Kidney Cancer (Renal Cancer): Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment
- Updated on: Jul 8, 2024
- 9 min Read
- Published on Oct 3, 2019
What is kidney cancer?
Kidneys are the two bean shaped organs that are used to filter the blood and remove all the impurities from it in the form of urine.
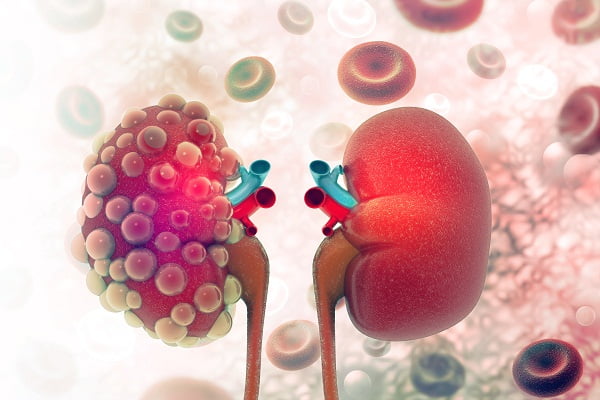
Kidney cancer is also known as renal cancer. Kidney cancer is a condition in which kidney cells become cancerous (malignant) and grows out of control, thus forming a tumor. Kidney cancer is first observed in the lining of tiny tubes called tubules present in the kidney. The good news is that most of the kidney cancers are generally detected before they metastasize to distant organs.
The cases of kidney cancer have increased tremendously in the recent years. In adults, the most common type of kidney cancer is renal cell carcinoma. In young children, the most common type of kidney cancer is known as Wilms’ tumor.
What are the different types of kidney cancer?
There are various types of kidney cancers:
Renal cell carcinoma
Renal cell carcinoma or RCC is also known as renal cell cancer or renal cell adenocarcinoma. RCC generally grows in the form of a single tumor but sometimes, there can be more number of tumors. RCC can be of many subtypes on the basis of its physiology under the microscope.
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Clear renal cell carcinoma is the most common type of RCC. According to various reports, 7 out of 10 people suffer from this kind of cancer.
Papillary renal cell carcinoma
Papillary renal cell carcinoma is the second most common type of RCC. In this type of cancer, certain finger like projections, called papillae, are formed. Doctors, sometimes, call this type of cancer as chromophilic as they appear pink due to a dye under a microscope.
Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma
This type of cancer is very uncommon in people. This cancer has pale cells that are easily observed under a microscope.
There are other rare types of RCC such as:
- Collecting duct RCC
- Medullary carcinoma
- Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma
- Neuroblastoma-associated RCC
Other types of kidney cancers
Some other types of kidney cancers are as follows:
Transitional cell carcinoma
Transitional cell carcinoma is also known as urothelial carcinomas. This type of cancer starts in the lining of renal pelvis and not in the kidneys. People with this cancer often notice blood in their urine and back pain.
Wilms tumor (nephroblastoma)
This type of cancer generally occurs in children and is very rare among adults.
What causes kidney cancer?
The exact cause of renal cancer is still unknown though several risk factors trigger the occurrence of kidney cancer. The most common cause of kidney cancer is any mutation at the gene level. There are various types of mutations that are associated with kidney cancer.
Mutation (changes in genes)
Certain changes in genes result in the occurrence of cancer in any part of the body. These changes occur due to mutation either due to use of some chemicals or due to environmental changes.
The genes which are responsible for the growth and division of cells are known as oncogenes and the genes which controls the life cycle of the cells is known as tumor suppressor genes. Due to mutation, the oncogenes become activated whereas the tumor suppressor genes are deactivated. This results in cancer.
There are generally two types of mutation that causes kidney cancer. They are as follows:
Inherited gene mutations
There are certain types of mutations or changes in the DNA which runs in families i.e. it is passed from one generation to another. There are high chances of a person to suffer from the condition if it is present in one’s family.
For example, VHL is a tumor suppressor gene that is responsible for causing a disease called as von Hippel-Lindau (VHL). It normally controls the growth of the cell. These mutations (changes) in this gene can be inherited from parents. When the VHL gene is mutated, it becomes unable to control the abnormal growth, which can result in the occurrence of kidney cancer.
Acquired gene mutations
Acquired gene mutations are those mutations which are acquired by the person in a certain period of time due to certain environmental triggers. Such mutations are not passed among generations. There are various environmental factors responsible for causing mutations in the genes such as the use of chemicals which causes cancers, use of tobacco, cigarette, etc.
What are the risk factors for kidney cancer?
Scientists have found several risk factors that can lead to the development of kidney cancer. Some of these factors are:
Smoking
Smoking increases the chances of developing renal cell carcinoma (RCC) in a person.
