Gallbladder Cancer Ultrasound
- Updated on: Aug 3, 2024
- 3 min Read
- Published on Feb 5, 2020
Gallbladder cancer is the most frequent malignant neoplasm of the biliary system and the fifth of the digestive system. It represents approximately 2% –4% of malignant tumors. This is one of the most aggressive cancers with the shortest median survival from the time of diagnosis.
The growth of tumors obstructs the flow of bile from the gallbladder and liver to the intestine. This causes bile to backup into the liver and eventually into the bloodstream, causing jaundice, a condition in which the skin turns yellow.
It is predominant in females and usually affects adults in their sixties and seventies.
This type of cancer is difficult to detect early because of the following reasons:
- The early stages of gallbladder cancer show no signs or symptoms
- The symptoms of gallbladder cancer are similar to the symptoms of many other illnesses
Diagnosing Gallbladder Cancer
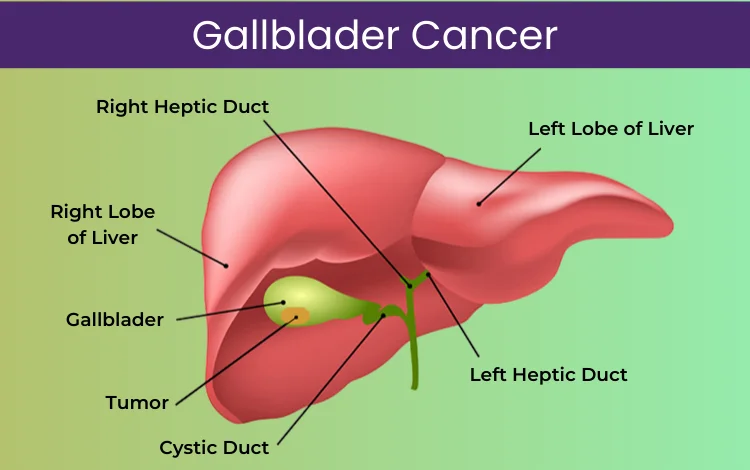
The diagnosis of gallbladder cancer is based on a combination of history and physical examination, laboratory tests, radiologic imaging.
The diagnosis includes:
- Blood tests
- Computed tomography (CT) scan
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Ultrasound
- Biopsy
- Endoscopic ultrasonography
- Positron emission tomography (PET) scan
More: Stage 4 Gallbladder Cancer
More: Coping With Cancer Symptoms
What is a Gallbladder ultrasound?
Ultrasound is the most effective, non-invasive, and typically painless initial diagnostic procedure used to diagnose conditions related to the gallbladder.
High-frequency sound waves in ultrasound are used to make images. It is also used to view the gallbladder and to check associated problems or cancer in people with abdominal pain or jaundice. Unlike X-ray, ultrasound does not use radiations.
Gallbladder Ultrasound Can Also –
- Help in determining the source of abdominal pain, such as gallstones, kidney stones, abscesses or an inflamed appendix due to appendicitis
- Help in detecting the presence and cause of an apparent enlarged abdominal organ
- Help in identifying the location of abnormal fluid in the abdomen
- Help in determining the causes of vomiting
How to Get Prepared for Gallbladder Ultrasound?
The specific preparation before an ultrasound for gallbladder cancer requires the following:
- It is advised to eat a fat-free meal the day before the test and then fast for 8 to 12 hours leading up to the exam
- Wear light and comfortable clothing that will make it easy to access the body parts that are being examined
- Taking medications with very little water
Preparation during an ultrasound includes:
- Changing clothes to a hospital gown and lie on an exam table
- A warm gel is applied to the abdomen that helps in optimizing the images
Role of Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS) in Gallbladder Cancer
In this type of ultrasound, a camera is inserted down through the mouth that allows the ultrasound probe to be placed closer to the gallbladder. This is more accurate than the traditional ultrasound.
Endoscopic ultrasound detects nodes and also identifies whether the tumor has spread beyond the gallbladder. This is the preferred method of diagnosing and staging gallbladder cancer.
How Does an Ultrasound help in Detecting Gallbladder Cancer?
Gallbladder Tumor Ultrasound is the imaging test done when doctors suspect gallbladder cancer. It confirms when the wall of the gallbladder is thicker than normal.
Ultrasound helps in showing the nearby lymph nodes that are enlarged, which can be a sign that cancer has reached them.
Other factors include:
- It helps to know how far the cancer has spread
- In making treatment decisions
- Finding if treatment is working
- Understanding for signs of cancer coming back after the treatment
Benefits of Ultrasound in Gallbladder Cancer
There are a number of benefits of ultrasounds in gallbladder cancer such as:
- Ultrasound is ideal, non-invasive, and safe among the various imaging modalities for the diagnosis of gallbladder cancer
- Ultrasound plays an important role in detecting the location and number of tumors
- It helps in defining the extension of the disease and involvement of surrounding structures including lymph nodes
- It helps to understand whether the tumor involves the main blood vessels
- It helps in distinguishing whether a mass is a cancer or a benign tumor
- Very little preparation is needed before going for a gallbladder ultrasound except restricting eating for a certain number of hours before the test
- It only takes 15 to 20 minutes to get the procedure done
Are There Any Side Effects of Ultrasound in Gallbladder Cancer?
- There are no known side effects from the sound waves used in an ultrasound. As compared to other scans, such as CT scans, an ultrasound doesn’t involve exposure to radiations
- Endoscopic ultrasounds can cause temporary side effects which include sore throat or bloating
- There is no serious complications, such as internal bleeding