How Does Cancer Detection Work?
- Updated on: Nov 17, 2025
- 3 min Read
- Published on Oct 18, 2024

Cancer detection is an important process that helps identify the presence of cancerous cells early enough to improve treatment outcomes. There are several methods used in detecting cancer, each with different levels of sensitivity and accuracy. The goal of cancer detection is to find abnormal cells before they become harmful or spread to other parts of the body. It’s essential for conditions like breast, lung, and prostate cancer, where early diagnosis can significantly increase survival rates.
So in this post, we’ll take a look at how cancer detection works and some of the most common methods used to detect it.

Source: Unsplash (CC0)
Understanding Cancer Detection Methods
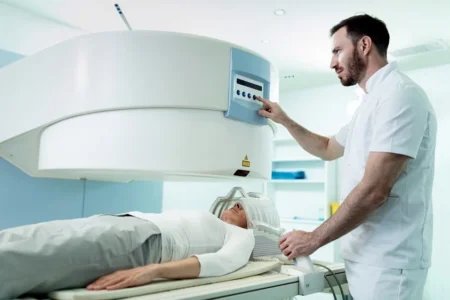
When it comes to detecting cancer, several techniques are commonly used. One of the most well-known methods is imaging, which helps doctors look inside the body for abnormal growths or tumors. These techniques include CT scans, X-rays, and MRIs. CT scans, in particular, are highly effective because they use multiple X-ray images taken from different angles to create a detailed picture of areas inside the body. These images help doctors locate tumors and determine their size.
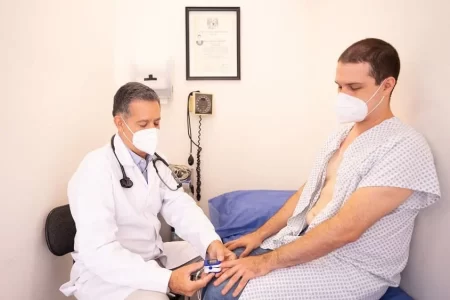
Another common technique is biopsy, where a small sample of tissue is removed from the body and examined under a microscope. This helps doctors see if the cells in the sample are cancerous. Biopsies are essential for many cancers, such as breast or lung cancer, because they provide definitive evidence of the presence of cancer cells.
The Role of Blood Tests
Blood tests also play a major role in cancer detection. These tests look for specific substances that are released by cancer cells into the bloodstream. One example is the PSA test for prostate cancer, which measures the level of prostate-specific antigen in the blood. Elevated levels can indicate the presence of prostate cancer, though further testing is usually required to confirm this.
In some cases, blood tests can detect markers that suggest cancer is present even before symptoms start to show. For example, the CA-125 test is used to screen for ovarian cancer, especially in women at high risk. Blood tests are non-invasive and can provide critical information, but they often need to be combined with other methods for a more accurate diagnosis.
Advances in Technology
Cancer detection technology is always progressing, and one of the newest and most exciting advances is the Quanterix Simoa platform. This platform is revolutionizing cancer detection by making it possible to detect cancer-related biomarkers at much lower levels than traditional methods. The technology is incredibly sensitive, detecting biomarkers at concentrations that are 1000 times lower than what could be seen before.
This means that cancers can be detected much earlier, even before symptoms appear, which significantly improves the chances of successful treatment. Quanterix technology is already being used in medical research to study different types of cancer, and it holds great promise for the future of early cancer detection.
Combining Detection Methods
No single test can detect all cancers. That’s why doctors often use a combination of techniques to make an accurate diagnosis. A person might have imaging done first, followed by a biopsy or blood tests, depending on what the imaging reveals. For example, if a CT scan shows a suspicious mass, a biopsy might be needed to determine if the mass is cancerous.
Early detection remains a powerful tool in the fight against cancer. Combining advanced technology with traditional methods gives patients the best chance at early treatment and recovery.