How Do Doctors Diagnose Cirrhosis?
- Updated on: Jun 26, 2024
- 4 min Read
- Published on Oct 3, 2019


Cirrhosis Diagnosis
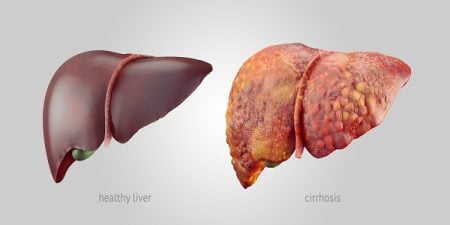
The normal functioning of liver is affected by cirrhosis. The diagnosis of a patient suspected with liver cirrhosis starts with detailed medical history. This identifies the presence of any risk factors that make the person more susceptible to cirrhosis.
For diagnosis, the doctor may do a physical exam and ask about the medical history of the patient. The doctor may also ask about symptoms and rule out the possibility of any other problem. Most often blood tests and imaging tests are done to diagnose cirrhosis.
A biopsy is another option suggested by the doctors as it can detect cirrhosis. Doctors will also try to rule out other conditions that may affect the liver to confirm the disease.
What are the tests and methods for diagnosis of cirrhosis?
Following are the techniques and procedures commonly suggested:
- Medical History of patient
- Physical examination
- Blood test to check liver function
- Blood test to check inflammation
- Diagnostic tests for cirrhosis
- Imaging test
- Liver Biopsy
- Other tests for cirrhosis
Medical History
A person suffering from cirrhosis shows certain symptoms like fatigue, weakness and weight loss. In addition, recurring infections and low sexual drive are common in people suffering from this condition.
The person may also have blood in vomiting and brown-black stool. The doctor may ask certain questions related to it for diagnosis. By analyzing the medical history and symptoms of the patient, a doctor can diagnose cirrhosis. Read more about cirrhosis symptoms.
All forms of chronic liver diseases have a potential to turn into cirrhosis. Any history of such past disease should be openly discussed with the doctor to rule out any possibility of cirrhosis.
Metabolic syndromes like diabetes and obesity are also taken into consideration. Information regarding past medical history of the patient helps the doctor to identify any hepatotoxic drug that might be used by the patient.
Physical examination
A variety of physical features related to cirrhosis is observed in detailed physical examination by the healthcare professional. These may be sometimes specific to the causative agent. Following are some of them:
- White nails
- Bruising
- Finger clubbing
- Cholesterol deposits
- Spider angiomata (Spider web-like veins under skin)
- Yellowing of eyes and skin
- Tender and firm enlarged breast bud
- Testicular atrophy (shrinkage) in men
- Loss of secondary sexual hair in men
- Breast atrophy (shrinkage) in women
The doctor may start the diagnosis with above-mentioned physical symptoms.
Blood Tests to check your liver function
The liver works in the production and breakdown of many substances. The level of certain chemicals that are produced in the liver can be measured to know about the working of the liver. Following substances are measured using a blood test:
- Albumin and total serum protein (the level of albumin decreases in the blood)
- Partial Thromboplastin Time (measuring the level of blood-clotting factors produced by liver)
- Bilirubin (breakdown hemoglobin present in blood and its high level causes jaundice)
Blood tests to check inflammation
The liver also functions to produce some enzymes. These tests, by checking the level of enzymes produced by the liver, can determine the inflammation in the liver. These include:
- Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) test (increased level of ALP may indicate bile duct blockage)
- Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) test (increased level of AST indicates liver cell injury)
- Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) test (increased level of ALT shows injury and death of liver cells)
- Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) test (increased level of LDH indicates death of liver cells)
- Gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT) test (increases level of GGT shows excessive alcohol use and bile duct complications)
- Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) test (screening of any signs of cancer in the liver)
Other Diagnostic Tests for cirrhosis
In addition to the tests mentioned above, there are other diagnostic procedures that help in the timely diagnosis of cirrhosis. These are:
- Antinuclear antibody (ANA) test (for finding possibility of an autoimmune disease)
- Anti-mitochondrial antibody (AMA) test (helps in detection of Primary Biliary cirrhosis)
- Ferritin and iron test (for the detection of hemochromatosis or iron overload due to breakdown of hemoglobin)
- Hepatitis B and C test (diagnosis of any viral infection with certain hepatitis virus)
- Blood Alcohol Level (BAL) test (for detecting over-excessive use of alcohol and detection of alcoholic cirrhosis)
- Serum Ceruloplasmin test (for the diagnosis of Wilson’s disease)
- Ammonia test (test to detect excess ammonia in the blood)
Imaging tests
Along with tests for enzymes and blood, imaging tests are also suggested by doctors to detect any tumor and blocked bile ducts. These imaging tests are also used to determine the size of the organ and blood flow through it. Following are the tests commonly used:
- Ultrasound of abdominal region
- CT scan of abdomen, liver, spleen and gallbladder
- MRI scan of abdomen
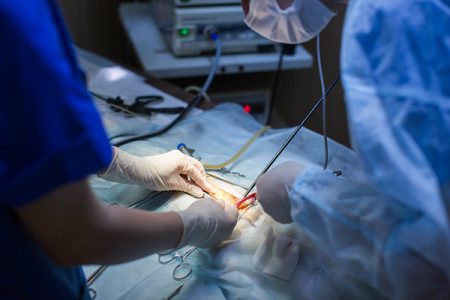
Liver Biopsy
Liver biopsy is the most specific and sensitive test for the diagnosis of Cirrhosis. It can also determine the underlying cause of liver disease.
A small needle is inserted into the liver to collect a tissue sample. This is done in the hospital by trained professionals. The tissue is then analyzed for the variety of disorders and diseases in the liver.
The procedure is bit expensive but the risk of internal bleeding is minimum with it.
Other tests for complications due to cirrhosis
There are other tests that may be done to confirm cirrhosis and other complications related to it. These are:
- Paracentesis (detection of fluid retention in the abdomen and any signs of infection or bacterial peritonitis)
- Endoscopy (diagnosis of enlarged veins and bleeding in digestive tract)