Browsing: Digestive Health

The page provides quick access to a list of common gastro-intestinal tract diseases, syndromes, health conditions, and other topics of health importance. The list is organized alphabetically. Links are provided to respective diseases sections that serve as a comprehensive and ultimate guide about the disease or health condition.
Some people experience certain gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms on a regular basis, such as heartburn, indigestion/dyspepsia, bloating and constipation. These symptoms may occur due to various digestive problems. Depending upon the condition, the gastrointestinal disease (GI disease) may be acute or chronic. The best way to prevent occurrence of any such disease is exercising on a regular basis and have a healthy diet.
Healthcare professionals indicate such prevalent occurrence of gastric diseases throughout the world, across all age groups. This is due to improper diet, obesity, gastroenteritis, inflammatory bowel disease, various gastric cancers and ulcers. Some doctors believe that digestive disorders occur due to malabsorption disorders and lack of gastric microbiome in an individual.
Gastrointestinal disorders include conditions such as constipation, irritable bowel syndrome, diverticular diseases, colitis, piles, gall stones and colon cancer, which are extremely common. These lead to inefficient digestion and absorption of nutrients in the body, causing severe effects in growth and development of an individual. Constipation and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) are two most widespread gastric diseases.
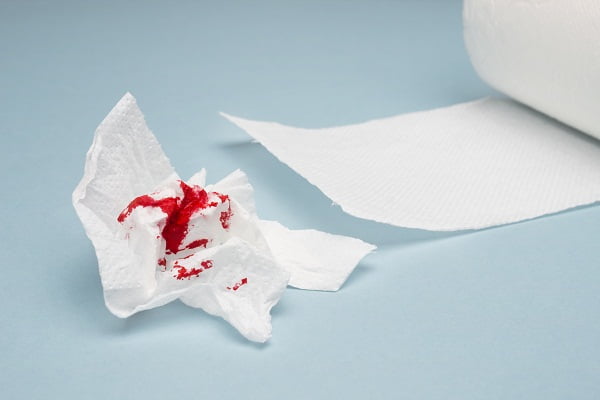
Bleeding Hemorrhoids (Piles): Why Do Hemorrhoids Bleed for Many Weeks?
Hemorrhoids (piles) are changed blood vessels that are located in the anal canal. Hemorrhoids do not cause any problem unless they become inflamed. Bleeding severity may vary depending on the severity of the condition, but the lumps and swelling around the anus due to bleeding hemorrhoids can be very painful.
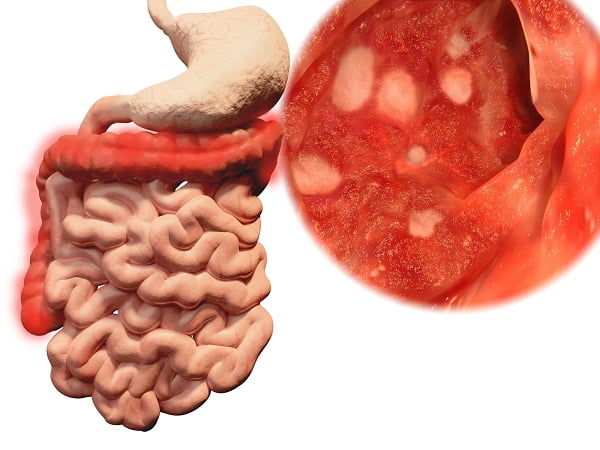
Ulcerative Colitis: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment
What is ulcerative colitis? Ulcerative Colitis is the most common type of inflammatory bowel disease. It is a chronic disease…
There are different types of creams and ointments available for application on internal and external haemorrhoids that can help relieve the symptoms. You should always consult your doctor before applying any such ointment on the skin. Some creams may work good for one but for others.
Weight Loss After Gallbladder Removal: Do You Put on Weight After Gallbladder Removal?
After cholecystectomy, you may experience trouble in digesting fatty foods until your body adjusts. For this reason, your doctor or dietician may instruct you to avoid high fats and fried foods until your body is not ready to tolerate them. In fact, gallbladder problems and your weight changes go hand in hand.
There are different dietary strategies to tackle diarrhea. Diarrhea can be controlled easily at home by taking rest, increasing fluid intake, and consuming easily digestible food items in the diet. The well-known diarrhea diet is the BRAT diet; it refers to Bananas, Rice, Applesauce, and Toast.
There are different forms of diarrhea – osmotic diarrhea, infectious diarrhea, secretory diarrhea, dysmotility diarrhea, and steatorrhea. Diarrhea is usually defined as three or more watery stools in a period of 24 hours. Diarrhea can be watery, bloody, mucoid, and loose.
Diarrhea: Causes, Symptoms, Complications, Treatment
Diarrhea is characterized by watery stools or recurrent bowel movement. Diarrhea lasts for a few days and often disappears without any treatment. It can be acute or chronic. Most cases of diarrhea occur due to bacteria, viruses, or parasitic infection. The general signs and symptoms of diarrhea involve passing loose, runny stools that may occur more than three times a day.
How to Protect Yourself From Antibiotic Resistant Foodborne Illnesses?
Antibiotic resistance in foodborne microbes has become a major public health concern. Most of the foodborne illnesses are mild and get cured without treatment. Most of the foodborne illnesses can be treated with antibiotics. However, some foodborne bacteria have developed antibiotic resistance and are difficult to treat.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a chronic condition caused due to the weakening or relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) valve. As a result, the stomach contents backflow into the esophagus. There are many causes behind GERD symptoms; however, tobacco and alcohol consumption can worsen the symptoms leading to irritation and heartburn.
Food poisoning is a common condition that occurs when certain microorganisms or germs contaminate the food and drinking water. Food poisoning can be prevented by taking various precautionary measures such as having good quality food, using pasteurized dairy products, cooking foods at proper temperatures, etc.