How Is Coronary Heart Disease Diagnosed?
- Updated on: Jun 26, 2024
- 3 min Read
- Published on Apr 19, 2021
Your doctor will ask questions about your personal medical history, family history, and your risk factors. He will do a physical exam and routine blood tests. He may suggest one or more diagnostic tests as well as appropriate.
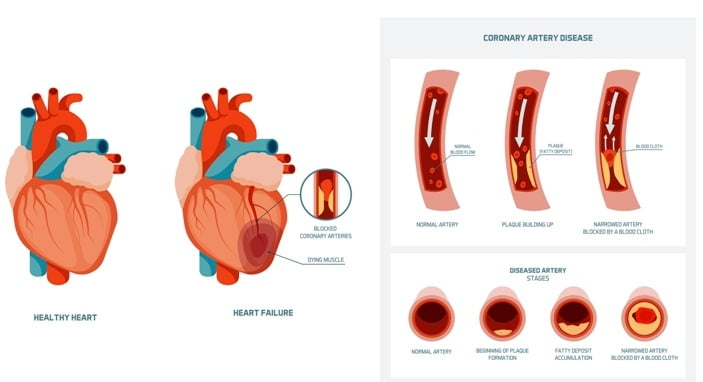
Based on the outcomes of the physical exam and the results from the diagnostic tests, your doctor will diagnose whether you have coronary heart disease (CHD), also known as coronary artery disease (CAD).
Tests for diagnosis of coronary heart disease
There is no single test that can diagnose CHD. If your doctor thinks you may have CHD, he may recommend one or several of the following tests.
EKG (Electrocardiogram)
An EKG is a simple and painless test that can detect your heart’s electrical activity. It can tell your doctor how fast your heart is beating and whether the rhythm is normal or not.
An electrocardiogram also records electrical signals travelled through the heart. It can often detect evidences of a previous heart attack or if one is in progress.
Echocardiography
An echocardiography is a diagnostic procedure which uses sound waves to produce images of your heart. The picture (echocardiogram) shows the size and shape of your heart and tells whether your heart chambers and valves are working normally or not.
Echocardiogram, sometimes called simply echo, can also show areas in your heart that have poor blood flow and any previous damage to the heart muscle due to poor blood flow.
Stress test
If your signs and symptoms of coronary heart disease occur mostly during exercise, your doctor may recommend a stress test. You will be asked to walk on a treadmill or ride a stationary cycle. This is called exercise stress test.
During the test, you are required to do exercise to make your heart work harder and beat faster. If you can’t do an exercise for some reason, you may be given medicine to increase heart rate.
Your doctor can identify several signs and symptoms of CHD through a stress test, such as:
- abnormal changes in your heart rate
- changes in blood pressure
- shortness of breath
- chest pain
- abnormal heart rhythm or your heart’s electrical activity
Sometimes stress tests are done with an echocardiogram. In such cases, your doctor may perform an ultrasound before and after you exercise.
Coronary Angiography and Cardiac Catheterization
Cardiac catheterization is an invasive diagnostic test that provides important information about your heart. It tells important information about the structure and function of the heart.
Your doctor will recommend coronary angiography (or simply angiography) if other tests are positive and indicate that you’re likely to have CHD.
Your doctor may inject a special dye into your coronary arteries to view blood flow through your heart. This is called an angiogram. The dye is injected into the arteries of the heart through a flexible and thin tube called catheter.
X-rays are used to see special X-ray images of your heart during the procedure. The dye shows blockages on the X-ray images. If a blockage is detected that requires treatment, your doctor can perform angioplasty at the same time. An inflatable balloon can be inserted through the catheter and inflated to increase the blood flow through your coronary arteries. A stent can then be placed at the location of blockage to keep the dilated artery open. Read more about treating coronary heart disease.
Cardiac catheterization is usually done in a hospital. You’re awake during the procedure. Your doctor will apply anesthetics before initiating the procedure to cause numbness in the area of cauterization either hand or leg generally).
The procedure causes little or no pain. You may however feel some soreness in the blood vessel where the catheter is injected.
Blood tests
Blood tests check the levels of fats, cholesterol, sugar, proteins, and other components in your blood that have some connection with the risk of developing a heart disease. Abnormal levels of these substances in your blood might be a sign that you’re at risk for CHD. Read more about sign and symptoms of coronary heart disease.
Blood tests are usually done in the beginning along with the physical exam.
Computerized tomography (CT)
CT technologies can help your doctor perform heart scans and identify calcium deposits in your arteries that can narrow down or block the arteries. If calcium deposits are identified, you may likely have a coronary artery disease.