Learn About Dialysis Side Effects and Risks Before Going For It
- Updated on: Jun 28, 2024
- 3 min Read
- Published on Apr 19, 2021
Dialysis
People who require dialysis often have a variety of health problems. Dialysis can prolong the life for many people, but life expectancy is still lesser than the general population.
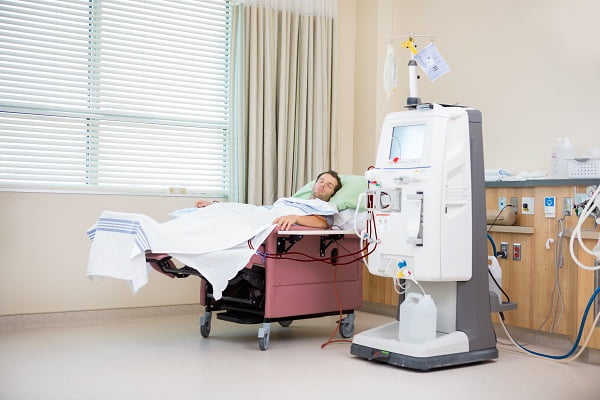
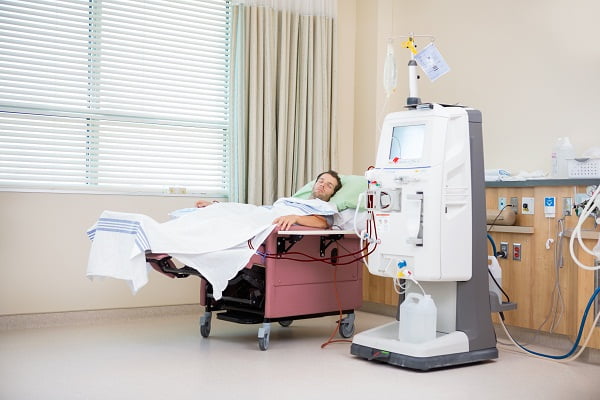
Dialysis is a treatment that is generally given in case of chronic kidney disease and kidney failure and helps to purify the blood with the help of an artificial system. This helps the function of the kidneys to be restored artificially.
There are two ways to do dialysis – haemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis.
Complications of dialysis: What are the risks and side effects of dialysis?
Both haemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis can cause side effects and are associated with risks. This is because of two reasons:
- the way the procedure of dialysis is carried causes some side effects
- dialysis can only partially compensate for the loss of kidney function.
A few complications of dialysis are listed below:
Fatigue
You feel tired and exhausted if you use dialysis on a long-term basis. Fatigue may be caused because of these reasons:
- loss of normal kidney function
- dietary restrictions associated with dialysis
- stress and anxiety that occurs with kidney failure experience
Low blood pressure
Low blood pressure (hypotension) is one of the most common side effects of dialysis. It is caused because of the drop in fluid levels during the procedure. Low blood pressure can also cause nausea, vomiting, and dizziness.
This is more common in people who have diabetes. Low blood pressure may be accompanied with shortness of breath, abdominal cramps, muscle cramps, and nausea.
Sepsis
Bacteria may enter into the body during dialysis. People who receive dialysis are at an increased risk of developing sepsis (blood poisoning). Bacteria can enter the body and spread through the blood which can lead to failure of multiple organs.
Muscle cramps
Some people may experience muscle cramps. This is more common in lower legs. This is caused because the muscles react to the fluid loss that occurs during the procedure.
The cramps can be eased by adjusting the hemodialysis fluid. Sodium intake between hemodialysis treatments may help prevent certain side effects.
Itching
Many people who undergo hemodialysis and may experience the problem of itchy skin, which is worse during or just after the procedure.
Anemia
Anemia can occur due to the body not having enough red blood cells in the blood. It is a common complication of dialysis.
Problems with sleep (insomnia)
People who receive dialysis often have trouble at sleep (insomnia). This is because of breaks in breathing during sleep (sleep apnea) or because of pain, discomfort or restless leg syndrome.
Bone diseases
If the kidneys are not able to process vitamin D, which helps in absorption of calcium, your bones may weaken.
A common risk associated with kidney failure is parathyroid hormone overproduction. This can cause the release of calcium from your bones. All this may lead to bone disease.
High blood pressure (hypertension)
Another common complication of dialysis is hypertension. Intake of too much salt or drinking too much fluid can cause high blood pressure. This can in turn cause problems with heart or brain such as heart attack, stroke etc.
Other risks associated with dialysis
- fluid overload
- high potassium levels (hyperkalemia)
- amyloidosis
- depression
- pericarditis: inflammation of the membrane surrounding your heart
- loss of libido (sex drive)
- dry mouth
- joint pains
- erectile dysfunction
- continuous feeling of being sick
- experiencing chills
- a high temperature – fever
- risk of developing hernia because the fluid remains inside the peritoneal cavity for a long time typically many hours and puts a strain on the abdomen muscles
- weight gain
- feeling too full
- bloating
- blood clots formation during access
- infections
- psychological distress
FAQs
What are the common side effects of dialysis?
Side effects may include low blood pressure, muscle cramps, nausea, and fatigue. It's crucial to discuss potential side effects with your healthcare team.
Can dialysis be done at home?
Yes, home dialysis is an option for some patients. However, it requires proper training and a suitable home environment.
Are there long-term risks associated with dialysis?
Prolonged dialysis may pose risks such as infection, vascular access complications, and changes in bone and mineral metabolism.
Can dialysis cure kidney disease?
Dialysis is a treatment, not a cure. It helps manage symptoms and maintains the body's balance while awaiting a kidney transplant or as a long-term solution.
How often is dialysis typically required?
The frequency of dialysis depends on individual needs and the type of dialysis. It can be scheduled several times a week for effective treatment.