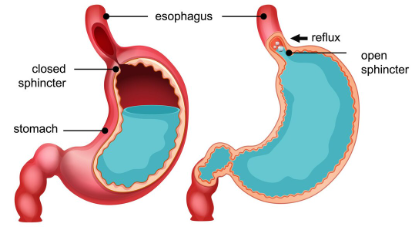
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a chronic condition caused due to the weakening or relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) valve. As a result, the stomach contents backflow into the esophagus. There are many causes behind GERD symptoms; however, tobacco and alcohol consumption can worsen the symptoms leading to irritation and heartburn.
Why Should You Avoid Alcohol and Tobacco for GERD?
Doctors usually recommend avoiding the consumption of alcohol and tobacco because they may lead to GERD. It has been suggested that consuming alcohol and tobacco damages the esophagus and ultimately leads to GERD symptoms such as burning sensation in the heart, chest pain, regurgitation, nausea, vomiting, and indigestion.
Effects of Alcohol
Alcohol can affect both the stomach and the esophageal tract. There are many ways in which alcohol may lead to heartburn symptoms:
- Alcohol causes the LES valve’s relaxation, which leads to the reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus called GERD.
- Alcohol irritates and damages the esophageal muscles and worsens the GERD symptoms.
- Alcohol products like beer and wine may increase acid production in the stomach, which causes the inflammation of the stomach’s inner lining and ultimately causes GERD.
- Alcoholic drinks generally contain sugar and fermented citrus fruits that can increase stomach acid secretion and therefore causes heartburn.
Effects of Smoking
Smoking worsens your GERD symptoms in the following ways:
- Smoking may relax the lower end of the esophagus, called LES, which increases the chances of backflow of acidic contents from the stomach into the esophagus, called GERD.
- Smoking also damages the salivary glands leading to digestive stress. The damaged salivary glands produce less saliva, due to which the acid refluxed into the esophagus is not appropriately neutralized. All these things impair the digestive process and produce harmful enzymes in the gastrointestinal tract that together worsen the GERD symptoms.
- Smoking damages the lining of the digestive tract. Smoking may also cause the flow of bile salts from the intestines into the stomach. Inside the stomach, these bile salts mix up with the stomach acid and ultimately lead to GERD.
Besides the symptoms mentioned above, the consumption of alcohol and stomach during GERD may cause:
- Esophageal ulcers
- Esophageal inflammation
- Barrette’s esophagus (Replacement of normal cells of the esophageal lining with the abnormal cells)
- Gastritis (inflammation of the stomach)
- Esophageal cancer
Does Avoiding Alcohol and Smoking Help With GERD?
Avoiding alcohol and smoking alone cannot help with GERD symptoms. Some dietary and lifestyle modifications, along with medications, are also necessary for avoiding the GERD symptoms. Some studies suggest that smoking cessation may decrease the LES valve’s pressure and may ultimately prevent acid reflux. Besides, avoiding smoking allows the proper functioning of salivary glands and increases saliva production. Increased saliva increases sodium bicarbonate content, which helps in the neutralization of stomach acid in the esophagus.
Although alcohol is one of the risk factors of GERD, it may affect different people differently. Some people with GERD may not get affected after having a little amount of alcohol; however, the same amount of alcohol may cause heartburn and other people’s symptoms. Therefore people with GERD should avoid alcohol-based on their symptoms.
Besides alcohol and smoking, some other things to avoid during GERD are:
- Avoid eating a big meal.
- Don’t eat spicy and oily, or greasy food.
- Beware of the foods and drinks that increase your reflux symptoms.
- Do some stress-relieving exercises.
- Don’t eat 3 hours before going to bed.
Treatment Required to Improve GERD
If you noticed that even after quitting alcohol and smoking, and other lifestyle modifications, your GERD symptoms do not reduce, you should immediately consult your doctor. A study has shown that avoiding alcohol and smoking can reduce the prevalence of GERD. Since only quitting alcohol and smoking can’t eliminate GERD symptoms, proper medical treatment is required to cure GERD completely.
Your doctor may advise you to take the following medications. These include:
- Antacids are given to neutralize the stomach acid, and these are Mylanta and Maalox.
- H2 (Histamine 2) blockers are advised to reduce the acid secretion from the stomach’s lining cells. These drugs include ranitidine, cimetidine, and famotidine.
- Proton-pump inhibitors also work by decreasing the stomach acid secretion, and these include omeprazole(Prevacid), pantoprazole(Protonix), dexlansoprazole(Dexilent), and lansoprazole(Prevacid).