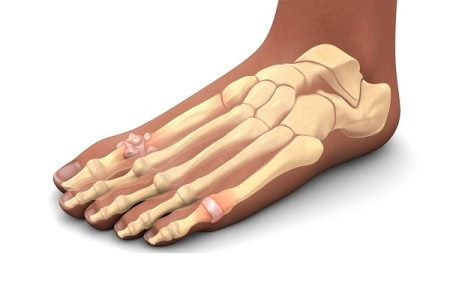
How Are Kidney Stones (Other Kidney Complications) Associated With Gout?
- Updated on: Jul 15, 2024
- 3 min Read
- Published on Oct 4, 2019
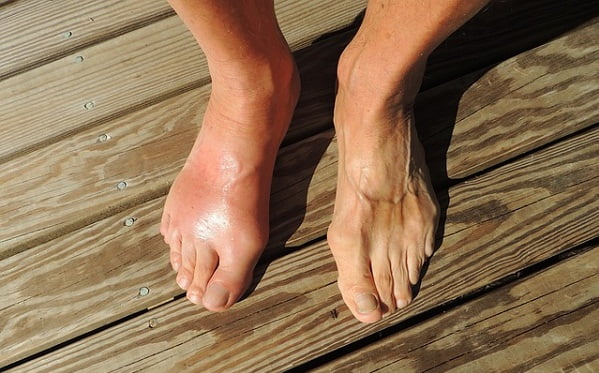
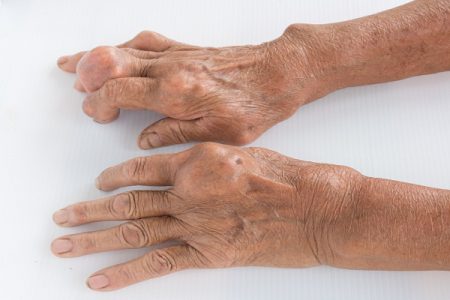
Gout and Kidneys: How Can Gout Affect Your Kidneys?
Individuals living with gout can face challenges, pain and unpredictability, especially if lifestyle changes haven’t brought their uric acid levels down to normal. If gout attacks become more frequent, you may develop chronic gout, which can stress other systems in your body, especially your renal system.
Kidneys hold a pivotal role in your renal system, and they manage the outflow of waste products. Uric acid is one of these natural waste products, and when it builds up it can form sharp uric acid crystals which are the main culprits in gout attacks. Since the kidneys are responsible for filtering out uric acid, it’s no surprise that gout and kidney health are closely dependant.
Kidney stones can be considered as a complication of gout because extra uric acid can collect in the urinary tract and crystallize into stones. In rare cases, uric acid crystals form right in the kidney and cause serious kidney problems.
When you are having gout, your health of kidney largely depends on how well you manage your condition, but simply keeping your blood uric acid level down may not be enough to prevent kidney trouble. In severe cases, gout can hamper your kidney health to the extent of chronic kidney disease and even kidney failure when the kidney is being overworked to dispose the excess of uric acid which have accumulated in gout condition.
More: Gout: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Prevention, Treatment
More: What Does Gout Look Like? How Do You Know You Have Gout?
How is gout a risk for kidney disease? What does gout do to the kidney?
The risk of developing a kidney disease gets multiplied when you are having gout. An estimated 40% of gout patients also have chronic kidney disease.
The relationship between gout and kidney disease is so marked because both conditions complement each other.
In normal physiology, a kidney excretes uric acid, and the deposition of this uric acid can crystallize, causing gout. On the other hand, high levels of uric acid in the blood due to gout can speed up the progression of kidney diseases and deterioration of kidney health due to overwork. This vicious cycle exposes your kidney to greater risk of damage, which may eventually result in kidney failure.
More: Most Common Places for Gout Where Do You Get Gout
More: What Are The Causes And Risk Factors For Chronic Kidney Disease?
How can kidney stones affect your gout?
Kidney stones severely affect the kidney’s ability to excrete uric acid efficiently, hampering the normal physiology and compounding the problem of gout. Kidney problem can also complicate the treatment and management of the gout.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) are often used as first line of treatment for the attack for acute gout, but if you are having chronic kidney disease, it’s not a good choice. Similarly, colchicine is often used for gout pain, but it brings side effects which can be unbearable if you are having a kidney disease simultaneously.
More: Kidney Stone Pain: How Does It Feel When You Have A Kidney Stone?
More: Kidney Stones (Renal Calculi): Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment
Drugs like allopurinol and febuxostat that block uric acid production can be a better solution, but any medication must be prescribed keeping in mind that further damage to kidney can be checked. There is no fit for all course of action for treating gout and kidney problems simultaneously; your doctor will have to choose to make a balance based on the severity of your gout pain, the severity of your kidney problems, and your overall health.