Diagnosing Diverticulitis
- Updated on: Jun 29, 2024
- 3 min Read
- Published on Sep 27, 2019
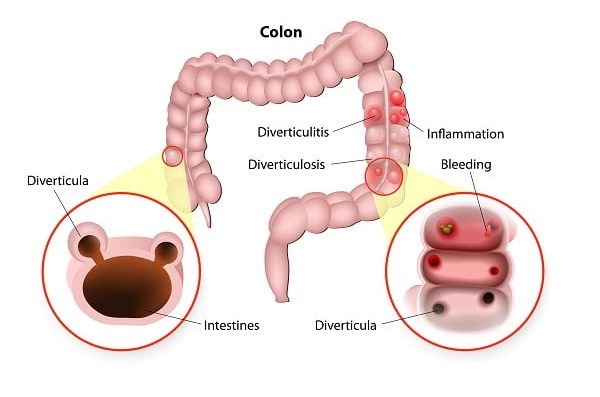
Severe abdominal pain on the lower left side of the belly is the main indicator of diverticulitis. Diagnosis of diverticulitis is usually done during an acute pain attack. The doctor may need to exclude other diseases that give similar symptom. Besides other diagnostic methods, women may also need to go through the pelvic examination.
The doctor may ask for following tests and procedures for evident diagnosis of diverticulitis:
- Blood test and urine test
- Medical history analysis
- Physical examination
- Colonoscopy
- CT scan
- Lower GI series
On the basis of medical history and physical examination, diagnosis of acute diverticulitis is done. Your doctor may ask some questions related to symptoms and medical record in order to diagnose the condition. Read about symptoms of diverticulitis.
Tests and methods for diagnosis of diverticulitis
Diverticulitis can be difficult to diagnose as its symptoms overlap other digestive tract conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Blood test and urine test are usually the first steps towards the diagnosis. These tests do not directly confirm the possibility of diverticulitis but clear doubt of any other disease like celiac disease or bowel cancer.
Following are the diagnostic procedures and tests used by doctors:
Blood test and Urine test
Blood test and urine test are not directly used for the diagnosis of diverticulitis but they rule out the possibility of any other disease with similar signs and symptoms. A healthcare professional takes a blood and urine sample for lab testing for the diagnosis of infection and anemia.
Medical History
The doctor usually asks questions related to the patient’s medical record and family history of the disease. For effective diagnosis of diverticulitis, doctors may ask questions related to:
- diet
- medicines
- bowel movement pattern
- symptoms
Physical Examination
In some cases, doctors may also physically diagnose diverticulitis. This may include a digital rectal examination and analysis of symptoms.
The patient is asked to bend over a table while holding knees close to the chest. Doctors use gloves for the examination. The doctor slides a lubricated finger into patient’s rectum and checks for any hemorrhoids, bleeding and pain.
Colonoscopy
Doctors recommend colonoscopy to reject any chances of other diseases like cancer and for the diagnosis of diverticulitis.
Colonoscopy is done using a thin tube called as colonoscope which is used to look inside the rectum or colon. Colonoscope is a thin, long and flexible tube with a tiny camera on one end. Before the procedure, doctors prescribe medications to prepare the patient for diagnosis. The procedure is performed by a trained professional in a hospital or clinical center.
The patient is asked to lie on a table. The colonoscope is inserted into patient’s rectum and slowly guided into it. Before the colonoscopy, the patient is given a laxative to clear out any bowel in the large intestine.
Colonoscopy is not painful but an uncomfortable option. The patient is offered a painkiller, sedative or anesthesia before the procedure to help relax and reduce the discomfort.
CT scan
Computerized Tomography scan or CT scan is another method to determine whether the person is suffering from diverticulitis or not. This diagnostic method uses X-rays and computer technology to create images of the digestive tract.
The procedure is performed by a trained x-ray technician in a hospital or clinical center. Reports developed by CT scan are analyzed by the radiologist.
Unlike colonoscopy, anesthesia or sedatives are not given in this procedure. However, a solution is given to drink and an injection of contrast dye is given to the patient before CT scan. The contrast dye or contrast medium makes the structures present inside the body clear to see through CT scan.
Doctor asks the patient to lie on the table that slides inside a tunnel-shaped device. This is the most commonly used procedure for the diagnosis of diverticulitis. CT scan is also done when symptoms suggest that inflamed sac has burst.
Lower GI series
Lower GI series or barium enema is a procedure in which doctor use x-rays and a chalky liquid called as barium to visualize large intestine.
The procedure is performed by trained professionals and radiologists. Barium has a property that makes large intestine more visible under x-rays. Just like colonoscopy, the doctor suggests some medications to prepare the patient for the Barium enema.
Anesthesia is not required for this procedure. The patient is asked to lie down on a table while radiologist inserts a thin flexible tube into the rectum of the patient to fill large intestine with barium. The patient is asked to change positions to take images from different sides and angles. The procedure is not done when the patient is having diverticulitis attack as at that time barium may spill over into the abdominal cavity. Diverticulitis is detected with the help of radiographs.
Other diagnosis methods
In addition to the above-mentioned diagnosis methods, there are other methods that are used for detection of diverticulitis. These are listed below:
- Complete blood count used for rectal bleeding (detection of infection)
- Urinalysis
- Fecal blood test
- Flexible sigmoidoscopy (to detect presence of any growth or ulcer in rectum)
- Liver test and lipase (to detect other possible causes of abdominal pain)
- Pregnancy test for women carrying child (to rule out possibility of ectopic pregnancy)
With early detection and proper medication, the patient can be saved from severe complications.