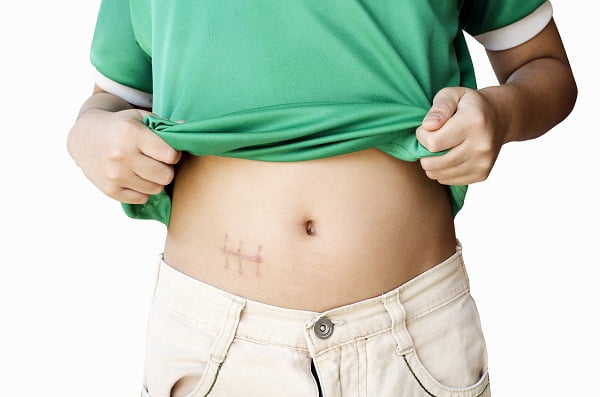
Appendectomy Recovery: How Long Does It Take to Recover From Appendix Surgery?
Appendectomy or appendicectomy is generally done to remove the appendix if you have appendicitis. Your doctor removes the appendix either by making many small incisions in your belly through a laparoscopic surgery or through an open procedure. You may feel sick and have diarrhea, constipation, gas, or a headache. This usually goes takes a few days to go.
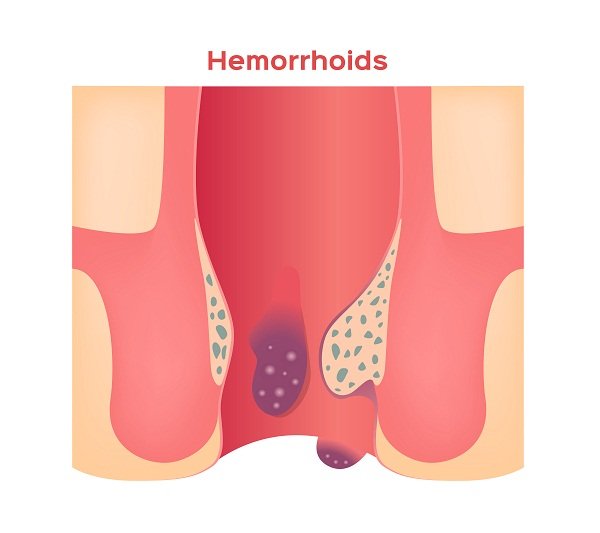
People who have doubts about their hemorrhoids time to heal often ask this question. The answer to this question differs case to case. Some hemorrhoids (piles) are severe while others are mild. Some are internal and others are external. The duration for which a hemorrhoid will last depends on its condition and the treatment taken by an individual.
Constipation occurs when the colon absorbs too much water from the stool thus making it hard and dry. This happens when the muscles in the colon contract slowly, and the stool too moves slowly. Constipation is generally not caused by one particular condition and it may be difficult to identify the exact cause.
The symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) can be managed by making changes in your diet and lifestyle. In some cases, medicines and psychological treatments are needed. Irritable bowel syndrome disease doesn’t have a cure. Your doctor will try to manage the symptoms through diet changes, medicines, probiotics, and psychological therapies.
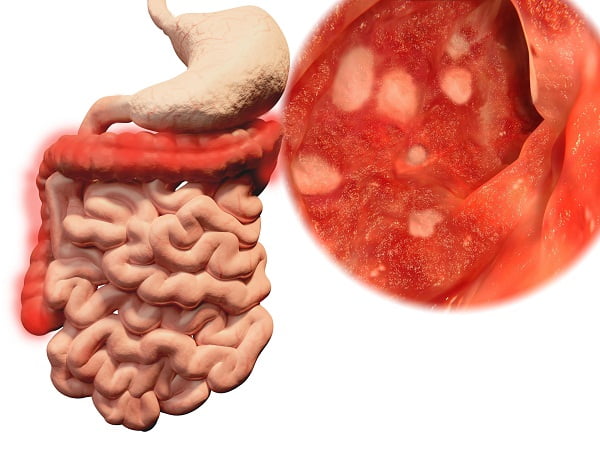
An ulcerative colitis flare-up is the recurrence of the symptoms of ulcerative colitis after a period of remission. This may involve return of the symptoms such as diarrhea, pain in abdomen, bloody stools, cramping, rectal pain, loss of appetite, unwanted weight loss, fatigue, and frequent or changed bowel movements.
The treatment for mild to moderate ulcerative colitis starts with anti-inflammatory and antidiarrheal medications and corticosteroids. The objective of treatment with drugs for ulcerative colitis is to reduce inflammation in the colon. They control or prevent inflammation in the intestines and help in various ways.
If you suspect you may have irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), it is important that you meet your general physician or a gastroenterologist to seek medical advice and for the diagnosis of the condition. IBS symptoms are similar to other gastrointestinal (GI) disease such as diverticulitis, polyps, Celiac disease etc.
What is Hemorrhoidectomy for Hemorrhoids (Piles)?
Hemorrhoidectomy is a surgical procedure to remove severe and extensive hemorrhoids. Hemorrhoidectomy is the most effective treatment for hemorrhoids, though there are many complications associated with the procedure. You will be given general or spinal anesthesia before the procedure so that you do not feel any pain.
Hemorrhoids can be one of the reasons of blood in your stool. Generally, hemorrhoids result in red-bright blood in the stool after bowel movements or blood may be noted on the toilet paper. In very rare cases, bleeding may be massive due to hemorrhoids. Colon cancer can also cause bleeding in GI.