An Overview of Overactive Thyroid (Hyperthyroidism)
- Updated on: Jul 10, 2024
- 3 min Read
- Published on Sep 25, 2019
Overview
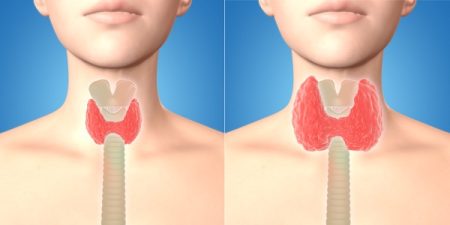
The term hyperthyroidism refers to any condition in which the body produces more than required amount of thyroid hormone. In other words, the thyroid gland is overactive and functioning abnormally. Another term that you might hear for this problem is thyrotoxicosis, which refers to high thyroid hormone levels in the bloodstream, irrespective of their source.
What is Thyroid Gland and Hyperthyroidism?
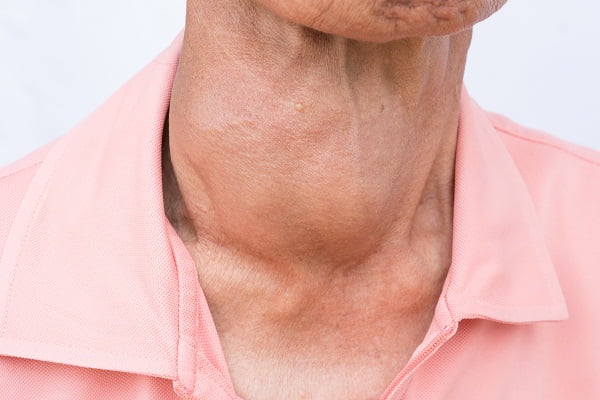
The thyroid gland is an endocrine gland which is normally located at the lower front side of the neck. It is a butterfly-shaped gland and works to make thyroid hormone. This thyroid hormone is secreted into the blood and then carried to every tissue of human body. The hormone secreted by this gland helps the body in staying warm and keeping other organs like brain, heart, and muscles in the functional state.
The term “Hyperthyroidism” refers to a common endocrine disorder. The condition occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the general term used for the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone production due to any reason and thus, includes hyperthyroidism. So the terms are used interchangeably.
This disease has significant morbidity associated with it. A report suggests that by the year 2020, there will be a steady increase in the number of Endocrine procedures. Another report states that endocrine surgeries and procedures may be more than 170,000 in the U.S only. Over 12% of U.S population will develop this condition in the coming years and estimated 20 million Americans are already suffering from some or the other form of thyroid disease. The reason is not yet known but statistics show that women are more prone to the thyroid condition.
Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism
Symptoms may include sleeping depravedness, muscle weakness, diarrhea, heat intolerance, sudden loss of weight and irritability.
Undiagnosed thyroid condition may put the person at-risk of developing more severe complications like cardiovascular diseases, infertility and osteoporosis.
If left untreated in pregnant women, hypothyroidism increases the risk of miscarriage and premature delivery. Also, it causes severe developmental problems in the foetus.
The symptoms may vary from person to person and are typically rife with old aged people and in the pregnant woman.
Hyperthyroidism begins quite slowly but in some people, the symptoms can be abrupt. Commonly, the symptoms are mistaken as anxiety and uneasiness due to stress. Read more about signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid).
Causes of Hyperthyroidism
Grave’s disease, being the most common cause of hyperthyroidism, contributes to about 50% to 80% of the cases and results in enlargement of eyes and elevation of upper eyelids.
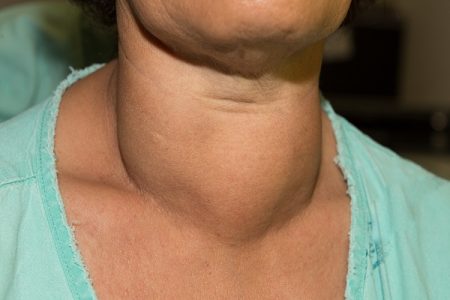
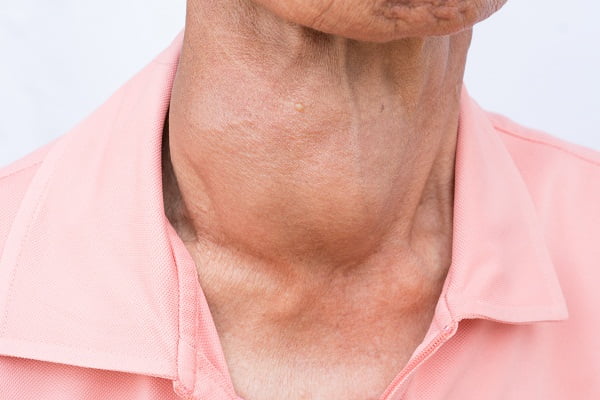
Some patients have swelling in the frontal portion of the neck (goiter) as a result of hyperthyroidism.
Toxic adenoma, thyroid inflammation, and multinodular goitre are other reasons for an overactive thyroid gland.
Taking too much of iodine and intake of synthetic thyroid hormone in excessive amount may also cause the thyroid gland to work in an abnormal way. Read more about causes of hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid).
Hyperthyroidism Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis is based on symptoms; however, it is confirmed by blood test only.
Another complication associated with this disease is Thyroid Storm. In a thyroid storm, an event like infection may worsen the symptoms and lead to the rise in body temperature and confusion. It is seen in very less number of people but sometimes proves to be fatal.
Read more about diagnosis of hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid)
The disease can be treated after confirming the cause and severity. Thyroid surgery and radioiodine therapy along with medications are the main treatment options.
Read more about treatment of hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid)