Blood Pressure Readings and Chart: What Is Your Blood Pressure Supposed to Be?
- Updated on: Jun 28, 2024
- 3 min Read
- Published on Apr 21, 2021
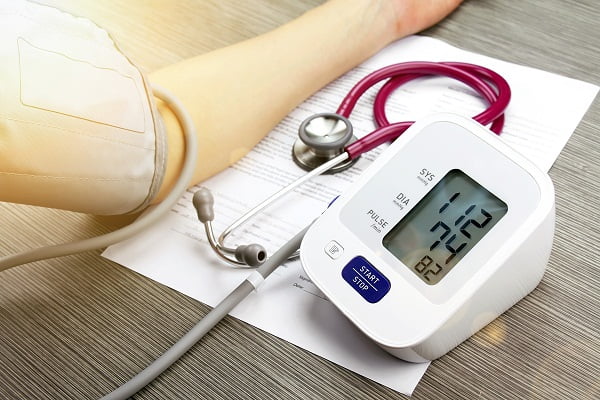
What is blood pressure?
Blood pressure can be described as the pressure of the blood circulating on the walls of the blood vessels. It is measured in mmHg (millimeters of mercury). The blood pressure is normally represented in terms of systolic pressure and diastolic pressure.
The systolic pressure can be explained as the amount of the pressure in the arteries of a patient during the heart muscle contraction. The diastolic pressure is the pressure within the arteries at the time or resting of the heart in between the beats.
Systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure
When your doctor monitors your blood pressure, it’s denoted with two numbers, with one number on top (systolic) and one on the bottom (diastolic). This can be denoted like a fraction – 120/80 mm Hg.
The top number in the reading indicates the amount of pressure in your arteries during the contraction of your heart muscle. This is called systolic blood pressure or simply systolic pressure. The bottom number refers to the blood pressure when your heart muscle is between beats. This is called diastolic pressure or diastolic blood pressure.
More: Blood Pressure (BP) during a heart attack and blood pressure before a heart attack
More: Hypotension (Low Blood Pressure): Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment
What is the normal blood pressure reading and elevated blood pressure? What is your blood pressure supposed to be?
The normal or optimal range of the blood pressure consists of systolic as well as diastolic pressure. The systolic pressure of 90-120 mmHg and the diastolic pressure of 60- 80 mmHg are considered to fall into the category of the normal blood pressure range. Blood pressure values above this are considered as elevated blood pressure readings.
The blood pressure can be measured by a blood pressure monitor, also known as a sphygmomanometer. Blood pressure should be monitored after a constant interval. The monitoring of the blood pressure helps in keeping a check on the level of the blood pressure. Read about blood pressure measurement.
Blood pressure chart (Blood pressure table)
The chart of the readings of the blood pressure will help in checking the level of the blood pressure and taking the necessary preventive steps. The following chart will help in figuring out whether the blood pressure is at an optimal level or not.
| Category | Systolic pressure in mmHg | Diastolic pressure in mmHg |
|---|---|---|
| Normal | 90-120 | 60-80 |
| Hypotension | <90 | <60 |
| Prehypertensive | 120-130 | 90-100 |
| Hypertension stage 1 | 140-160 | 90-199 |
| Hypertension stage 2 | 160-180 | 100-109 |
| Isolated systolic hypertension | >or = 160 | <90 |
| Hypertensive urgency | >Or = 180 | >or =110 |
The above-given chart can be used to classify the blood pressure readings into different categories for men as well as women. The perfect blood pressure range for men and women is 90-120 mmHg of systolic pressure and 60-80 mmHg of diastolic pressure. The blood pressure is supposed to be 120/80 mmHg for a healthy adult. The blood pressure higher or lower than this is not considered as perfect.
Why a change in the blood pressure should not be neglected?
The ideal blood pressure should be below 120/80 mmHg. This is considered as the optimal blood pressure and the person is considered to be healthy. The blood pressure reading below 90/60 is considered to be the case of a low blood pressure (Hypotension).
The readings of the blood pressure ranging above than average are considered to be the case of high blood pressure (Hypertension). This elevation in the blood pressure can lead to cardiovascular diseases. The increase or decrease in the level of the blood pressure should not be neglected.
The constant fluctuation in the average blood pressure for a longer period of time can lead to a number of heart-related diseases like stroke, formation of the blood clot in the arteries going to the brain, and dementia.
Common blood pressure problems
- Damage to your arteries
- Damage to your heart
- Coronary artery disease
- Enlarged heart
- Heart failure
- Stroke
- Dementia
- Mild cognitive impairment
- Kidney failure
- Glomerulosclerosis
- Kidney artery aneurysm
- Retinopathy
- Choroidopathy
- Optic neuropathy
- Sexual dysfunction
- Sleep apnea
- Preeclampsia or eclampsia
- Chest pain
- Heart attack
- Pulmonary edema
- Lightheadedness
- Dizziness
- Fainting












1 Comment
I must thank you for the efforts you have put in penning this blog. I am hoping to view the same high-grade content by you in the future as well. In fact, your creative writing abilities has motivated me to get my own, personal blog now 😉