Living Without a Gallbladder: What is a No Gallbladder Diet?
- Updated on: Nov 27, 2020
- 5 min Read
- Published on Nov 27, 2020

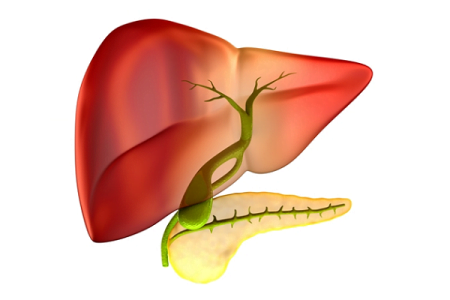
The gallbladder is a small sac-like digestive organ present in the abdominal region, behind the liver. It connects the liver through a common bile duct. The common bile ducts transport bile from the liver through hepatic ducts to the gallbladder and duodenum (first part of the small intestine).
The gallbladder is a major organ that stores bile in the body. Bile juice helps in the breakdown of food particles and digests fat in the body. Bile produced in the liver gets stored in the gallbladder and then released into the small intestine when food is digested.
Bile juice helps in the breakdown of fats present in the food within the small intestine food.
Removal of Gallbladder
The process of removal of the gallbladder is known as a cholecystectomy. The gallbladder is removed due to several reasons, which are as follows:
- Infection in the gallbladder
- Inflammation of the gallbladder, known as cholecystitis
- Gallstones
- Gallbladder polyp
When the gallbladder is removed, bile juice is not stored in the body and is directly released into the small intestine. This does not lead to any major difficulty in the digestion of food. But, large amounts of fat, greasy or high fiber foods become difficult to digest. This results in gas, bloating, and diarrhea.
Read About Can you Get Gallstones without a Gallbladder?
Life Without a Gallbladder
You can live a perfectly normal life without a gallbladder. When the gall bladder is removed, the bile juice produced in the liver is not stored in the body and directly released into the small intestine. People may be advised to take a special diet before removing the gallbladder, but there is no such need after surgery. You can easily survive on a healthy balanced diet.
Some people may experience certain digestive issues such as gas, bloating, diarrhea, and abdominal pain after the surgery, which will remain for a few weeks. These symptoms occur due to change in the way of transport of bile juice to the small intestines and difficulty in digesting fatty food.
If you experience digestive issues for a longer time, you may change to a no gallbladder diet. This specialized diet helps identify specific triggers that cause digestive problems.
What Are the Side Effects Due to Absence of Gallbladder?
You may experience certain side effects due to the removal of the gallbladder. These include:
Stomach and Shoulder Pain
Stomach and shoulder pain occurs due to excessive acid formation, resulting in acidity. In most cases, the pain is not severe. But if it becomes unbearable, then certain over-the-counter painkillers can be consumed.
Digestive Issues
You may experience bloating and flatulence (accumulation of gas in the alimentary canal). Relief from these digestive issues can be provided by making certain dietary changes and starting a no gallbladder diet. In some cases, the doctor may prescribe certain medications to reduce the symptoms.
Diarrhea
Diarrhea occurs in about 10% of patients after the removal of the gallbladder. This occurs due to a change in the way bile juice is transported to the small intestine. This change in transport speeds up the passage of food through the intestines and leads to diarrhea.
Fatigue, Mood Swings, and Irritability
These feelings will improve as you recover from surgery, and your symptoms will improve. If you experience severe symptoms, then you should immediately consult a doctor. These symptoms include:
- Persistent abdominal pain, if it worsens
- Severe nausea or vomiting
- Jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes)
- If no stool is passed for more than three days after surgery
- Frequent diarrhea that lasts more than three days after surgery
- If gas is not passed even after three days from surgery
What is a No Gallbladder Diet?
Without a gallbladder, the digestion of fatty and high-fiber foods becomes difficult, and you may experience certain digestive troubles. With the help of some basic dietary changes, these dietary issues can be easily resolved. The no gallbladder diet helps the body adjust the way it releases bile juice into the small intestine. It consists of the following changes:
Limit Your Fat Intake
You should avoid food products which contain more than 3 grams of fat in a single serving. You should check the labels of processed meats, dairy products, sauces, and topping before buying, as they may contain a large amount of fat. After the removal of the gallbladder, fat should only make up about 30% of your diet.
Food items that should be avoided after the removal of the gallbladder include:
- Sausages
- Beef
- Fried foods
- Chips
- Chocolate
- Full-fat milk, yogurt, or cheese
- Cream
- Skin-on poultry
- Foods containing a large amount of vegetable, canola, peasant and olive oil
Read About What Happens When You Have Your Gallbladder Removed?
Eat Regular, Small Portions Throughout the Day
A person without a gallbladder should not eat food over the course of three large meals. Consumption of food over three large meals affects food digestion as the liver produces a small amount of bile in one go. This bile juice produced is not sufficient for the digestion of a large amount of fat present in food.
Rather than eating a 3-course meal throughout the day, you should have six meals, which contain about 300-400 calories at a time. You can include lean meat such as fish or skinless chicken, or other non-processed protein sources in your diet. You can also have a diet rich in fruits and vegetables.
Limit Your Fiber Intake
People without a gallbladder should not consume a high fiber diet. It leads to severe bloating, abdominal pain, and diarrhea.
You should avoid the following high-fiber foods products, such as:
- Broccoli
- Cauliflower
- Cabbage
- Beans
- Nuts, such as peanuts and almonds
- High-fiber bread, such as whole-grain or whole-wheat
- High-fiber cereals, such as bran
The consumption of these food items should be reduced after removal of the gallbladder. Gradually they can be consumed, depending upon how your body reacts to them.
Limit Your Caffeine
Caffeine present in tea, coffee, or soft drinks can aggravate gallbladder removal symptoms such as gas, bloating, and abdominal pain.
Caffeine increases acid production in the stomach, which makes it empty the food faster than usual. An insufficient amount of bile is released into the small intestine, which leads to incomplete digestion of fats. This incomplete digestion can lead to digestive issues.
You should limit the consumption of caffeinated products after surgery and gradually consume them to monitor its effect on the body.
What Lifestyle Changes Are Required After Gallbladder Removal?
You can record your diet in a journal or a mobile app. The recordings help modify your day-to-day eating and drinking habits and identify the cause of the occurrence of digestive problems due to the consumption of certain food items.
The way your body reacts after consuming specific food items such as those containing large amounts of fats, species, and acids should also be recorded. Record every food item consumed along with its amount per serving.
This close monitoring of your diet will help you identify the pattern of your symptoms. It will guide about which food items can be avoided, limited, and increased in your diet.
These simple lifestyle changes will help you recover faster after the surgery and reduce digestive difficulties and symptoms due to removing the gallbladder. They help in living a healthy and comfortable life ahead.
Can You Live Without a Gallbladder? Is Your Life Expectancy Affected Without a Gall Bladder?
The presence or absence of a gallbladder does not affect the life expectancy of a person. After removing the gallbladder, you can make certain dietary changes that will increase your life expectancy. These dietary changes include minimum consumption of fats, oils, dairy products, and processed foods, which result in loss of weight in an individual.
Consuming fewer calories per day can help you live longer, as it helps your body digests food more efficiently and uses limited energy. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the chances of developing high blood pressure, heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers.