Outbreak of Nipah Virus
- Updated on: Jun 26, 2024
- 5 min Read
- Published on Apr 23, 2021
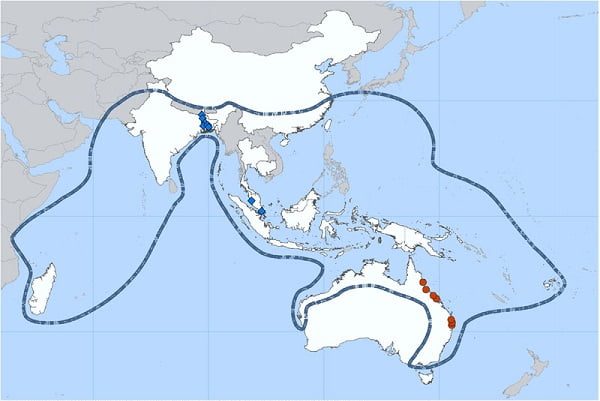
Countries with reported outbreak of at risk based on serological evidence or molecular detection in Pteropus bats are Australia, Bangladesh, Cambodia, China, India, Indonesia, Madagascar, PNG Taiwan, and Thailand.
Home range of Pteropus bats: Bhutan, Brunei, China, India, Indonesia, Laos, Madagascar, Myanmar, Nepal, Philippines, PNG, Singapore, Taiwan, Thailand, Vietnam
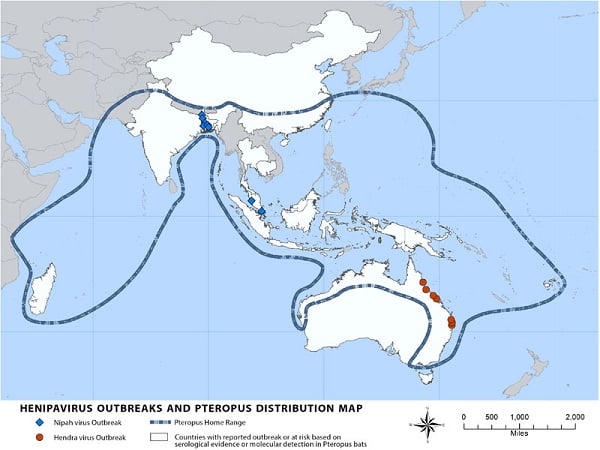
Image Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
See also: Nipah Virus (NiV) Disease Symptoms, Prevention, and More
See also: Nipah Virus (NiV) Infection Epidemiology, Etiology, and Management
The Nipah virus is a highly contagious and deadly zoonotic virus that can cause severe respiratory illness, encephalitis, and even death. The virus is primarily transmitted to humans from infected animals, especially fruit bats, through direct contact with their bodily fluids. In humans, the virus can spread rapidly through close contact with infected individuals, leading to community outbreaks.
The outbreak of Nipah virus is a serious global health threat that demands immediate attention and action. It has the potential to cause significant harm to public health, as well as economic and social disruption. If left unchecked, it could quickly become a widespread pandemic, with devastating consequences.
Therefore, it is crucial that we take this outbreak seriously and address it with urgency, by implementing effective measures to prevent its spread, providing resources to affected areas, and conducting research to develop vaccines and treatments. The Nipah virus outbreak is not just a local problem, but a global one that requires a coordinated international response. We must act now to contain the virus and prevent it from becoming a global crisis.
History of Nipah outbreaks
Nipah virus was first identified during an outbreak in Malaysia in 1998. Since then, there have been several outbreaks in different parts of the world, including Bangladesh, India, and Singapore. These outbreaks have resulted in hundreds of deaths and have raised concerns about the potential for the virus to become a global health threat.
How the virus spreads
The Nipah virus is primarily transmitted to humans through direct contact with infected animals or their bodily fluids. Fruit bats are the natural reservoir of the virus and are thought to be the primary source of human infections. The virus can also be transmitted through close contact with infected humans, including respiratory secretions, saliva, and urine.
Symptoms of Nipah infection
Nipah infection can cause a range of symptoms, including fever, headache, muscle pain, vomiting, and respiratory illness. In severe cases, the virus can cause encephalitis, or inflammation of the brain, which can lead to coma or death. The symptoms of Nipah infection can appear anywhere from 4 to 14 days after exposure, making it difficult to identify and contain outbreaks.
