Lumps Behind the Ears
- Updated on: Jan 21, 2025
- 6 min Read
- Published on Feb 17, 2021
What Does a Lump Behind Ear Look Like?
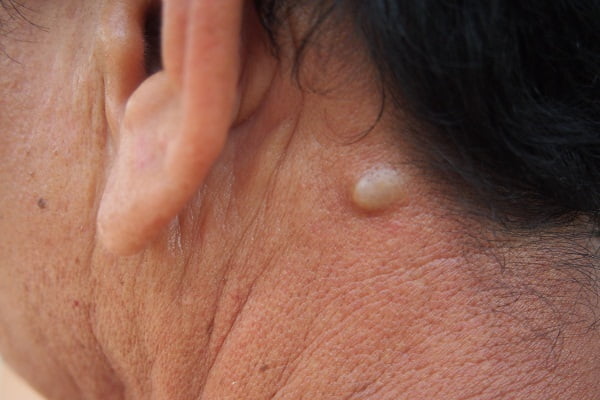
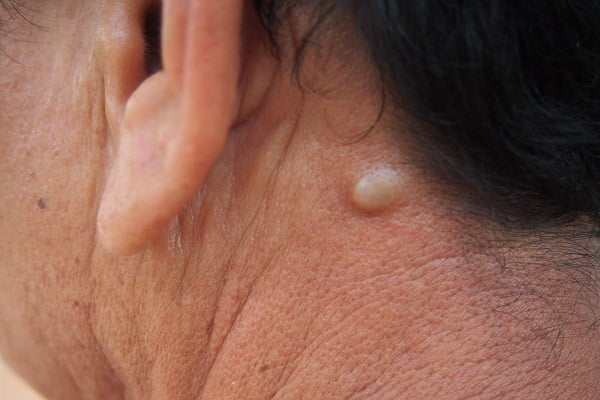
A lump behind an ear is usually an indication of a localized area of swelling of certain glands called retro auricular lymph nodes or posterior auricular glands which are a small group of lymph nodes, usually two in number, located just beneath the ear. Swelling in these lymph nodes can result in the formation of one or multiple lumps that can occur not just behind your ear but other part of your ear as well such as your earlobe or your ear canal. Sometimes a lump behind ear is also described by other names such as a bump, cyst, nodule and a tumour.
Usually, lumps behind ear have a tendency to swing both ways. They can either be very painful or completely painless. They can appear in all sizes either big or small. They can be both soft and firm on touch.
These lumps behind the ear maintain their size all throughout. In some cases they can grow larger as well either very rapidly or very slowly. However, the lumps behind the ear rarely grow larger than the size of a pea. They either appear as single lump or multiple lumps growing in the form of a cluster.
Most cases of lumps behind the ear do not present a cause of concern and resolve without any treatment however in some cases you may need to visit your doctor especially if the lumps are persistent and painful.
???? Stay informed and consult your doctor when in doubt.
What are the causes of a lump behind the ears?
Lumps behind ears are usually harmless and a common occurrence. They are not an indication of something serious in most cases. Several skin conditions can be associated as cause of a lump behind the ears which includes:
- Infection
- Mastoiditis
- Abscess
- Otitis media
- Lymphadenopathy (secondary to ear or throat infections)
- Sebaceous cysts
- Acne vulgaris
- Lipoma
Infection
A lump behind the ears may be a result of a bacterial and viral infection which cause swelling in and around your neck and face. Examples of such infections are strep throat and infection with Epstein-Barr virus. Other conditions such as AIDS, measles, and chickenpox can also cause swelling in and around your neck and face leading to appearance of a lump behind your ear.
Mastoiditis
An untreated infection of your ear may develop into a more serious ear infection known as mastoiditis. In case of mastoiditis a bony protrusion called as mastoid develops behind your ear. It may cause pus-filled cysts to develop which appears to you as a lump or knot behind your ear.
Abscess
When a tissue or cells in an area of the body become infected it presents itself in the form of an abscess. As a result of defence mechanism your body tries to kill off the invading bacteria or virus. During this process your body sends white blood cells to the infected areas to fight the infection causing bacteria or virus. As more and more of white blood cells begin accumulating in the infected area, it results in pus formation there. This pus filled area may appear to you as a lump behind your ears. Abscesses are often warm to touch and painful.
Otitis media
Otis media is another term for an ear infection either by a bacteria or virus. It causes painful swelling and fluid build up at the infection site. These infections may result in visible swelling or lump behind your ear.
Lymphadenopathy (secondary to ear or throat infections)
Lymphadenopathy is the disease of your lymph nodes where they become abnormal in size, number, or consistency. Lymph nodes are very small, organ-like structures that are present throughout your body such as under your arms, in your neck, in your pelvis, and behind your ears. Many times these lymph nodes swell in a natural response to an infection. As the number of cells fighting the infection increases they begin to build up in the lymph nodes. Conditions such as inflammation and cancer can also cause your lymph nodes to swell which may appear as lump behind the ears.
Sebaceous cysts
Sebaceous cysts can occur anywhere in the skin around sebaceous glands including behind your ears as noncancerous bumps beneath the skin. The most frequent places where they develop include the head, neck, and torso. Sebaceous glands are responsible for producing oil that lubricates your skin and hair. Although they may be uncomfortable and irritating but most sebaceous cysts cause little to no pain.
Acne vulgaris
When hair follicles in the skin become clogged they lead to a common skin condition known as acne. The follicles may get clogged by dead skin cells and oil which appear as pimples and bumps. In some cases, these bumps may grow to be large, solid, and painful.
Lipoma
A lipoma can develop anywhere on your body. It is a harmless, fatty lump that develops between the layers of your skin. Lipomas are usually not get detected from the skin’s surface, but you will be able to feel them with your hand as they grow larger.
Usually the lumps or bumps behind the ears caused by sebaceous cysts, lipoma, benign tumours and malignant cancers are found to be painless while the lumps behind the ears that are caused by abscess, dermatitis, mastoiditis, acne and Otitis media are quite painful.
According to Dana Farber Cancer Institute [1], some other infections that can commonly cause lymph nodes behind the ear or elsewhere to swell may include such as:
- Impacted teeth: when your tooth remains stuck in gum tissue or jawbone
- Gum disease or infections: such as gingivitis, periodontitis
- Oral herpes or other sexually transmitted infection
- Tonsillitis
- Influenza
- Lyme disease: lyme disease is caused from a tick-borne virus
- Mononucleosis: it is a highly transmissible virus that is commonly known as mono

???? Infections
???? Abscesses
???? Lymphadenopathy
???? Sebaceous Cysts
???????? Lipomas
Can lump behind an ear be cancer?
Yes, while it’s rare, certain cancers can manifest as a lump behind the ear, such as parotid or salivary gland cancers. However, not every lump behind the ear is indicative of cancer. Several factors can help pinpoint the cause of the lump, but it’s crucial to consult a physician. They will be able to definitively determine if the lump behind the ear warrants concern or if it’s due to another benign cause.
Tumor
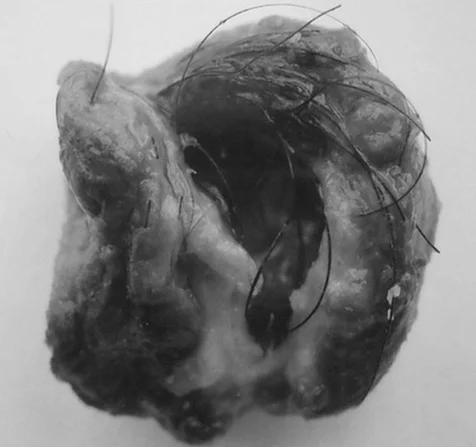
The lump behind your year could be a tumor. A research report published in [Journal Name] highlighted a case study of a patient who was a 22-year-old male presenting a lump that had grown gradually under the skin of the right mastoid for 2 years [2]. The patient did not had any hearing loss or vertigo. There was no pain and no inflammation in the lump of the patient. The patient was healthy overall except that he had the lump. The patient was treated with antibiotics, which were ineffective.
A surgical biopsy was then performed using local anesthesia on the patient. When the skin flap was lifted, a pink, capsule-like lump was found. The lump extended from the layer beneath the skin to the mastoid bone without causing any damage to the bone itself. The surface of the lump had a grainy texture, and strands of hair were visible inside when it was cut open. It was a tumor that measured about 1.3 cm in diameter (see Fig. below). It is important for someone to meet a doctor when a lump is noticed. In most cases the tumors can be benign but they may be cancerous as well and an early diagnosis and treatment can be quite effective.
How you can diagnose a lump behind an ear on your own?
There are some kinds of lumps behind the ears that require medical attention, while some are harmless and resolve without any treatment. However, it is always recommended to visit a doctor when you notice a lump behind the ear. You can detect these lumps by using your hands. Below are some tips to decide what such a lump could be.
- If the lump feels soft and pliable, most probably it may be a lipoma.
- If the lump is painful and tender on touching then it could be a pimple or an abscess.
- If you feel the lump to be inflamed and it feels warm and painful, it could be caused by an abscess.
• Soft and pliable: It could be a lipoma.
• Painful and tender: Could be a pimple or abscess.
• Warm and inflamed: Watch for signs of infection.
When to visit a doctor?
Generally lumps or bumps behind the ears are quite harmless and resolve on their own. However you should seek medical attention if:
- Your lump is persistent for beyond two weeks, even though it is painless.
- The lump is too painful and causing you discomfort.
- You are unable to move your head or your neck.
- You find difficulty in swallowing.
- You feel the area of lump is spreading or growing.
- The swelling behind the ears gets inflamed, begins to leak out pus, or ruptures on its own.
- The symptoms accompanying the lump do not lessen over time or are getting worse.
Can an ear lump be cancer?
Some lumps behind the ear may be cancers such as of parotid or salivary glands. However, tumors behind the ear are not quite common.
Tumors (benign or malignant) are evaluated by an ear, nose, and throat doctor (ENT surgeon). If the lump is malignant / cancerous, you will need to meet an oncologist.
Trusted sources:
- Harnisch-Weidauer, Lukas. “Lump Behind the Ear: Possible Causes.” Dana-Farber Cancer Institute | Insight (blog), February 13, 2023.
https://blog.dana-farber.org/insight/2023/02/lump-behind-the-ear-when-to-be-concerned/ - Daqing Zhao, Yu Han, Yang Chen, and Jianhua Qiu, “An Unusual Dermoid Cyst in Subcutaneous Tissue of the Mastoid Region: A Case Report,” Spandidos Publications, April 26, 2013.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3735589/