HCC Liver Ultrasound
- Updated on: Feb 7, 2024
- 3 min Read
- Published on Feb 5, 2020
A significant number of HCC patients are asymptomatic and may be diagnosed following the screening. Patients who are at risk of HCC should be kept under proper surveillance with HCC liver ultrasound at 6-month intervals.
Diagnostic Features of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
Patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) often present a range of clinical presentations that may vary from being asymptomatic to presenting with a life-threatening illness like variceal hemorrhage. Some people with HCC do not present any specific symptoms while others may present a large number of symptoms particularly due to underlying cirrhosis.
HCC diagnosis can be difficult and therefore involves the use of one or more imaging modalities. Different treatment options can be offered for the tumors especially the ones which are detected when they are ≤2 cm in size. Some hepatocellular carcinomas are diagnosed in late stages due to their asymptomatic nature and the reluctance of many primary care physicians to provide surveillance for their high-risk patients. Due to this reason, some patients have an incurable disease at the time of diagnosis.
In the majority of HCC patients, imaging procedures alone are sufficient for the diagnosis, however, a biopsy may be required in patients who do not have any history of cirrhosis or other chronic liver diseases. Biopsy may also be performed in patients who present suspicious nonspecific findings on imaging.
What is HCC Liver Ultrasound?
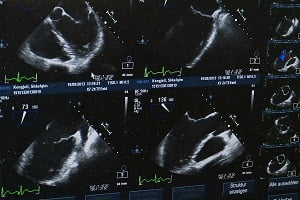
Hepatocellular (HCC) liver ultrasound is a non-invasive tool for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma with no risk of radiation exposure. Conventional ultrasound is usually considered as the first choice for the surveillance of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
High-risk group patients of HCC require ultrasound imaging at 6-month intervals as the standard of care. Ultrasound plays an important role in the screening, diagnosis, and treatment of HCC because it can provide real-time and non-invasive observation by a simple and easy technique.
Ultrasound Findings of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) Patients
The liver ultrasound of HCC patients may reveal the following findings depending on an individual lesion, size, and echogenicity of background liver:
- Small focal HCC appears as a solid dense mass (hypoechoic) compared with normal liver
- Heterogeneous larger lesions due to fibrosis, fatty change, necrosis, and calcification
- Peripheral halo of hypoechogenicity may be found with focal fatty sparing
- Diffuse HCC is difficult to differentiate from the background cirrhosis
- Tumor thrombus may be visible
More: How Long Do You Have to Live with Liver Cancer?
More: Coping with Cancer Treatment
Advantages of Liver Ultrasound in the Diagnosis of HCC
Following are the advantages of liver ultrasound in the diagnosis of HCC:
- Liver ultrasound is the key modality for the screening of hepatocellular carcinoma.
- It is a non-invasive, low-cost screening tool in the diagnosis of HCC that demonstrated adequate sensitivity (60 to 90%) and excellent specificity (90%).
- Patients with liver cirrhosis have been suggested an ultrasound every six months as the first level of investigation for HCC, however, the early diagnosis is not so easy due to the limited sensitivity of ultrasound, not exceeding 60% in very early HCC.
- Ultrasound (US) plays an important role in the diagnostic algorithm of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
- Ultrasound (US) is the recommended tool for the surveillance of patients at risk of developing HCC.
- Ultrasound is the most commonly used imaging technique that is used worldwide for guiding biopsy on suspicious nodules.
- The sensitivity and specificity of ultrasound have substantially increased due to the introduction of US contrast agents and the development of contrast-specific scanning techniques and is therefore used in the detection and characterization of focal liver lesions found in HCC.
- Studies suggest that USG has a sensitivity of 94% for identifying HCC at all stages and 63% for detecting HCC at an early stage.
- Ultrasound diagnosis of HCC is a very simple, non-invasive, and low-cost procedure. It is also a safe procedure due to lack of radiation exposure