Obesity
People who are overweight and come in the range of obesity are at an increased risk of developing RCC. In obesity, the body secretes certain hormones which can increase the risk of having kidney cancer.
High blood pressure (Hypertension)
People with high blood pressure are more prone to kidney cancer. According to some reports, certain medicines used to treat high blood pressure contain chemical compounds which can increase the risk of kidney cancer.
Family history of kidney cancer
People with a family history of renal cell cancer are more prone to suffer from kidney cancer. The chances of having a kidney cancer become very high when the family member suffering from cancer is a sibling.
Medicines
There are certain medicines which can result in the occurrence of kidney cancer. Some of such medicines are as follows:
Phenacetin
This drug was once a popular non-prescription pain killer and was responsible for causing RCC. It has been banned now and is no longer prescribed by healthcare professionals.
Diuretics
According to some reports, diuretics (water pills) may lead to a small increase in the risk of RCC.
Gender
Kidney cancer is more likely to occur in males than in females. This may be because of the fact that, males are in a habit of smoking more than females.
Genetic diseases
There are certain genetic and hereditary diseases which result in the occurrence of kidney cancer. Some of these diseases are as follows:
von Hippel-Lindau disease
In this condition, many kinds of tumors and cysts are formed in different parts of a patient’s body. Such patients are at an increased risk of developing kidney cancer at a very young age. The tumors can form in organs like brain, eyes, spinal cord, pancreas, etc.
Hereditary papillary renal cell carcinoma
In this condition, a person develops many papillary RCCs. This is an inherited condition.
Familial renal cancer
In familial renal cancer, people develop tumors known as paragangliomas (head and neck) and pheochromocytomas (adrenal glands and thyroid cancer). People suffering from this cancer are also prone to kidney cancer.
What are the symptoms of kidney cancer?
In many cases of kidney cancer, patients do not show early signs of kidney cancer but as the condition progresses, many severe symptoms are visible. Some of the most common symptoms of kidney cancer are as follows:
- Blood in urine
- Loss of appetite
- A lump in the side or in abdomen
- Sudden weight loss
- Constant pain in side
- Continuous fever
- Anemia
- Swelling in the ankles or legs
There are some uncommon symptoms that a patient may experience when his or her cancer spreads to other parts of the body. Some such symptoms are as follows:
- Shortness of breath
- Bone pain
- Coughing up blood
How is kidney cancer diagnosed?
A patient should immediately contact a healthcare specialist as soon as he or she notices the symptoms of kidney cancer. Any delay in the diagnosis and treatment can lead to life time consequences.
To confirm the presence of kidney cancer, the doctors conducts physical exams, collects health history, and performs tests. The doctor will check for high blood pressure and fever, presence of lumps.
Diagnostic tests and methods for diagnosing kidney cancer
There are various diagnostic tests which are used to know the presence and status of kidney cancer. Some of the important ones are listed here.
Blood test
Blood tests are done to examine the signs of kidney cancer but are not the sure shot method for diagnosing cancer. These tests are also helpful in observing the overall health of a person. There are some tests which are covered under blood tests.
Urinalysis (urine testing)
Urinalysis (urine testing) is a test that is performed to detect any kidney problem in a patient. In this test, the urine is treated with some chemicals and observed under a microscope for the presence of blood or any other substance which is otherwise not visible through naked eyes. The most common symptom of kidney cancer is the presence of blood in patient’s urine.
Complete blood count (CBC)
Complete blood count (CBC) is used to measure the amount of different cells in blood. In a patient with kidney cancer, the results of this test are abnormal.
Blood chemistry test
Cancer can severely affect the level of certain chemical compounds in the blood. For example, high level of liver enzymes, calcium is observed in a kidney cancer patient. Therefore, the blood chemistry test is done in order to analyze the level of chemicals present in such cases.
Imaging tests for kidney cancer
Imaging tests play a major role in correctly diagnosing the body parts. In case of cancer, such tests have proved to be very important in telling the exact status of the condition such as to see the area which has signs of cancer, how is the treatment working for the cancer, etc.
There are many imaging techniques used to diagnose cancer. For example:-
Computed tomography (CT) scan
In CT scan, x-rays are used to produce cross-sectional images of the body. This test is very useful to study the physiology of the tumor such as finding out the shape, size, and location of the tumor in the body.
The test also checks whether the cancer is localized or has spread to the nearby areas. In a CT scan, a contrast dye is used for better viewing of certain organs. This test may be followed by a tissue biopsy as needed.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan
MRI scan is used less frequently as compared to the CT scan in kidney cancer patients. MRI is generally done when performing a C scan is difficult.
