Is Meningitis Contagious?
- Updated on: Jul 11, 2024
- 3 min Read
By
- Published on Oct 3, 2019
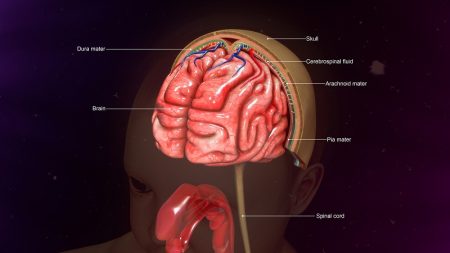
How does meningitis start out?
Meningitis is a relatively rare condition, but it evolves as a life-threatening emergency as symptoms of meningitis can develop rapidly.
Meningitis can affect people of any age, gender, age, background or class. The main group at risk of meningitis is babies and toddlers. Teenagers are two and a half times more likely than adults to develop this deadly condition.
People over 50 years of age are also at risk of this disease because the immune system weakens as people get older.
Read about meningitis in children and toddlers.
Is meningitis contagious?
Meningitis is contagious. Prolonged close contact with an infected person can spread the bacteria that cause meningitis. The bacteria can spread through kissing, coughs and sneezes, shared cutlery or sharing items like toothbrushes, towels, handkerchief or cigarettes.
Outbreaks of the disease most commonly occur where many young people live close to each other. These may include societies, universities, student housing, boarding schools, and military bases.
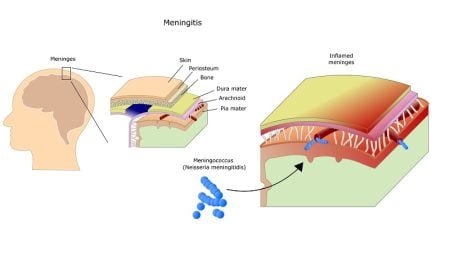
Contagiousness in different types of meningitis: How does it spread from person to person?
The contagiousness of meningitis is related to the specific agents that are responsible for causing the disease.
Given below are the five types of meningitis and how they may or may not be contagious.
Is viral meningitis contagious?
In most of the cases, meningitis caused by viruses is usually contagious. However, there are certain viruses that usually do not spread person to person. Such viruses include those transmitted by mosquitoes and are noncontagious.
Is bacterial meningitis contagious?
Bacterial meningitis is contagious including some bacteria which are more contagious. Examples include Neisseria meningitidis in young adults and Streptococcus pneumoniae in all ages.
Is fungal meningitis contagious?
Fungal meningitis is considered noncontagious meningitis. An example includes Cryptococcus meningitis.
Is parasitic meningitis contagious?
Parasitic meningitis is a type of meningitis which is rare. An example includes Naegleria fowleri, and it is not considered to be contagious and does not spread from person to person.
Non-infectious meningitis
Non-infectious meningitis results from an underlying condition or disease rather than an infection. It is not considered contagious.
Causes of non-infectious meningitis may include cancers in and around the brain or spinal cord, drugs, head injury, and autoimmune diseases.
Prevention: How can a meningitis infection be avoided?
The risk of getting or spreading virus and bacteria can be reduced in following ways:
- Wash your hands frequently with warm water and soap. Wash for at least 20 seconds, taking care to clean hands properly particularly under fingernails. Rinse and dry them thoroughly after washing.
- Always wash your hands before eating, after using the toilet, after playing outdoors or after attending to someone who is ill or has meningitis.
- Don’t ever share eating utensils, straws, spoons, tumblers, or plates etc.
- Cover your nose and mouth when you cough or sneeze.
- Stay up to date on immunizations (vaccines) and booster shots for meningitis.
Read about meningitis vaccine and their side effects and risks.
- People planning trip to parts of the world (which include places where meningitis is very common) should seek medical advice about getting a travel jab for meningitis.
- Crowded places like cinema halls, market and malls and religious gatherings such as the Hajj or Kumbh Mela should be avoided. Such places put people at an increased risk of the disease.
- In addition to vaccinations, some common sense precautions should be followed to help prevent meningitis.
- Be careful around people infected with the disease. Meningitis spread through contact with bodily fluids. So the chances of spread by kissing, sneezing, coughing, or sharing utensils or toothbrushes are high. If somebody in the family has it, his contact with other family members should be limited.
- Seek medical advice in case of close contact with someone with meningitis.