Screening and Diagnosis of Glaucoma
- Updated on: Jun 24, 2024
- 4 min Read
- Published on Apr 25, 2021
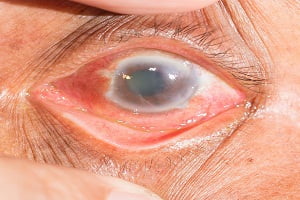
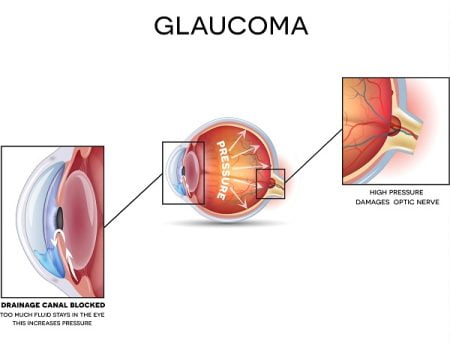
Glaucoma is a disease caused by an increased fluid pressure in eyes which damages the optic nerve of the eye. It is a slowly progressive disease. The progressive damage of optic nerve leads to vision impairement and gradually loss of vision.
An early detection is not easy as the signs and symptoms are not visible in the early stages and by the time they become visible, the disease advances to an extent where vision loss is irreversible.
Glaucoma diagnosis
Regular eye checkups by doctors and monitoring of the problems in eyes can help diagnose glaucoma at an early stage.
People who are at risk of getting glaucoma such as those having a family history of glaucoma and with an age of 40 years and above need more care and monitoring.
If glaucoma is detected early, treatment and medication can possibly maintain eye sight and avoid complete blindness. This may also prevent other symptoms from worsening. Read about glaucoma symptoms.
How is diagnosis of glaucoma done?
A doctor usually dilates the pupil with the help of eye drops and tests your vision and examines the eyes. He also checks the optic nerve for any damage to check glaucoma-related conditions. Visual field test is done to check peripheral vision and detect any impairement in it.
Screening and tests for glaucoma
Screening for glaucoma is done:
- by knowing detailed medical history of a person for any disease and other condition which can affect eye sight
- if your age is 40 and above as age is one of the risk factors for glaucoma
- if you have a family history of glaucoma such as having your mother, sibling or child with glaucoma
Your doctor may test glaucoma by examination eyes using a number of comprehensive tests which may include:
- Measuring the eye pressure
- Checking drainage angle of eye
- Optic nerve evaluation for any change or damage and taking computerized picture of optic nerves
- Visual field testing of both eyes
- Measuring thickness of cornea
Some procedures for glaucoma diagnosis are discussed here.
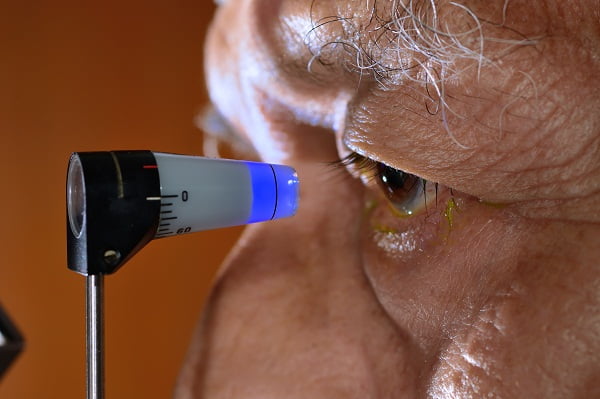
Tonometry
This test determines Intraocular Fluid Pressure (IOP) in eye with the help of an instrument called tonometer. There are several types of tonometers available for doing this test such as-
- Air puff or noncontact tonometer– it emits puff of air and measures resistance of eyes to air
- Applanation tonometer– the intraocular pressure is measured based on the force required to flatten (applanate) a constant area of the cornea
- Electronic indentation– it measures eye pressure by directly contracting the eyes with pen like digital pen after anesthetizing the eyes
Applanation tonometer is the most commonly used device for tonometry.
Abnormally high IOP indicates either the eye is producing too much fluid or fluid drainage is not working properly indicating a problem with the amount of fluid (aqueous humor).
Normal IOP should be below 21 mm of Hg. IOP of 30 or more mm of Hg increases the risk of glaucoma 40 times more in a person than a person with IOP of 15 mmHg or below.
Pachymetry
This test measures the thickness of the cornea with the help of pachymeter. The eye is numbed with anesthetic eye drop before pachymetry. The tip of pachymeter is touched slightly to the cornea of the eye.
Cornea thickness affects the measurement of intraocular pressure as thick cornea gives false high eye pressure and thinner cornea give false low eye pressure measurements. Thin cornea is an additional risk factor for glaucoma.
Perimetry Test
This test measures peripheral vision and central vision and is also known as Visual field testing. It is used for early detection of glaucoma and also to check whether you are facing any vision loss due to glaucoma.
In this method, the visual field of each eye is tested separately – one eye at a time. Patient is allowed to see inside a machine or bowl in which lights of different intensities and sizes are projected. As one eye is tested at a time, during the test, the second eye is covered and the patient presses the button each time he notices a flash of light.
A computerized map of visual field of each eye is made through this process depicting areas where eyes can see and cannot see. If a person has glaucoma, then remarkable changes are observed in the visual field of each eye.
The test is done at regular intervals of time to make sure any blind spot development is not occurring due to damage of optic nerves and also to determine vision loss progression from glaucoma.
Gonioscopy
This test is done by doctors in which they use a mirror instrument to see and analyse anterior parts of eye (anterior chamber) from different directions to determine whether the iris is closer to the back of cornea unusually or not.
The test is done after numbing of the eyes with anaesthetic eye drops first. It helps in diagnosing close angle glaucoma. Special lenses are used with bio-macroscope to enable a doctor to see drainage angle of the eye so as to make sure that aqueous humor is flowing freely from the eye avoiding intraocular pressure development which damages the optic nerve.
The test also determines whether eye’s blood vessels are normal or not.
Ophthalmoscopy
In this test doctors observe the optic nerve and detect any damage caused by glaucoma. Doctors use a head- mounted handled device and slit lamp to look through pupil directly. The cupping of the optic disc is observed. An indentation of the optic disc shows damage to the optic nerve caused by an increased intraocular pressure in the eye.
Asymmetry in the degree of cupping of the optic nerve disc between two eyes shows glaucoma. Pale colour of optic nerve shows damage due to poor regulation of the blood flow in the optic nerve. Images of the optic nerve are taken every time to compare any changes over the time.
Blindness caused by glaucoma is irreversible. Even medications and surgeries are not able to regain the vision once lost due to glaucoma. Early detection and diagnosis of glaucoma helps in choosing proper treatment option and medications so as to save sight for future. An early diagnosis and treatment also helps to slow down the disease progression and avoid other disease symptoms from worsening. Read about glaucoma treatment.