How Are Hemorrhoids Diagnosed?
- Updated on: Jul 1, 2024
- 3 min Read
- Published on Oct 3, 2019
When in normal condition, hemorrhoids help control the bowel movement. However, when constant strain is applied on the walls of the rectum, hemorrhoids swell and cause extreme pain and discomfort to the person.
The signs and symptoms of hemorrhoids vary with the location. Though preventable, hemorrhoids are most commonly found digestive tract disease worldwide.
Proper diagnosis and consultation are required from a healthcare professional to treat piles (or swollen hemorrhoids). The symptoms of hemorrhoids are somewhat similar to other rectal and anal problems like fissures, abscesses, warts etc.
Your doctor will rule out any other serious reason behind the rectal bleeding, as hemorrhoids are not the only cause of rectal bleeding. Read about causes of hemorrhoids.
Tests and procedures for diagnosing hemorrhoids
Generally, doctors use digital examination for the diagnosis of rectal diseases. Following are the tests and procedures performed by the doctors for the diagnosis of hemorrhoids:
Physical examination
Your doctor may perform a physical examination to look for hemorrhoids. This generally involves visual examination of the rectal area.
The doctor may also use a lubricated finger or a tool called as anoscope for rectal examination. An anoscope is a type of endoscope with a hollow and lighted tube. This tube is inserted few inches into the anus to help the doctor see inside the rectum and visualize any hemorrhoid.
Apart from hemorrhoids, the doctor also looks for any other rectal condition. In cases where the patient is above 40 years of age, some additional tests are recommended to rule out any other cause of bleeding.
Medical History
Your doctor will ask questions related to the patient’s medical record and family history of the disease. For an effective diagnosis of hemorrhoids, doctors may ask questions related to the following:
- diet
- medicines
- bowel movement pattern
- symptoms
Read about symptoms of hemorrhoids.
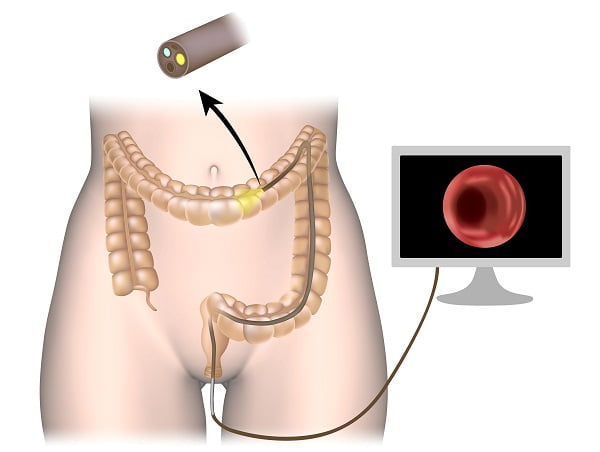
Colonoscopy
Doctors recommend colonoscopy to reject any chances of other diseases like cancer and for the diagnosis of hemorrhoids.
Colonoscopy is done using a thin tube called as colonoscope which is used to look inside rectum or colon. The tube is long and flexible with a tiny camera on one end. Before the procedure, doctors prescribe medications to prepare the patient for diagnosis.
The procedure is performed by a trained professional in hospital or clinical center. The patient is asked to lie on a table. The colonoscope is inserted into patient’s rectum and slowly guided into it. Before performing colonoscopy, the patient is given a laxative to clear out any bowel in the large intestine.
Colonoscopy is not painful but an uncomfortable option. The patient is offered a painkiller, sedative or anesthesia before the procedure to help them relax and reduce the discomfort. Colonoscopy can help to discover ulcers, polyps, tumors, and other areas of inflammation or bleeding.
Sigmoidoscopy
Sigmoidoscopy is somewhat similar to colonoscopy. Like colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy also uses a tube to visualize the inner portion of the rectum.
However, it uses a shorter tube for the examination. The name sigmoidoscopy came from “sigmoid colon” or lower portion of the colon. A camera attached at the one end of the tube helps to diagnose internal hemorrhoid. The doctor gets a clear view of the inside of patient’s rectum with this procedure.
Barium enema X-ray
A barium enema is a procedure in which a doctor uses X-rays and a chalky liquid called barium to visualize large intestine. The procedure is performed by trained professionals and radiologists. Barium has a property that makes large intestine more visible under x-rays.
Just like colonoscopy, the doctor suggests some medications to prepare the patient for the Barium enema. Anesthesia is not required for this procedure.
The patient is asked to lie down on a table while a radiologist inserts a thin flexible tube into the rectum of the patient to fill large intestine with barium. The patient is asked to change positions to take images from different sides and angles.
The procedure is not done when the patient is having diverticulitis attack as at that time barium may spill over into the abdominal cavity. Hemorrhoids are detected in this procedure with the help of radiographs.