The Current Outbreak
Location of the current outbreak:
The current outbreak of Nipah virus is centered in the Indian state of Kerala, which has experienced several outbreaks of the virus in recent years. The outbreak was first reported in June 2021, and since then, it has spread to other parts of the state, including Kozhikode, Malappuram, and Thrissur districts.
Number of cases and deaths:
As of the latest reports, there have been over 20 confirmed cases of Nipah infection in Kerala, including several deaths. The number of cases and deaths is expected to rise as the virus continues to spread. This outbreak is particularly concerning because it has occurred during the COVID-19 pandemic, which has already placed a significant strain on India’s healthcare system.
Possible causes of the outbreak:
The exact cause of the current outbreak is not yet known, but it is thought to be linked to the consumption of contaminated fruits or exposure to infected animals. Fruit bats are the primary source of Nipah virus, and they are known to feed on fruits such as mangoes and dates, which are common in the region. The virus can also be transmitted from person to person through close contact, which may have contributed to the spread of the outbreak.
It is imperative that we take swift and decisive action to address the current outbreak of Nipah virus in Kerala. The potential for the virus to spread beyond the region and become a global crisis cannot be ignored. We must work together to identify the causes of the outbreak, contain the virus, and provide support to those affected. By taking proactive measures, we can prevent the spread of the virus and save countless lives.
The Impact of the Outbreak
Effects on public health
The outbreak of Nipah virus has had a significant impact on public health in Kerala and the surrounding regions. The virus is highly infectious and can cause severe respiratory illness and encephalitis, which can lead to death. The outbreak has already resulted in several deaths and has placed a strain on the healthcare system, which is already dealing with the COVID-19 pandemic. If the virus continues to spread, it could overwhelm healthcare resources and lead to a public health crisis.
Economic impact
The outbreak of Nipah virus could also have a significant economic impact on the affected regions. The virus has the potential to disrupt supply chains, reduce productivity, and damage industries such as agriculture and tourism. Furthermore, the costs associated with containing the outbreak and providing medical treatment to those affected could be significant.
Social impact
The outbreak of Nipah virus can also have a social impact, causing fear, anxiety, and social disruption. People may be reluctant to leave their homes or engage in public activities, which can lead to isolation and social disconnection. The outbreak can also lead to stigmatization and discrimination against those affected by the virus, exacerbating the social impact of the outbreak.
Why We Must Take Action Now
The current outbreak of Nipah virus in Kerala has the potential to become a global health crisis if left unchecked. The virus is highly infectious and can spread rapidly through close contact, making it difficult to contain. If the virus were to spread beyond Kerala, it could quickly become a pandemic, with devastating consequences for public health, the economy, and social stability.
The urgency of containing the virus
It is imperative that we take urgent action to contain the Nipah virus outbreak in Kerala. The longer we wait to take action, the more difficult it will be to contain the virus and prevent it from spreading further. We must act quickly to identify and isolate infected individuals, trace their contacts, and provide them with appropriate medical care. By taking swift and decisive action, we can prevent the outbreak from escalating and save countless lives.
The need for a coordinated international response
The Nipah virus outbreak is not just a local problem but a global one that requires a coordinated international response. It is essential that we work together to share information, resources, and expertise to contain the outbreak and prevent it from becoming a global crisis. We must collaborate with international organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to develop and implement effective measures to prevent the spread of the virus.
What We Can Do to Address the Outbreak
Providing resources to affected areas
One of the most critical steps we can take to address the Nipah virus outbreak is to provide essential resources to the affected areas in Kerala. This includes medical supplies, personal protective equipment, and financial resources to support public health efforts. We must also provide additional support to healthcare workers who are on the front lines of the outbreak response.
Implementing effective measures to prevent the spread of the virus
Preventing the spread of the Nipah virus is crucial to controlling the outbreak. We must implement effective measures to limit the spread of the virus, such as contact tracing, quarantine, and isolation of infected individuals. We must also prioritize public health education to raise awareness about the virus and how to prevent its transmission. It is also essential to implement measures to ensure the safety of food and water sources in the affected areas.
Conducting research to develop vaccines and treatments
To address the Nipah virus outbreak, we must also invest in research to develop vaccines and treatments. This includes identifying potential drug candidates, conducting clinical trials, and expediting regulatory processes to ensure that vaccines and treatments are available as quickly as possible. We must also encourage international cooperation in research efforts and share data and resources to accelerate progress.











