Diagnosis of Dental Caries
- Updated on: Jul 10, 2024
- 3 min Read
- Published on Sep 27, 2019
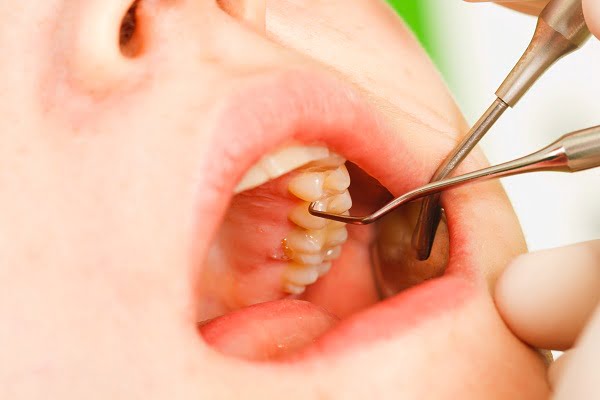
Dental caries is a scientific term used for tooth decay and cavities. Around the world, about 2.3 billion populations have dental caries in their permanent teeth. That is roughly 32% of total world’s population.
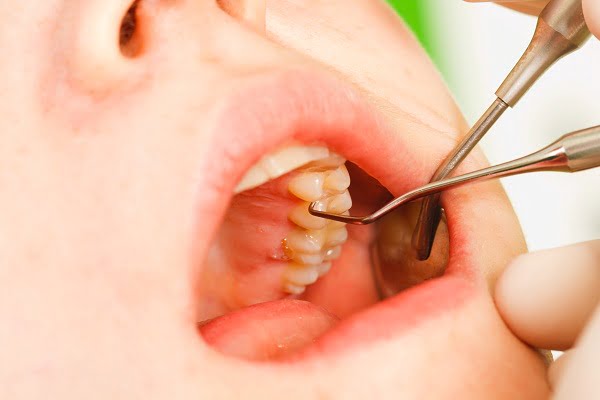
Signs and symptoms of the dental cavity are highly variable depending on the level and severity of the infection. At first, it may appear as a chalky spot which can eventually develop into a large visible cavity. In primary diagnosis, dentist inspects all visible tooth surfaces using a good light source and other dental equipment.
How to identify and diagnose dental cavities?
Uncavitated dental caries is often diagnosed by blowing air across the suspected areas. This removes the moisture and changes the optical properties of unmineralized enamel.
Some dentists do not recommend the use dental explorers for the diagnosis of caries as sometimes using a probe on the already demineralized area may create a cavity which was not there earlier. These are called as “hidden caries”. In such cases, it may be difficult to reverse the damage (cavity) created by the probe as demineralized un-cavitated teeth are comparatively easier to restore.
Read about treatment of dental cavities
Regular dental visits and oral checkups are required for the diagnosis of dental caries. Following are the reliable methods used for the diagnosis of dental caries:
- examination of medical history and lifestyle
- inspection of teeth
- periodontal screening and recording (PSR)
- dental x-rays
Examination of Medical History and Lifestyle
During the diagnosis, the first thing a doctor examines is the medical history of the patient suffering from dental caries. Just like many other diseases, tooth decay is also hereditary. A person can inherit deep tooth crevices and enamel issues from their family.
Another reason for the development of tooth caries is the age factor. It becomes more common with growing age.
Doctors also look for any other prescription (medicine) patient might be taking. Common medical prescriptions which cause dry mouth like anti-allergic drugs and anti-depressants can also promote tooth decay. In most of the people suffering from dental decay, diseases affecting teeth are not the main cause of cavities.
Apart from medical conditions, there are certain medicines that promote dryness in the mouth and reduce saliva flow. The medications like methylamphetamine and Tetrahydrocannabinol work as a stimulant to drop down saliva formation in the mouth.
Other than having diseases that make a person susceptible to dental caries, life style of a person is another important factor. Smoking and alcohol consumption makes a person more prone to oral problems. Doctors may ask certain questions related to the lifestyle and eating habits of the person for a better diagnosis.
Inspection of Teeth
Dentist inspects the color and shape of teeth on the cheek side and on the tongue side of every tooth. A thorough examination of teeth is done and compared with healthy teeth.
The earliest sign that doctors look is the presence of white chalky spot on the surface of the tooth. This spot is because of demineralization of enamel. These spots if not treated early turn brown to black. Further erosion creates a cavity in teeth.
A black or brown spot is a definite sign of infection. When disease advances to mild and active state, gums also start bleeding.
Read about signs and symptoms of dental cavities
Periodontal Screening and Recording (PSR)
Periodontal Screening and Recording (PSR) is a simple and commonly used procedure used to diagnose the severity and stage of dental caries. The diagnosis is done by using a minor periodontal probe. It is a fine instrument calibrated in millimeters (mm). It is used to measure the depth of cavity formed in between gums and teeth.
An advanced automatic probe is being currently used by dentists for the diagnosis. The automatic probe is more sensitive and accurate than manual probes. This probe is held along the length of the tooth and tip is placed in the pocket. The tip of the probe is touched where gum attaches to the tooth. The dentist will slide the probe to specific six points on each tooth and measures the depth of the pit. The measurement of depth helps in determining the condition of gum tissue and amount of damage in the tooth. This technique is more reliable as compared to x-ray diagnosis.
Dental X-Rays
X-ray images or radiographs are taken to score any damage or loss of bone structure supporting the teeth. Dental radiography may show dental caries more clearly before it is visible to naked eyes.
Often large cavities and spots are clearly visible; the problem arises with the identification of small pits and lesions. Generally, doctors use both visual inspections as well as radiographs for the early diagnosis of dental caries.