How Do Doctors Diagnose Tuberculosis (TB)?
- Updated on: Jul 15, 2024
- 4 min Read
- Published on Oct 3, 2019
Tuberculosis Diagnosis (TB Diagnosis)
The diagnosis of tuberculosis is based on the detection of the presence of M.tuberculosis in the clinical specimen taken from the patient. The healthcare professional may evaluate the medical history of the patient along with physical examination and X-ray.
Tuberculosis Test
No single test is used for the diagnosis in all circumstances. Following are the common methods used for its diagnosis:
- Medical History and physical evaluation
- Chest X-ray
- Serological tests
- Drug susceptibility test
- Microbiological tests
- Blood tests
- Tuberculin skin test
- Nucleic acid amplification test
Medical History and Physical examination
Before confirmation of any respiratory disease, the doctor evaluates the medical history of the affected person. The doctor checks if:
- the person is already diagnosed with tuberculosis (latent) or not
- has some other respiratory syndrome with overlapping symptoms
In addition, constant “mucus” production in the respiratory pipe is also taken into account before diagnosis. Tuberculosis is suspected when a patient shows respiratory illness and pneumonia-like symptoms. It includes analysis of various symptoms like:
- Prolonged cough (more than 3 weeks)
- Chest pain
- Blood in sputum
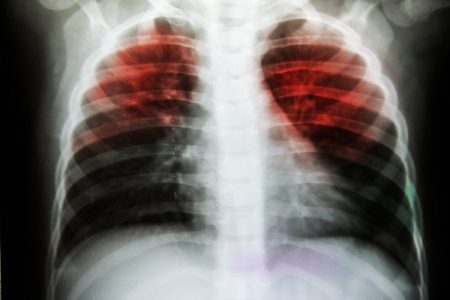
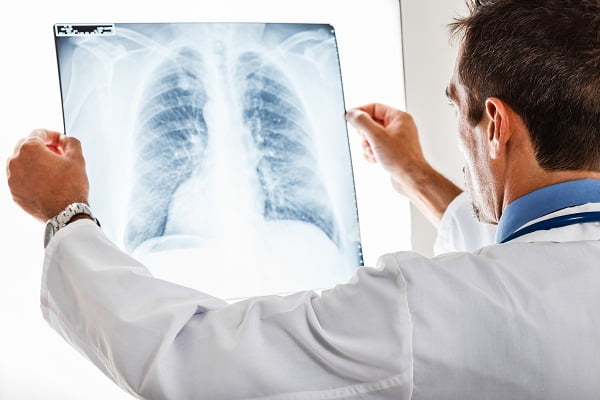
Chest X-rayand CT scan
Chest X-ray and CT scan are other methods to determine whether the person is suffering from tuberculosis or not. These diagnostic methods use X-rays and computer technology to create images of the respiratory system.
The procedure is performed by trained X-ray technician in hospital and clinical center. A solution is given to drink and an injection of contrast dye is given to the patient before CT scan. The contrast dye or contrast medium makes the structures present inside the body clear to see through CT scan.
Doctor asks the patient to lie on the table that slides inside a tunnel-shaped device.
Active tuberculosis (pulmonary) is characterized by the presence of cavities in the upper lobe of lungs. These cavities may or may not have fluid and/or pus in them. When X-ray test or CT scan of the chest is done, tiny nodules or lesions appear. These abnormalities are suggestive of tuberculosis but are not confirmatory.
Serological tests
A serological test or serodiagnostic test for tuberculosis is based on the presence of antibodies in the blood against tuberculosis bacteria. However, detecting antibodies in blood is difficult as some people have antibody response even without tuberculosis infection.
In addition, antibodies may develop against some other infection which may give the false positive test for tuberculosis. These tests are quite complicated and banned in certain countries due to inaccuracy and unreliability of these tests.
Drug Susceptibility test
This test is done to detect whether the patient has drug-resistant tuberculosis or not. This test is helpful in finding out the drug to which tuberculosis bacteria are sensitive.
The test is helpful in diagnosing and treating the patient with appropriate drug. Conventionally, the test was done by culturing bacteria in laboratories and testing the antibiotic against it. Though important, the tests were time taking. A much easier test called GeneXpert Test is commercially available now.
Microbiological tests
A confirmatory diagnosis is done by culturing (growing) microorganism present in the specimen taken from the patient. It generally consists of sputum, pus or biopsied tissue.
Diagnosis by culturing requires both positive and negative controls along with the specimen. The symptom of tuberculosis generally overlaps with other respiratory issues, thus microbial culturing is important for effective diagnosis.
Despite being accurate, culturing test may take more than a week for confirmation.
Blood tests
A blood test is also used for the confirmation of tuberculosis. These are quite sophisticated tests used to measure the response of immune system against tuberculosis bacteria.
The human immune system is known to produce cytokines (response molecules) against the foreign body. These blood tests work on the detection of interferon gamma cytokine. The test is done by taking a blood sample from the patient and mixing it with substances for the identification of the presence of cytokine.
Two most common blood tests used for the tuberculosis diagnosis are:
- QuantiFERON-TB Gold test
- T-Spot TB test
The tests are quick and generally, require only one clinic visit. The only disadvantage of this test is to process the blood sample quickly.
Tuberculin skin test (TST)
Tuberculin skin test is most often used test for the diagnosis of tuberculosis. Tuberculin is a glycerol extract of the tubercle bacillus. The diagnostic procedure is done by trained professionals.
A standard dose of tuberculin solution is injected between the layers of skin (intra-dermally). The injection is called as Mantoux technique and results are seen after 48 hours. The person who is infected with tuberculosis bacteria is expected to mount an immune response in the skin.
The diagnosis is completed by measuring the diameter of hardened area and erythema (redness) due to the immune response.
Nucleic acid amplification tests (NAAT)
These tests are based on amplification of nucleic acids methods done by Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). The tests vary with the type of nucleic acid and accuracy.
Two most common nucleic acid amplification tests are:
- Direct test (MTD, Gen-Probe)
- Amplicor (Roche Diagnostics)
These tests depend on the genetic material of the tuberculosis bacteria. The nucleic acid (genetic material) of bacteria present is isolated after culturing the bodily fluids like sputum and pus. After extraction of nucleic acid, it is amplified and tested for the presence of tuberculosis genome.