MRI is generally used to look at abnormal areas in brain and spinal cord due to cancer, blood vessels where the cancer has spread, etc.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is a technique that can be used to find kidney tumors. Different echo patterns also can help the doctors tell exact place of the tumor in kidneys.
Positron emission tomography (PET) scan
In PET scan, a form of radioactive sugar is put into the blood. Body cells, depending upon their growth rate, take in different amounts of the sugar. Cancer cells grow quickly and take up larger amounts of the sugar than normal cells. A special camera is then used to create a picture of areas of radioactivity in the body. The picture provides helpful information about the area having the cancer.
Angiography
Angiography is a type of x-ray test which is used for looking at blood vessels. In this test, a dye is injected in the renal artery and x-rays are taken to map those blood vessels that supply blood to the kidney tumor.
This test helps in planning surgery in some severe cases of kidney cancer. Angiography can also be used to diagnose renal cancers.
Kidney biopsy
In case of kidney cancer, a biopsy is done in order to know the grade of cancer, mainly Fuhrman grade. The doctors are then able to determine how fast the cancer will grow and expand. Kidney biopsy is also done to determine the stage of kidney cancer.
What are the stages of kidney cancer?
As soon as the doctor identifies the kidney tumor, the next step is to know the extent of the cancer. This is known as stage of kidney cancer. Stage of kidney cancer is defined as the extent to which the kidney cancer has spread.
There are various staging tests for kidney cancer such as CT scan, etc.
The stages of kidney cancer involve:
- Stage I. At this stage, the tumor can grow up to 2 3/4 inches (7 centimeters) in diameter. The tumor is confined to the kidney and does not spread to other parts of the body.
- Stage II. A stage II kidney cancer is large as compared to stage I tumor. The size of the tumor starts increasing but it’s still confined to the kidney.
- Stage III. At this stage, the tumor starts spreading the surrounding tissue and may also spread to nearby lymph nodes.
- Stage IV. In this stage, cancer spreads outside the kidney, to distant parts of the body, such as the bones, lymph nodes, liver or lungs.
How is kidney cancer treated?
As soon as the kidney cancer is diagnosed and the stage of the cancer is determined, the doctor opts for the suitable treatment. There are various types of treatment options available for treating kidney options.
Surgery
Surgery is the main treatment option for kidney cancer. Its main objective is to remove the tumor and preserve normal kidney function. Surgical procedures used for the treatment of kidney cancer include:
Nephrectomy
Nephrectomy is the surgical procedure for removing kidneys. Based on the severity of the case, the doctor may also remove some lymph nodes, adrenal gland or other organs. In this technique, the surgeon either makes a single incision in the abdomen (known as open nephrectomy) or many small cuts (known as robotic-assisted laparoscopic nephrectomy).
Partial nephrectomy
Partial nephrectomy is also called as nephron-sparing or kidney-sparing surgery. In this technique, the surgeon removes the tumor along with a small part of healthy tissue surrounding the tumor rather than the entire kidney. It can be done either as an open procedure, or with robotic assistance. Kidney-sparing surgery is a commonly performed procedure for small kidney cancers.
Non surgical treatment for kidney cancer
In some kidney cancers, where surgery is not required, alternate options are used for the treatment of kidney cancer. Some of them are as follows:
Cryoablation
Cryoablation is a technique in which the cancer cells are frozen and prevented from growing further. In this technique, a hollow needle is inserted into the kidney tumor through the skin with the help of ultrasound or other imaging techniques.
A cold gas present in the needle is then used to cool down and freeze the cancer cells.
Radiofrequency ablation
In this technique, a special probe is inserted into the kidney cancer with the help of any imaging technique. An electrical current is then passed through the needle into the cancer cells, thus causing the cancer cells to heat up and burn.
Arterial embolization
In arterial embolization, some material is inserted into an artery that leads to the kidney tumor. This blocks blood flow to the tumor and shrinks the tumor before surgery.
Alternative therapy
Apart from the above therapies, there are many other types of therapies used to treat kidney cancer. Some of them are:
Biologic therapy for kidney cancer
This therapy uses the immune system of the patient’s body to fight cancer by activating, directing, or restoring body’s natural defenses. Substances for biologic therapy are made by the body or in a laboratory.
Examples of biologic therapy for kidney cancer are interferon alpha or interleukin-2.
Targeted therapy for kidney cancer
In this therapy, certain drugs or other substances are used to find and target cancer cells in such a way that it causes less toxicity to normal cells. One such therapy is anti-angiogenic agents. These agents shrink the blood vessels and prevent it from feeding a tumor.
Chemotherapy for kidney cancer
This therapy uses certain types of drugs which are used to kill cancer cells or stop them from multiplying. This procedure is less effective for kidney cancer as compared to other types of cancer.