Browsing: Diabetes Mellitus
Comprehensive Information, Resources, and Support on Diabetes Mellitus
Beyond Diabetes: Benfotiamine’s Potential Benefits for Cardiovascular Wellness
While benfotiamine’s association with diabetes management is well-established, its potential benefits extend beyond glucose regulation. Recent research has unveiled intriguing…
Path to Wellness: Exploring Effective Diabetes Reversal Plans
Explore diabetes reversal plans for improved health. Personalized nutrition, exercise, and expert support guide individuals to manage type 2 diabetes effectively. Join Care4Sugar for a transformative journey towards wellness.
Diabetes Progression: Understanding How Likely it is to Worsen Over Time and the Worsening of Diabetes
Diabetes affects insulin production or usage, leading to health complications. Types include autoimmune Type 1 and insulin resistance-based Type 2. Global diabetes cases are projected to rise. Managing diabetes prevents complications like heart disease, stroke, blindness, kidney disease, and nerve damage. Risk factors include inactivity, poor diet, and obesity.
Diabetes progresses over time, worsened by poor management, age, duration of diabetes, genetics, and unhealthy lifestyle factors. HbA1c, a laboratory blood test that measures average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months, is critical in managing diabetes and allows healthcare providers to monitor the effectiveness of treatments. The American Diabetes Association recommends an HbA1c goal of less than 7% for most people with diabetes.
If you are struggling with diabetes, you will be glad to hear that a reversal of this disease is possible.…
Diabetic neuropathy is a type of nerve damage that can occur in diabetics due to the presence of high blood sugar (glucose) levels. The exact cause behind diabetic neuropathy progression is still unknown. Prolonged high blood sugar levels seem to be one of the major causes. The nerve damage caused by diabetes often gets worse over time especially in people with chronic diabetes.
A blood sugar or blood glucose chart identifies ideal blood sugar levels in your body throughout the day, including before meals and after meals. If you have to keep a track of blood sugar levels, during the day or over a period of weeks or months, you can use the chart as a reference.
Peripheral neuropathy is the most common form of diabetic neuropathy that mostly affects the legs and feet first and then moves to the arms and hands. It progresses over many years and worsens over time. Diabetic neuropathy often presents symptoms like numbness, tingling or pain (diabetic nerve pain) in fingers, toes, hands, and feet.
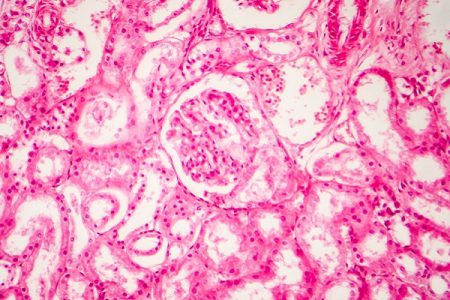
Changes in kidney function and structure are found even at the beginning of diabetes mellitus. Studies performed over the last decade now help in the recognizing various stages of diabetic renal diseases and also in the development of renal changes that occur due to diabetes. Such a classification may be helpful for both clinical as well as research purposes.
Diabetic nephropathy is a serious kidney-related complication of diabetes, and is also called diabetic kidney disease. Almost 40 % of people with diabetes ultimately develop kidney disease. Diabetic nephropathy interferes with the ability of kidneys to do their usual work of removing waste products and extra fluids from the body.